CakePHP is an open-source tool used to implement dynamic programming applications as well as it provides a different kind of functionality to the developer. Validation is one of the functionalities that is provided by the CakePHP, by using validation we can provide the validation to the arbitrary arrays of data as per our requirement. In CakePHP, we need to build the entities before the data validation in terms of shape and size. Here we also need to consider default entities, these entities will be validated before the conversation of entities. We can also apply validation rules as per our requirements.
Start Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
What is CakePHP Validation?
Information approval is a significant piece of any application, as it assists with ensuring that the information in a Model adjusts to the business rules of the application. For instance, you should ensure that passwords are somewhere around eight characters in length, or guarantee that usernames are special. Characterizing approval rules makes structure dealing with a whole lot simpler.
There are various perspectives to the approval cycle. What we’ll cover in this segment is the model side of things. Basically: what happens when you call the save () technique for your model. For more data about how to deal with the showing of approval blunders.
CakePHP Validation Methods
Now let’s see different validation methods in CakePHP as follows.
1. Add
Adds another standard to a field’s standard set. On the off chance that subsequent contention is a cluster, the rules list for the field will be supplanted with second contention and third contention will be overlooked.
Syntax
Add(string $specified field, array|string $specified name, array|Cake\Validation\ValidationRule $required rule [])
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the add method with different parameters. In the above syntax specified name is used to define the name of the rule that we need to add. The array is used to define this rule or multiple rules as per requirement and this returns $this.
2. allowEmpty
By using this method, we can allow empty field
Syntax
allowEmpty(string $specified field, boolean|string|callable $whentrue, string|null msgull)
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the add method with different parameters. In the above syntax specified name is used to define the name of the rule that we need to add. A boolean parameter is used to indicate when we empty we need to allow, here we can also validate in terms of true or false when we perform create or update operation. The message is used to show the message field and this returns $this.
3. Alphanumeric
By using this method, we can add alphanumeric rules to the field as per our requirements.
Syntax
alphanumeric (string $specified field, string|null $Msgnull, string|callable|null $whennull)
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the alphanumeric method with different parameters. In the above syntax specified name is used to define the name of the rule that we need to add. Adds another standard to a field’s standard set. In the event that subsequent contention is a cluster, the rules list for the field will be supplanted with second contention and third contention will be overlooked and it returns $this.
4. Creditcard
By using this method, we can add credit card rules to the specified field as per requirement.
Syntax
creditCard(string $specified field , string $type'all', string|null $msgnull, string|callable|null $whennull)
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the credit card method to add the rule with different parameters. The field you need to apply the standard to.
The sort of cards you need to permit. Defaults to ‘a(chǎn)ll’. You can likewise supply a variety of acknowledged card types, for instance, ‘mastercard’, ‘visa’, ‘a(chǎn)mex’.
The mistake message when the standard falls flat. Either ‘make’ or ‘update’ or a callable that profits valid, when the approval rule ought to be applied and it returns $this.
5. Email
By using this method, we can add an email validation rule to the field as per our requirement.
Syntax
Email(string $specified field , boolean $checkMXfalse, string|null $msgnull, string|callable|null, $whennull)
Explanation
By using the above syntax, we can implement the email validation rule. The field you need to apply the standard too.
Regardless of whether to check the MX records.
The blunder message when the standard fizzles.
Either ‘make’ or ‘update’ or a callable that profits valid, when the approval rule ought to be applied.
6. maxLength
By using this method, we can apply string validation to the field.
Syntax
maxLength(string $specified field, integer $max, string|null $msgnull, string|callable|null $whennull)
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the maxLength method with different parameters. Here the specified field is used to define the field to which we want to apply the rule, max is used to define the maximum length of string, msgnull is used to show an error message when the rule fails.
7. minLength
By using this method, we can apply string validation to the field.
