Sails.js: A Node.js MVC Framework for Rapid Application Development

Sails.js is a robust Node.js framework built upon Express.js and Socket.io, adhering to the "convention over configuration" principle. Inspired by Ruby on Rails, it streamlines the creation of REST APIs, single-page applications, and real-time applications leveraging WebSockets. Its extensive code generation capabilities significantly reduce development time, particularly for common application scaffolding. While version 1.0 is not yet officially released, it's already being used in production environments and recommended for new projects.
Key Advantages:
- Rapid Development: Sails.js accelerates development using conventions and automated code generation.
- Real-time Capabilities: Built-in Socket.io support enables real-time, bidirectional communication.
- Database Agnosticism: The integrated Waterline ORM/ODM supports various databases without requiring initial configuration. A built-in file-system database simplifies early development.
- Simplified Database Interactions: Waterline abstracts database complexities, providing a consistent interface across different database systems.
- RESTful API Generation: Automatically generates RESTful APIs, minimizing manual coding.
- Front-end Integration: Seamlessly integrates with front-end tools like Grunt (and others via custom generators), optimizing the development workflow.
- CLI Tool: Provides a command-line interface for efficient project scaffolding.
Current Limitations:
- Waterline Limitations: Currently lacks support for SQL JOIN queries and transactions (planned for future releases).
Sails.js vs. Express.js:
Sails.js acts as a higher-level abstraction over Express.js, providing additional features like an ORM/ODM, the MVC architectural pattern, and a powerful CLI. While Express.js offers flexibility, it requires more manual configuration and code for database interaction and application structure. Sails.js simplifies these aspects, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and development.
Waterline ORM/ODM:
Waterline is a core component of Sails.js, offering a consistent interface for interacting with both SQL and NoSQL databases. It eliminates the need to choose a database initially; a built-in file-system database (sails-disk) facilitates early testing. Switching databases later is straightforward by installing the appropriate adapter. Waterline supports popular databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Redis, with community-supported adapters for many others. While it generally simplifies database interactions, using raw SQL or native NoSQL APIs might bypass some Waterline features.
Getting Started:
- Prerequisites: Node.js (and npm) and a database system (or sails-disk).
-
Install Sails.js CLI:
sudo npm install sails -g(ornpm install sails@beta -gfor the latest 1.0 beta). -
Create a New Project:
sails new my-sails-app(orsails new my-sails-app --no-frontendto skip the front-end scaffolding). -
Project Structure: The generated project includes folders for controllers (
api/controllers), models (api/models), views (views), assets (assets), and configuration (config). -
Run the Project:
sails lift -
Create Models:
sails generate model product -
Create Controllers:
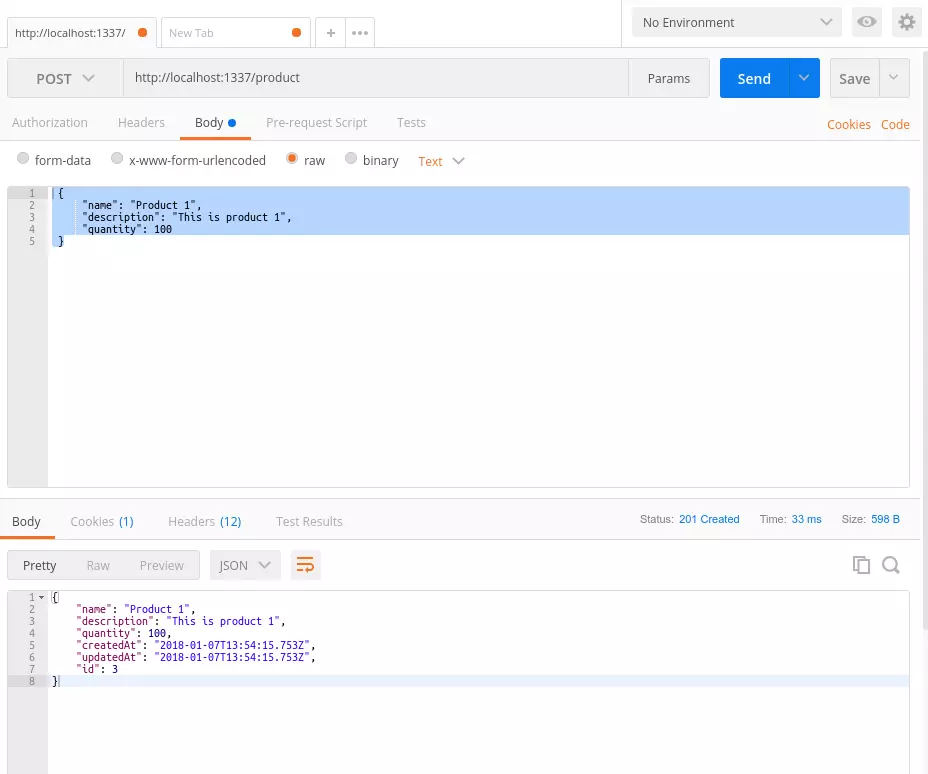
sails generate controller product - Testing: Use tools like Postman to test the automatically generated REST API endpoints.


