 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 Create Stunning Gradual Div Reveals with JavaScript setTimeout and CSS Transitions
Create Stunning Gradual Div Reveals with JavaScript setTimeout and CSS Transitions
Create Stunning Gradual Div Reveals with JavaScript setTimeout and CSS Transitions
Jan 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PMThis tutorial demonstrates how to gradually reveal webpage elements using JavaScript's setTimeout function and CSS transitions. The effect creates a visually engaging, staggered appearance of divs, each fading in sequentially.
Overview
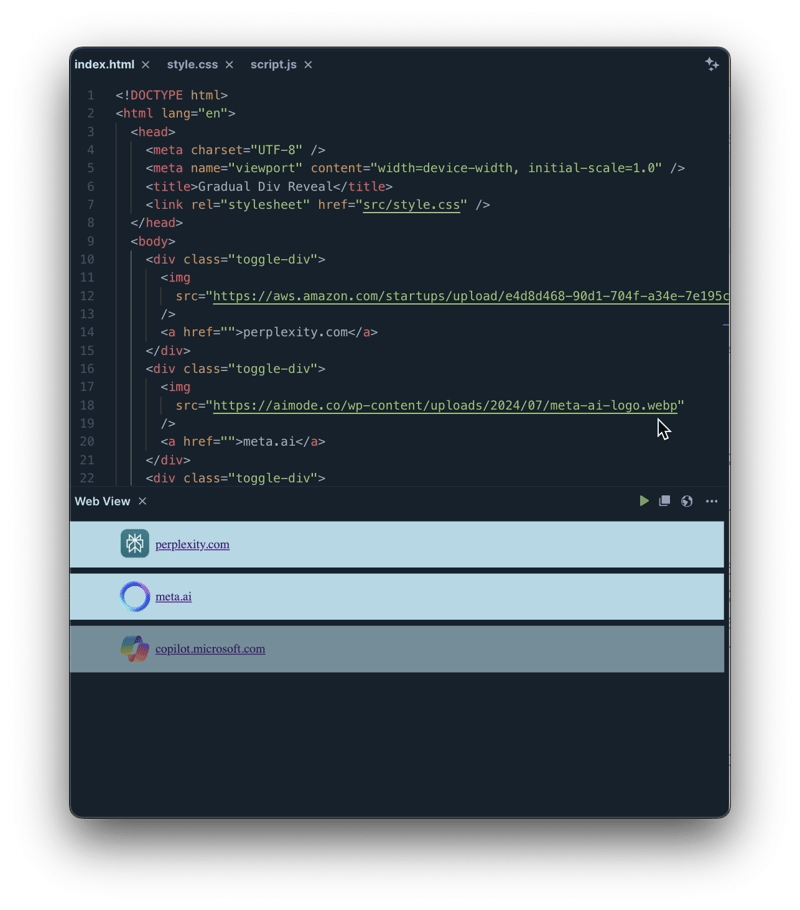
This example showcases a series of divs, each containing an image and link, that fade in one by one. setTimeout controls the timing, while CSS handles the smooth transition.
HTML Structure
The HTML consists of several divs, each holding an image and a link. This structure is ready to receive the styling and JavaScript functionality. (Note: The provided HTML snippet is incomplete and lacks closing tags. A complete, functional HTML file is required.)
CSS Transitions
The CSS defines the visual transition:
.toggle-div {
opacity: 0; /* Initially hidden */
transition: opacity 1s ease; /* 1-second fade-in transition */
height: 50px; /* Ensure visibility */
background-color: lightblue; /* For visual clarity */
margin: 10px 0;
padding: 12px 80px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.toggle-div img {
height: 100%;
margin-right: 8px;
}
.toggle-div a {
font-size: 20px;
}
opacity: 0;: Hides the divs initially.transition: opacity 1s ease;: Specifies a 1-second smooth opacity transition.
JavaScript for Gradual Reveal
The JavaScript code orchestrates the staggered appearance:
// JavaScript to reveal divs
const divs = document.querySelectorAll('.toggle-div');
divs.forEach((div, index) => {
setTimeout(() => {
div.style.opacity = 1; // Make div visible
}, index * 500); // Delay based on index (0.5 seconds per div)
});
-
document.querySelectorAll('.toggle-div'): Selects all elements with the classtoggle-div. -
forEach: Iterates through each div. -
setTimeout: Sets a timer before settingopacityto 1, causing each div to fade in after a delay. The delay increases by 500 milliseconds (0.5 seconds) for each subsequent div.
