How to Build a Simple LLM Application with LCEL? - Analytics Vidhya
Mar 20, 2025 am 09:55 AMThis article demonstrates building a multilingual application using LangChain to translate text from English to other languages, specifically focusing on English-to-Japanese translation. It guides you through creating a basic application, explaining key LangChain concepts and workflows.

Key Concepts Covered:
The tutorial covers several crucial LangChain aspects:
-
Large Language Model (LLM) Interaction: The application directly interacts with an LLM (like OpenAI's GPT-4) to perform the translation, sending prompts and receiving translated text.
-
Prompt Engineering and Output Parsing: Prompt templates are used to create flexible prompts for dynamic text input. Output parsers ensure the LLM's response is correctly formatted and only the translated text is extracted.
-
LangChain Expression Language (LCEL): LCEL simplifies the process of chaining together multiple steps (prompt creation, LLM call, output parsing) into a streamlined workflow.
-
Debugging with LangSmith: The tutorial integrates LangSmith for monitoring, tracing data flow, and debugging the application's components.
-
Deployment with LangServe: LangServe is used to deploy the application as a cloud-accessible REST API.
Step-by-Step Guide (Simplified):
The tutorial provides a detailed, step-by-step guide, but here's a condensed version:
-
Install Libraries: Install necessary Python libraries (
langchain,langchain-openai,fastapi,uvicorn,langserve). -
Set up OpenAI Model: Configure your OpenAI API key and instantiate the GPT-4 model.
-
Basic Translation: Demonstrates a simple translation using system and human messages.
-
Output Parsing: Introduces output parsers to extract only the translated text from the LLM's response.
-
Chaining Components: Shows how to chain the model and parser together using the
|operator for a more efficient workflow. -
Prompt Templates: Creates a prompt template for dynamic text input, making the translation more versatile.
-
LCEL Chaining: Demonstrates chaining the prompt template, model, and parser using LCEL for a complete translation pipeline.
-
LangSmith Integration: Explains how to enable LangSmith for debugging and tracing.
-
LangServe Deployment: Guides you through deploying the application as a REST API using LangServe.
-
Running the Server and API Interaction: Shows how to run the LangServe server and interact with the deployed API programmatically.




The article concludes with a FAQ section addressing common questions about LangChain, its components, and the overall workflow. The tutorial provides a solid foundation for building more complex multilingual applications using LangChain.
The above is the detailed content of How to Build a Simple LLM Application with LCEL? - Analytics Vidhya. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Investing is booming, but capital alone isn’t enough. With valuations rising and distinctiveness fading, investors in AI-focused venture funds must make a key decision: Buy, build, or partner to gain an edge? Here’s how to evaluate each option—and pr
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
 Build Your First LLM Application: A Beginner's Tutorial
Jun 24, 2025 am 10:13 AM
Build Your First LLM Application: A Beginner's Tutorial
Jun 24, 2025 am 10:13 AM
Have you ever tried to build your own Large Language Model (LLM) application? Ever wondered how people are making their own LLM application to increase their productivity? LLM applications have proven to be useful in every aspect
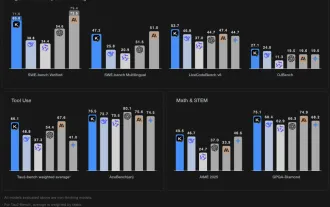 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
 AMD Keeps Building Momentum In AI, With Plenty Of Work Still To Do
Jun 28, 2025 am 11:15 AM
AMD Keeps Building Momentum In AI, With Plenty Of Work Still To Do
Jun 28, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Overall, I think the event was important for showing how AMD is moving the ball down the field for customers and developers. Under Su, AMD’s M.O. is to have clear, ambitious plans and execute against them. Her “say/do” ratio is high. The company does
 Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). For those readers who h
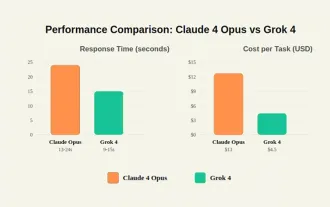 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
For example, if you ask a model a question like: “what does (X) person do at (X) company?” you may see a reasoning chain that looks something like this, assuming the system knows how to retrieve the necessary information:Locating details about the co






