PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PMPHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals.
This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivatives. Although it is possible to compile PHP from source, installing it from an APT repository as explained below is often faster and more secure because these repositories will provide the latest bug fixes and security updates in the future.
PHP 8.4 is not available in current Debian and Ubuntu software repositories. This guide uses the repositories maintained by Ond?ej Sury. Ondrej's PHP repositories have been the de-facto repositories for PHP on Ubuntu, Debian, and their derivatives for several years.

Potential Backward Compatibility Impact in PHP 8.4
PHP 8.4 brings several new features such as property hooks, asymmetric visibility, improvements in DOM, Curl, PCRE extensions, and more.
However, PHP 8.4 also deprecates some PHP functionality and removes four PHP extensions from PHP core to PECL. This can affect existing PHP applications to emit additional PHP notices/warnings, or fail in certain conditions.
Some of the notable changes that are likely to affect existing applications include:
- Implicitly nullable parameter declarations deprecated
- E_STRICT constant deprecated
- Extensions moved from PHP core to PECL: Pspell, IMAP, OCI8, and PDO_OCI.
When a PHP extension is moved from PHP core to PECL, the extension will follow its own release cycle. The repositories used in the guide will provide updates for them if the PECL project for that extension releases updates. However, this also means the PECL extension can (and often does) fall behind on maintenance.
Before continuing, make sure to backup the system. This guide installs PHP 8.4 side-by-side along any existing PHP installations, which offers an easy way to switch back to the other PHP installation if necessary.
This step only applies when upgrading an existing PHP setup. The following command lists all installed PHP packages with the text php in its name, shows it on screen, and writes it to a file called packages.txt. This file comes in handy at a later step when installing the PHP 8.4 packages, to ensure the same list of PHP 8.4 versions of the extensions are installed.
dpkg?-l?|?grep?php?|?tee?packages.txt
2. Add ondrej/php PPA/DPA
Because PHP 8.4 packages are not available in any of the current Debian or Ubuntu software repositories, the PHP packages must come from another repo.
Ond?ej Sury maintains a package archive that contains compiled binaries of all current PHP versions, for Ubuntu and Debian. It also ships several PECL extensions including PECL extensions for PHP core extensions unbundled in PHP 8.4.
Once this repository is added, the initial installation and updates can be done with the standard apt commands.
Ubuntu PPA
dpkg?-l?|?grep?php?|?tee?packages.txt
Debian DPA
sudo?LC_ALL=C.UTF-8?add-apt-repository?ppa:ondrej/php?#?Press?enter?to?confirm.sudo?apt?update
3. Install PHP 8.4 Server API packages
In the Ondrej's PPA and DPA, PHP 8.4 packages follow the php8.1-NAME pattern. PECL and shared PHP extensions also follow the same pattern.
Before installing PHP extensions, make sure to install one of the following PHP Server API (SAPI) packages:
Install PHP-CLI only
To install PHP CLI, install the php8.1-cli package, along with the extensions desired.
sudo?apt-get?updatesudo?apt-get?-y?install?lsb-release?ca-certificates?curl?apt-transport-httpssudo?curl?-sSLo?/tmp/debsuryorg-archive-keyring.deb?https://packages.sury.org/debsuryorg-archive-keyring.debsudo?dpkg?-i?/tmp/debsuryorg-archive-keyring.debsudo?sh?-c?'echo?"deb?[signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/deb.sury.org-php.gpg]?https://packages.sury.org/php/?$(lsb_release?-sc)?main"?>?/etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list'sudo?apt-get?update
PHP-CLI and PHP as an Apache module
To install PHP CLI and PHP 8.4 as an Apache module, install the libapache2-mod-php8.4 package:
sudo?apt?install?php8.4-cli
Unless the PHP application requires PHP to be installed as an Apache module, consider installing PHP-FPM instead.
PHP CLI and PHP-FPM (recommended)
It is recommended to install PHP-FPM to integrate PHP with web-servers such as Apache, Nginx, and Caddy.
sudo?apt?install?php8.4-cli?libapache2-mod-php8.4
This installs the php8.4-fpm service and automatically enables it. See the FPM web-server integration section for the additional steps required later.