Syntax
minLength(string $specified field, integer $min, string|null $msgnull, string|callable|null $whennull)
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the minLength method with different parameters. Here the specified field is used to define the field which we want to apply the rule, min is used to define the minimum length of string, msgnull is used to show an error message when the rule fails.
How to Create CakePHP Validation?
Now let’s see how we can create CakePHP validation with examples as follows.?First, we need to make the changes in routes.php file as follows.
<?php
use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('validation',['controller'=>'Valid','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
?>
Now create an index.php file and write the following code as follows.
<?php
if($errors) {
foreach($errors as $error)
foreach($error as $mssg)
echo '<font color="red">'.$mssg.'</font><br>';
} else {
echo "There is no errors.";
}
echo $this->Form->create(NULL,array('url'=>'/validation'));
echo $this->Form->control('username of person');
echo $this->Form->control('password');
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
Now execute the above code we will get the following screen as shown below screenshot.
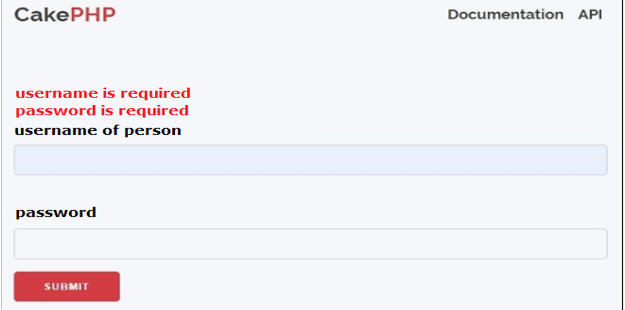
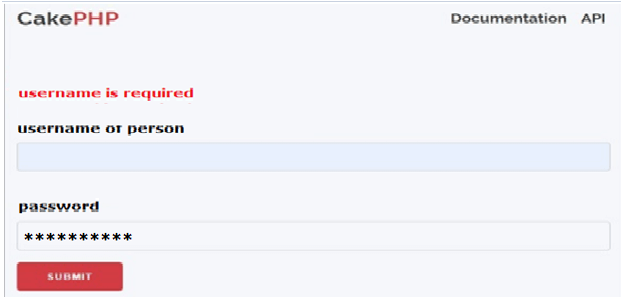
Suppose let’s consider, if we enter only password then it shows username is required as shown in the following screenshot.
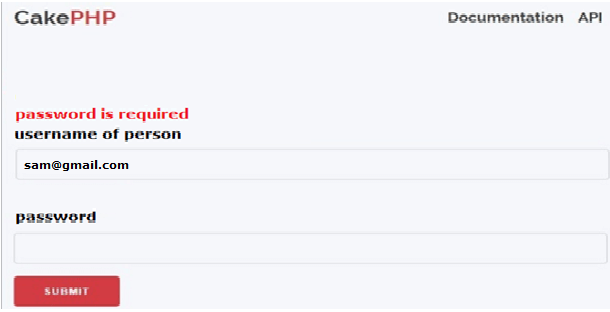
Similarly, we can apply validation for username of person filed as shown in the following screenshot as follows.
In this way, we can implement different methods such as to get, post as per our requirement.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn more about the CakePHP validation. From the above article, we have taken in the essential idea of the CakePHP validation and we also see the representation and example of the CakePHP validation. From this article, we learned how and when we use the CakePHP validation.
The above is the detailed content of CakePHP Validation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to combine two php arrays unique values?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
How to combine two php arrays unique values?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
To merge two PHP arrays and keep unique values, there are two main methods. 1. For index arrays or only deduplication, use array_merge and array_unique combinations: first merge array_merge($array1,$array2) and then use array_unique() to deduplicate them to finally get a new array containing all unique values; 2. For associative arrays and want to retain key-value pairs in the first array, use the operator: $result=$array1 $array2, which will ensure that the keys in the first array will not be overwritten by the second array. These two methods are applicable to different scenarios, depending on whether the key name is retained or only the focus is on
 How to use php exit function?
