 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Path Manipulation in Laravel: Secure Your App from Vulnerabilities
Path Manipulation in Laravel: Secure Your App from Vulnerabilities
Introduction
Laravel is a popular PHP framework, valued for its clean architecture and developer-friendly environment. However, improper handling of file paths can expose your application to Path Manipulation Vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities occur when attackers manipulate file paths to access restricted files or directories.

In this blog, we’ll explore what path manipulation is, its risks, and how you can prevent it in Laravel with hands-on coding examples. Additionally, we'll show you how our free Website Security Scanner tool can detect such vulnerabilities in your application.
What is Path Manipulation?
Path manipulation happens when user-controlled input allows access to files outside the intended directory. This can lead to:
- Unauthorized Data Access: Attackers might access sensitive files like configuration or logs.
- File Modification: Attackers could alter critical files.
- Execution of Malicious Scripts: Executing scripts stored in unintended locations.
How Does Path Manipulation Work?
Attackers craft input that exploits the file system’s directory traversal mechanism. For instance:
$file = $_GET['file'];
include("/var/www/html/uploads/" . $file);
If the user sends file=../../etc/passwd, the script could read sensitive server files:
include("/var/www/html/uploads/../../etc/passwd");
Preventing Path Manipulation in Laravel
Laravel provides built-in methods to mitigate such risks. Let’s dive into practical solutions:
1. Validate and Sanitize Inputs
Always validate user inputs to ensure they don’t contain malicious paths.
$request->validate([
'file' => 'required|string|alpha_dash'
]);
2. Use Laravel’s Storage Class
Leverage Laravel’s Storage facade to manage file paths securely:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Storage;
$file = $request->input('file');
// Securely fetch the file path
$path = Storage::path('uploads/' . basename($file));
if (Storage::exists($path)) {
return response()->download($path);
}
Coding Example: Secure File Retrieval
Here’s a complete example of securely retrieving files:
$file = $_GET['file'];
include("/var/www/html/uploads/" . $file);
Why This Code is Secure
- basename() prevents directory traversal.
- storage_path() confines file paths to Laravel’s storage directory.
- Ensures the file exists before serving.
How Our Free Tool Detects Path Manipulation
 Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Using our free Website Security Checker, tool you can scan your web application for path manipulation vulnerabilities. The tool generates a detailed vulnerability assessment report, helping you secure your application.
Real-Time Example with Our Tool
Below is a screenshot of a Vulnerability Assessment Report generated by our tool:
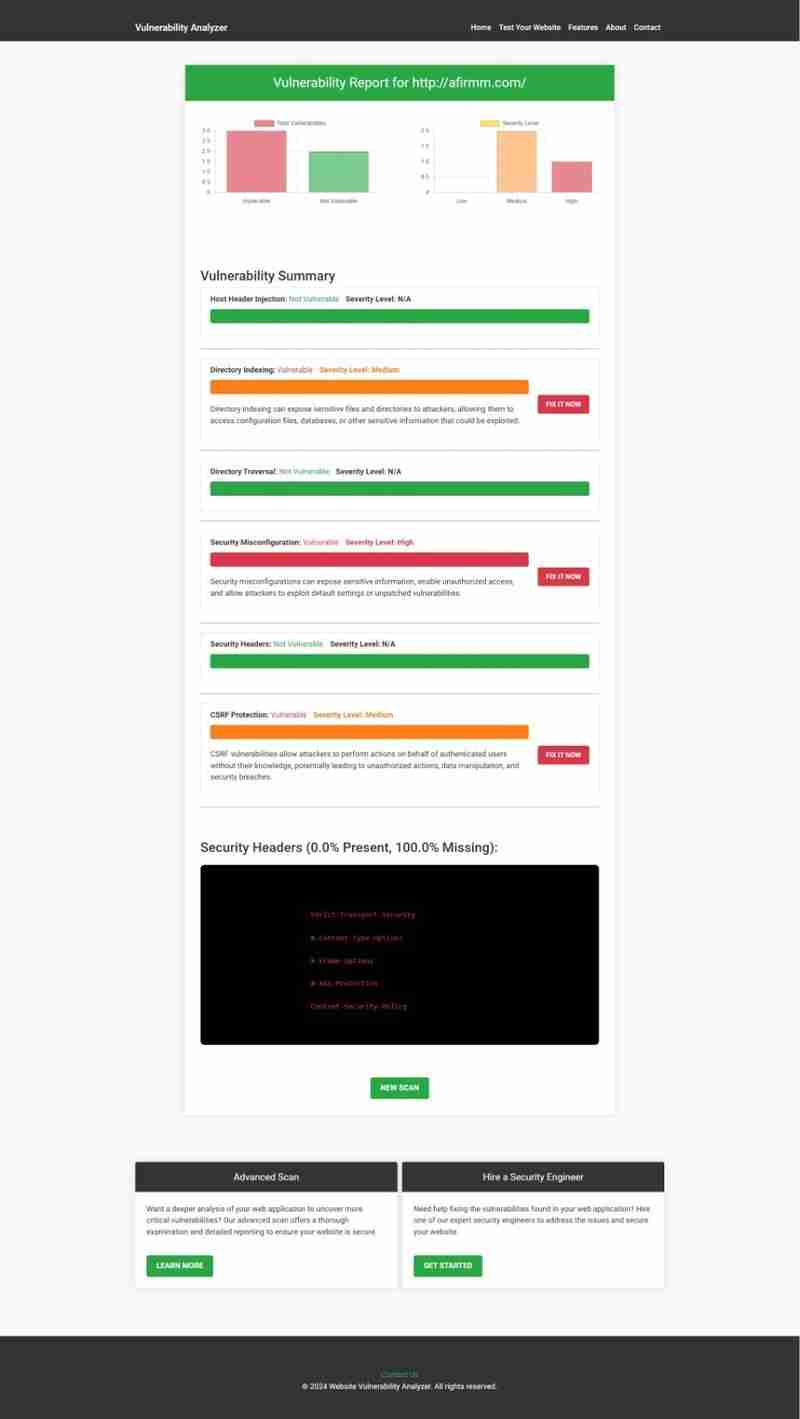 An example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool provides insights into possible vulnerabilities.