Explanation of JavaScript
The JavaScript uses a forEach loop to iterate through the selected divs. setTimeout is crucial; it introduces a delay before setting the opacity to 1, thus creating the staggered reveal effect. The delay is calculated as index * 500, resulting in a 0.5-second delay between each div's appearance.
Conclusion
This technique, combining setTimeout and CSS transitions, provides a simple yet effective way to enhance user experience by creating visually appealing, gradual element reveals. Experiment with different timings and styles to customize the effect further. The provided link (http://m.miracleart.cn/link/48fd3e91841d8619c84400e661895675) offers a live demonstration.
The above is the detailed content of Create Stunning Gradual Div Reveals with JavaScript setTimeout and CSS Transitions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What is 'render-blocking CSS'?
Jun 24, 2025 am 12:42 AM
What is 'render-blocking CSS'?
Jun 24, 2025 am 12:42 AM
CSS blocks page rendering because browsers view inline and external CSS as key resources by default, especially with imported stylesheets, header large amounts of inline CSS, and unoptimized media query styles. 1. Extract critical CSS and embed it into HTML; 2. Delay loading non-critical CSS through JavaScript; 3. Use media attributes to optimize loading such as print styles; 4. Compress and merge CSS to reduce requests. It is recommended to use tools to extract key CSS, combine rel="preload" asynchronous loading, and use media delayed loading reasonably to avoid excessive splitting and complex script control.
 External vs. Internal CSS: What's the Best Approach?
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:45 AM
External vs. Internal CSS: What's the Best Approach?
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:45 AM
ThebestapproachforCSSdependsontheproject'sspecificneeds.Forlargerprojects,externalCSSisbetterduetomaintainabilityandreusability;forsmallerprojectsorsingle-pageapplications,internalCSSmightbemoresuitable.It'scrucialtobalanceprojectsize,performanceneed
 Does my CSS must be on lower case?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:29 AM
Does my CSS must be on lower case?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:29 AM
No,CSSdoesnothavetobeinlowercase.However,usinglowercaseisrecommendedfor:1)Consistencyandreadability,2)Avoidingerrorsinrelatedtechnologies,3)Potentialperformancebenefits,and4)Improvedcollaborationwithinteams.
 CSS Case Sensitivity: Understanding What Matters
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:09 AM
CSS Case Sensitivity: Understanding What Matters
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:09 AM
CSSismostlycase-insensitive,butURLsandfontfamilynamesarecase-sensitive.1)Propertiesandvalueslikecolor:red;arenotcase-sensitive.2)URLsmustmatchtheserver'scase,e.g.,/images/Logo.png.3)Fontfamilynameslike'OpenSans'mustbeexact.
 What is Autoprefixer and how does it work?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:15 AM
What is Autoprefixer and how does it work?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:15 AM
Autoprefixer is a tool that automatically adds vendor prefixes to CSS attributes based on the target browser scope. 1. It solves the problem of manually maintaining prefixes with errors; 2. Work through the PostCSS plug-in form, parse CSS, analyze attributes that need to be prefixed, and generate code according to configuration; 3. The usage steps include installing plug-ins, setting browserslist, and enabling them in the build process; 4. Notes include not manually adding prefixes, keeping configuration updates, prefixes not all attributes, and it is recommended to use them with the preprocessor.
 What are CSS counters?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:34 AM
What are CSS counters?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:34 AM
CSScounterscanautomaticallynumbersectionsandlists.1)Usecounter-resettoinitialize,counter-incrementtoincrease,andcounter()orcounters()todisplayvalues.2)CombinewithJavaScriptfordynamiccontenttoensureaccurateupdates.
 CSS: When Does Case Matter (and When Doesn't)?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:27 AM
CSS: When Does Case Matter (and When Doesn't)?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:27 AM
In CSS, selector and attribute names are case-sensitive, while values, named colors, URLs, and custom attributes are case-sensitive. 1. The selector and attribute names are case-insensitive, such as background-color and background-Color are the same. 2. The hexadecimal color in the value is case-sensitive, but the named color is case-sensitive, such as red and Red is invalid. 3. URLs are case sensitive and may cause file loading problems. 4. Custom properties (variables) are case sensitive, and you need to pay attention to the consistency of case when using them.
 What is the conic-gradient() function?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:16 AM
What is the conic-gradient() function?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:16 AM
Theconic-gradient()functioninCSScreatescirculargradientsthatrotatecolorstopsaroundacentralpoint.1.Itisidealforpiecharts,progressindicators,colorwheels,anddecorativebackgrounds.2.Itworksbydefiningcolorstopsatspecificangles,optionallystartingfromadefin