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:15 AM
How to use php exit function?
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:15 AM
exit() is a function in PHP that is used to terminate script execution immediately. Common uses include: 1. Terminate the script in advance when an exception is detected, such as the file does not exist or verification fails; 2. Output intermediate results during debugging and stop execution; 3. Call exit() after redirecting in conjunction with header() to prevent subsequent code execution; In addition, exit() can accept string parameters as output content or integers as status code, and its alias is die().
 Applying Semantic Structure with article, section, and aside in HTML
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:03 AM
Applying Semantic Structure with article, section, and aside in HTML
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:03 AM
The rational use of semantic tags in HTML can improve page structure clarity, accessibility and SEO effects. 1. Used for independent content blocks, such as blog posts or comments, it must be self-contained; 2. Used for classification related content, usually including titles, and is suitable for different modules of the page; 3. Used for auxiliary information related to the main content but not core, such as sidebar recommendations or author profiles. In actual development, labels should be combined and other, avoid excessive nesting, keep the structure simple, and verify the rationality of the structure through developer tools.
 The requested operation requires elevation Windows
Jul 04, 2025 am 02:58 AM
The requested operation requires elevation Windows
Jul 04, 2025 am 02:58 AM
When you encounter the prompt "This operation requires escalation of permissions", it means that you need administrator permissions to continue. Solutions include: 1. Right-click the "Run as Administrator" program or set the shortcut to always run as an administrator; 2. Check whether the current account is an administrator account, if not, switch or request administrator assistance; 3. Use administrator permissions to open a command prompt or PowerShell to execute relevant commands; 4. Bypass the restrictions by obtaining file ownership or modifying the registry when necessary, but such operations need to be cautious and fully understand the risks. Confirm permission identity and try the above methods usually solve the problem.
 How to create an array in php?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:01 PM
How to create an array in php?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:01 PM
There are two ways to create an array in PHP: use the array() function or use brackets []. 1. Using the array() function is a traditional way, with good compatibility. Define index arrays such as $fruits=array("apple","banana","orange"), and associative arrays such as $user=array("name"=>"John","age"=>25); 2. Using [] is a simpler way to support since PHP5.4, such as $color
 php raw post data php
Jul 02, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
php raw post data php
Jul 02, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
The way to process raw POST data in PHP is to use $rawData=file_get_contents('php://input'), which is suitable for receiving JSON, XML, or other custom format data. 1.php://input is a read-only stream, which is only valid in POST requests; 2. Common problems include server configuration or middleware reading input streams, which makes it impossible to obtain data; 3. Application scenarios include receiving front-end fetch requests, third-party service callbacks, and building RESTfulAPIs; 4. The difference from $_POST is that $_POST automatically parses standard form data, while the original data is suitable for non-standard formats and allows manual parsing; 5. Ordinary HTM
 How to handle File Uploads securely in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:37 AM
How to handle File Uploads securely in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:37 AM
To safely handle PHP file uploads, you need to verify the source and type, control the file name and path, set server restrictions, and process media files twice. 1. Verify the upload source to prevent CSRF through token and detect the real MIME type through finfo_file using whitelist control; 2. Rename the file to a random string and determine the extension to store it in a non-Web directory according to the detection type; 3. PHP configuration limits the upload size and temporary directory Nginx/Apache prohibits access to the upload directory; 4. The GD library resaves the pictures to clear potential malicious data.
 How Do You Pass Variables by Value vs. by Reference in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:42 AM
How Do You Pass Variables by Value vs. by Reference in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:42 AM
InPHP,variablesarepassedbyvaluebydefault,meaningfunctionsorassignmentsreceiveacopyofthedata,whilepassingbyreferenceallowsmodificationstoaffecttheoriginalvariable.1.Whenpassingbyvalue,changestothecopydonotimpacttheoriginal,asshownwhenassigning$b=$aorp