5. Check Installation
For a quick check of the PHP installation, run the following:
sudo?apt?install?php8.4-cli?php8.4-fpm
It should show the PHP version, build time, and more information:
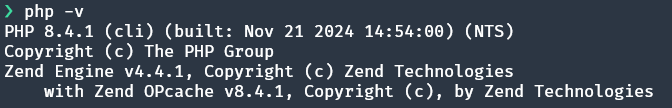
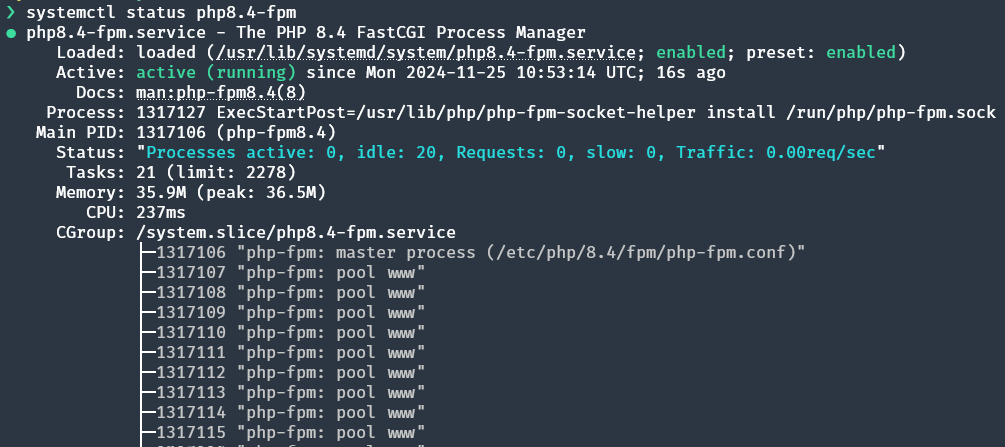
If the PHP-FPM service is installed, its status can be checked as follows:
php?-v
If the PHP-FPM server is running successfully, it should show an output similar to below:
4. Install PHP Extensions
All of the shared PHP extensions and PECL extensions follow the php8.4-EXTNAME pattern, where extname is the name of the extension.
When upgrading an existing system, refer to the packages.txt file created in the first step to check the existing PHP 8.3 or older PHP extensions.
To install a PHP extension, use the apt install command with the PHP extension name with the php-8.4- prefix. For example, the gd extension is installed with the php8.4-gd package:
sudo?systemctl?status?php8.4-fpm
The following command installs a set of most common PHP extensions required by a majority of PHP libraries and frameworks:
sudo?apt?install?php8.4-gd
To search for additional PHP extensions, use the apt search command:
dpkg?-l?|?grep?php?|?tee?packages.txt
Development Tools
Development tooling such as Xdebug and code coverage tools can also be installed following the same package naming convention.
This step is not recommended on production servers.
Xdebug
sudo?LC_ALL=C.UTF-8?add-apt-repository?ppa:ondrej/php?#?Press?enter?to?confirm.sudo?apt?update
PCOV
sudo?apt-get?updatesudo?apt-get?-y?install?lsb-release?ca-certificates?curl?apt-transport-httpssudo?curl?-sSLo?/tmp/debsuryorg-archive-keyring.deb?https://packages.sury.org/debsuryorg-archive-keyring.debsudo?dpkg?-i?/tmp/debsuryorg-archive-keyring.debsudo?sh?-c?'echo?"deb?[signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/deb.sury.org-php.gpg]?https://packages.sury.org/php/?$(lsb_release?-sc)?main"?>?/etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list'sudo?apt-get?update
5. Web Server Integration
Depending on the server API installed in step 3, web server integration might require additional configuration for the PHP 8.4 upgrade to take effect.
PHP-FPM
When using PHP-FPM (by installing the php8.4-fpm package), the web server needs to be reconfigured to communicate with the PHP 8.4 FPM server over the updated the socket path.
Apache: This configuration change is made easy by switching on the PHP 8.4 configuration file:
sudo?apt?install?php8.4-cli
Nginx: Update the fastcgi_pass directive from the old PHP FPM socket path to the new PHP 8.4 path:
sudo?apt?install?php8.4-cli?libapache2-mod-php8.4
See Nginx documentation for more information
Caddy Server: Update the reverse_proxy directive to use the new PHP 8.4 FPM server socket path:
sudo?apt?install?php8.4-cli?php8.4-fpm
See How to use Caddy Server with PHP for more configuration details.
PHP as an Apache module
If PHP is installed as an Apache module, the following command disables the previous PHP module (8.3 in this example) and enables the new PHP version:
php?-v
The above is the detailed content of PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to handle File Uploads securely in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:37 AM
How to handle File Uploads securely in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:37 AM
To safely handle PHP file uploads, you need to verify the source and type, control the file name and path, set server restrictions, and process media files twice. 1. Verify the upload source to prevent CSRF through token and detect the real MIME type through finfo_file using whitelist control; 2. Rename the file to a random string and determine the extension to store it in a non-Web directory according to the detection type; 3. PHP configuration limits the upload size and temporary directory Nginx/Apache prohibits access to the upload directory; 4. The GD library resaves the pictures to clear potential malicious data.