Conclusion:
Sails.js offers a compelling blend of rapid development features and flexibility. While it has some limitations, its strengths in code generation, database abstraction, and real-time support make it a strong contender for various application types. Further exploration of its advanced features, such as services, policies, blueprints, and hooks, will enhance your proficiency with this powerful framework.
(Note: Image URLs were assumed to be valid and were not altered. The text was paraphrased and reorganized for improved clarity and flow while maintaining the original meaning.)
The above is the detailed content of An Introduction to Sails.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java and JavaScript are different programming languages, each suitable for different application scenarios. Java is used for large enterprise and mobile application development, while JavaScript is mainly used for web page development.
 Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
JavaScriptcommentsareessentialformaintaining,reading,andguidingcodeexecution.1)Single-linecommentsareusedforquickexplanations.2)Multi-linecommentsexplaincomplexlogicorprovidedetaileddocumentation.3)Inlinecommentsclarifyspecificpartsofcode.Bestpractic
 How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
The following points should be noted when processing dates and time in JavaScript: 1. There are many ways to create Date objects. It is recommended to use ISO format strings to ensure compatibility; 2. Get and set time information can be obtained and set methods, and note that the month starts from 0; 3. Manually formatting dates requires strings, and third-party libraries can also be used; 4. It is recommended to use libraries that support time zones, such as Luxon. Mastering these key points can effectively avoid common mistakes.
 Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
PlacingtagsatthebottomofablogpostorwebpageservespracticalpurposesforSEO,userexperience,anddesign.1.IthelpswithSEObyallowingsearchenginestoaccesskeyword-relevanttagswithoutclutteringthemaincontent.2.Itimprovesuserexperiencebykeepingthefocusonthearticl
 JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScriptispreferredforwebdevelopment,whileJavaisbetterforlarge-scalebackendsystemsandAndroidapps.1)JavaScriptexcelsincreatinginteractivewebexperienceswithitsdynamicnatureandDOMmanipulation.2)Javaoffersstrongtypingandobject-orientedfeatures,idealfor
 JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScripthassevenfundamentaldatatypes:number,string,boolean,undefined,null,object,andsymbol.1)Numbersuseadouble-precisionformat,usefulforwidevaluerangesbutbecautiouswithfloating-pointarithmetic.2)Stringsareimmutable,useefficientconcatenationmethodsf
 What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
Event capture and bubble are two stages of event propagation in DOM. Capture is from the top layer to the target element, and bubble is from the target element to the top layer. 1. Event capture is implemented by setting the useCapture parameter of addEventListener to true; 2. Event bubble is the default behavior, useCapture is set to false or omitted; 3. Event propagation can be used to prevent event propagation; 4. Event bubbling supports event delegation to improve dynamic content processing efficiency; 5. Capture can be used to intercept events in advance, such as logging or error processing. Understanding these two phases helps to accurately control the timing and how JavaScript responds to user operations.
 How can you reduce the payload size of a JavaScript application?
Jun 26, 2025 am 12:54 AM
How can you reduce the payload size of a JavaScript application?
Jun 26, 2025 am 12:54 AM
If JavaScript applications load slowly and have poor performance, the problem is that the payload is too large. Solutions include: 1. Use code splitting (CodeSplitting), split the large bundle into multiple small files through React.lazy() or build tools, and load it as needed to reduce the first download; 2. Remove unused code (TreeShaking), use the ES6 module mechanism to clear "dead code" to ensure that the introduced libraries support this feature; 3. Compress and merge resource files, enable Gzip/Brotli and Terser to compress JS, reasonably merge files and optimize static resources; 4. Replace heavy-duty dependencies and choose lightweight libraries such as day.js and fetch