An example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool provides insights into possible vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Path manipulation vulnerabilities can compromise your Laravel applications. By validating inputs, using secure methods like Storage, and conducting regular vulnerability assessments with tools like ours to test website security free, you can significantly reduce risks.
Take proactive steps to secure your application today, and don’t forget to test your application regularly with our tool for enhanced protection.
Have you scanned your Laravel application for vulnerabilities? Check it now with our free Website Security Scanner and stay secure!
The above is the detailed content of Path Manipulation in Laravel: Secure Your App from Vulnerabilities. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How do I implement authentication and authorization in PHP?
Jun 20, 2025 am 01:03 AM
How do I implement authentication and authorization in PHP?
Jun 20, 2025 am 01:03 AM
TosecurelyhandleauthenticationandauthorizationinPHP,followthesesteps:1.Alwayshashpasswordswithpassword_hash()andverifyusingpassword_verify(),usepreparedstatementstopreventSQLinjection,andstoreuserdatain$_SESSIONafterlogin.2.Implementrole-basedaccessc
 How do I stay up-to-date with the latest PHP developments and best practices?
Jun 23, 2025 am 12:56 AM
How do I stay up-to-date with the latest PHP developments and best practices?
Jun 23, 2025 am 12:56 AM
TostaycurrentwithPHPdevelopmentsandbestpractices,followkeynewssourceslikePHP.netandPHPWeekly,engagewithcommunitiesonforumsandconferences,keeptoolingupdatedandgraduallyadoptnewfeatures,andreadorcontributetoopensourceprojects.First,followreliablesource
 What is PHP, and why is it used for web development?
Jun 23, 2025 am 12:55 AM
What is PHP, and why is it used for web development?
Jun 23, 2025 am 12:55 AM
PHPbecamepopularforwebdevelopmentduetoitseaseoflearning,seamlessintegrationwithHTML,widespreadhostingsupport,andalargeecosystemincludingframeworkslikeLaravelandCMSplatformslikeWordPress.Itexcelsinhandlingformsubmissions,managingusersessions,interacti
 How to set PHP time zone?
Jun 25, 2025 am 01:00 AM
How to set PHP time zone?
Jun 25, 2025 am 01:00 AM
TosettherighttimezoneinPHP,usedate_default_timezone_set()functionatthestartofyourscriptwithavalididentifiersuchas'America/New_York'.1.Usedate_default_timezone_set()beforeanydate/timefunctions.2.Alternatively,configurethephp.inifilebysettingdate.timez
 How do I install PHP on my operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux)?
Jun 20, 2025 am 01:02 AM
How do I install PHP on my operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux)?
Jun 20, 2025 am 01:02 AM
The method of installing PHP varies from operating system to operating system. The following are the specific steps: 1. Windows users can use XAMPP to install packages or manually configure them, download XAMPP and install them, select PHP components or add PHP to environment variables; 2. macOS users can install PHP through Homebrew, run the corresponding command to install and configure the Apache server; 3. Linux users (Ubuntu/Debian) can use the APT package manager to update the source and install PHP and common extensions, and verify whether the installation is successful by creating a test file.
 How do I validate user input in PHP to ensure it meets certain criteria?
Jun 22, 2025 am 01:00 AM
How do I validate user input in PHP to ensure it meets certain criteria?
Jun 22, 2025 am 01:00 AM
TovalidateuserinputinPHP,usebuilt-invalidationfunctionslikefilter_var()andfilter_input(),applyregularexpressionsforcustomformatssuchasusernamesorphonenumbers,checkdatatypesfornumericvalueslikeageorprice,setlengthlimitsandtrimwhitespacetopreventlayout
 How do I destroy a session in PHP using session_destroy()?
Jun 20, 2025 am 01:06 AM
How do I destroy a session in PHP using session_destroy()?
Jun 20, 2025 am 01:06 AM
To completely destroy a session in PHP, you must first call session_start() to start the session, and then call session_destroy() to delete all session data. 1. First use session_start() to ensure that the session has started; 2. Then call session_destroy() to clear the session data; 3. Optional but recommended: manually unset$_SESSION array to clear global variables; 4. At the same time, delete session cookies to prevent the user from retaining the session state; 5. Finally, pay attention to redirecting the user after destruction, and avoid reusing the session variables immediately, otherwise the session needs to be restarted. Doing this will ensure that the user completely exits the system without leaving any residual information.
 What are the best practices for writing clean and maintainable PHP code?
Jun 24, 2025 am 12:53 AM
What are the best practices for writing clean and maintainable PHP code?
Jun 24, 2025 am 12:53 AM
The key to writing clean and easy-to-maintain PHP code lies in clear naming, following standards, reasonable structure, making good use of comments and testability. 1. Use clear variables, functions and class names, such as $userData and calculateTotalPrice(); 2. Follow the PSR-12 standard unified code style; 3. Split the code structure according to responsibilities, and organize it using MVC or Laravel-style catalogs; 4. Avoid noodles-style code and split the logic into small functions with a single responsibility; 5. Add comments at key points and write interface documents to clarify parameters, return values ??and exceptions; 6. Improve testability, adopt dependency injection, reduce global state and static methods. These practices improve code quality, collaboration efficiency and post-maintenance ease.