 How Do You Pass Variables by Value vs. by Reference in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:42 AM
How Do You Pass Variables by Value vs. by Reference in PHP?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:42 AM
InPHP,variablesarepassedbyvaluebydefault,meaningfunctionsorassignmentsreceiveacopyofthedata,whilepassingbyreferenceallowsmodificationstoaffecttheoriginalvariable.1.Whenpassingbyvalue,changestothecopydonotimpacttheoriginal,asshownwhenassigning$b=$aorp
 How Do Generators Work in PHP?
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:12 AM
How Do Generators Work in PHP?
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:12 AM
AgeneratorinPHPisamemory-efficientwaytoiterateoverlargedatasetsbyyieldingvaluesoneatatimeinsteadofreturningthemallatonce.1.Generatorsusetheyieldkeywordtoproducevaluesondemand,reducingmemoryusage.2.Theyareusefulforhandlingbigloops,readinglargefiles,or
 PHP header location ajax call not working
Jul 10, 2025 pm 01:46 PM
PHP header location ajax call not working
Jul 10, 2025 pm 01:46 PM
The reason why header('Location:...') in AJAX request is invalid is that the browser will not automatically perform page redirects. Because in the AJAX request, the 302 status code and Location header information returned by the server will be processed as response data, rather than triggering the jump behavior. Solutions are: 1. Return JSON data in PHP and include a jump URL; 2. Check the redirect field in the front-end AJAX callback and jump manually with window.location.href; 3. Ensure that the PHP output is only JSON to avoid parsing failure; 4. To deal with cross-domain problems, you need to set appropriate CORS headers; 5. To prevent cache interference, you can add a timestamp or set cache:f
 How to prevent session hijacking in PHP?
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:15 AM
How to prevent session hijacking in PHP?
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:15 AM
To prevent session hijacking in PHP, the following measures need to be taken: 1. Use HTTPS to encrypt the transmission and set session.cookie_secure=1 in php.ini; 2. Set the security cookie attributes, including httponly, secure and samesite; 3. Call session_regenerate_id(true) when the user logs in or permissions change to change to change the SessionID; 4. Limit the Session life cycle, reasonably configure gc_maxlifetime and record the user's activity time; 5. Prohibit exposing the SessionID to the URL, and set session.use_only
 How to URL encode a string in PHP with urlencode
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:22 AM
How to URL encode a string in PHP with urlencode
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:22 AM
The urlencode() function is used to encode strings into URL-safe formats, where non-alphanumeric characters (except -, _, and .) are replaced with a percent sign followed by a two-digit hexadecimal number. For example, spaces are converted to signs, exclamation marks are converted to!, and Chinese characters are converted to their UTF-8 encoding form. When using, only the parameter values ??should be encoded, not the entire URL, to avoid damaging the URL structure. For other parts of the URL, such as path segments, the rawurlencode() function should be used, which converts the space to . When processing array parameters, you can use http_build_query() to automatically encode, or manually call urlencode() on each value to ensure safe transfer of data. just
 How to access a character in a string by index in PHP
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:15 AM
How to access a character in a string by index in PHP
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:15 AM
In PHP, you can use square brackets or curly braces to obtain string specific index characters, but square brackets are recommended; the index starts from 0, and the access outside the range returns a null value and cannot be assigned a value; mb_substr is required to handle multi-byte characters. For example: $str="hello";echo$str[0]; output h; and Chinese characters such as mb_substr($str,1,1) need to obtain the correct result; in actual applications, the length of the string should be checked before looping, dynamic strings need to be verified for validity, and multilingual projects recommend using multi-byte security functions uniformly.
 PHP find the position of the last occurrence of a substring
Jul 09, 2025 am 02:49 AM
PHP find the position of the last occurrence of a substring
Jul 09, 2025 am 02:49 AM
The most direct way to find the last occurrence of a substring in PHP is to use the strrpos() function. 1. Use strrpos() function to directly obtain the index of the last occurrence of the substring in the main string. If it is not found, it returns false. The syntax is strrpos($haystack,$needle,$offset=0). 2. If you need to ignore case, you can use the strripos() function to implement case-insensitive search. 3. For multi-byte characters such as Chinese, the mb_strrpos() function in the mbstring extension should be used to ensure that the character position is returned instead of the byte position. 4. Note that strrpos() returns f






