Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.

introduction
Before exploring the best uses of Linux, let’s first think about one question: What is the best thing for Linux? As an open source operating system, Linux is highly regarded for its flexibility, stability and security. Whether you are a developer, system administrator, or just a technology enthusiast, Linux provides powerful tools and environments to meet your needs. This article will take you into the deep understanding of the many uses of Linux, from server management to embedded systems, and then to desktop environments, helping you fully grasp the power of Linux.
Review of basic knowledge
Linux is a Unix-based operating system first released by Linus Torvalds in 1991. It is known for its open source features, meaning that anyone can view, modify and distribute its source code. The core components of Linux include kernel, shell, file system, etc. These elements together form a powerful and flexible operating system.
If you are not familiar with the basic concepts of operating systems, you can simply understand that an operating system is software that manages computer hardware resources and provides services to applications. Linux performs particularly well in this regard, supporting a variety of hardware platforms, from servers to embedded devices, everything can be done.
Core concept or function analysis
The versatility of Linux
One of the biggest advantages of Linux is its versatility. It is not just an operating system, but an ecosystem that can adapt to various application scenarios. Whether used as a server operating system or in embedded systems, Linux demonstrates its powerful adaptability and flexibility.
For example, in the server field, Linux is widely used to host websites, databases, and applications. Its stability and reliability make it the first choice for many companies. In addition, the open source nature of Linux also means that it can be customized to meet specific needs, which is particularly important in enterprise-level applications.
How it works
How Linux works can be understood from its kernel and file system. The kernel is the core part of the operating system, responsible for managing hardware resources and providing basic services. The Linux kernel is known for its modular design, which allows it to load and uninstall functional modules as needed, enabling efficient resource management.
File system is another key component, and Linux uses a tree structure to organize files and directories, which is different from Windows' file system, but is just as intuitive and efficient. Understanding these fundamentals will help you better utilize the power of Linux.
Let's look at a simple example of how to create a directory and write a file in Linux:
# Create a new directory called 'my_directory' mkdir my_directory # Enter the newly created directory cd my_directory # Create a new file named 'my_file.txt' and write something echo "Hello, Linux!" > my_file.txt # View file content cat my_file.txt
This simple script demonstrates the use of basic Linux commands to help you understand how they operate.
Example of usage
Server Management
Linux is widely used in server management. Whether it is hosting a website, running a database, or as a mail server, Linux provides powerful tools and stability. Let's look at a simple example of how to install an Apache web server on Ubuntu:
# Update package list sudo apt update # Install Apache sudo apt install apache2 # Start the Apache service sudo systemctl start apache2 # Check whether Apache is running sudo systemctl status apache2
This script shows how to install and start a web server on Linux, simple and efficient.
Embedded system
Linux is also widely used in embedded systems. From smart home devices to automotive electronic systems, Linux's flexibility and stability make it the preferred operating system for embedded development. Let's look at a simple example of how to install Linux on a Raspberry Pi and run a simple Python script:
# Download Raspberry Pi Imager wget https://downloads.raspberrypi.org/imager/imager_latest_amd64.deb # Install Raspberry Pi Imager sudo dpkg -i imager_latest_amd64.deb # Use Raspberry Pi Imager to burn Raspberry Pi OS to SD card# This step requires manual operation. For details, please refer to the official documentation # Start Raspberry Pi and log in # Create and run a simple Python script echo "print('Hello, Embedded Linux!')" > hello.py python3 hello.py
This script shows how to use Linux on an embedded device and run a simple Python script.
Desktop environment
While Linux is more common in servers and embedded systems, it also provides a powerful desktop environment. Whether it is Ubuntu, Fedora or Linux Mint, Linux desktop systems provide rich applications and efficient performance. Let's look at a simple example of how to install and use GIMP image editing software on Ubuntu:
# Update package list sudo apt update # Install GIMP sudo apt install gimp # Start GIMP gimp
This script shows how to install and use a commonly used application software in a Linux desktop environment.
Common Errors and Debugging Tips
When using Linux, you may encounter some common problems. For example, permission issues, package dependency issues, etc. Let's look at some common errors and their solutions:
- Permissions issue : If you encounter permission errors when executing certain commands, you can use the
sudocommand to elevate permissions. For example:
# Execute the command sudo apt update
- Package dependency problem : When installing software, if you encounter dependency problems, you can use the
aptcommand to solve it. For example:
# Fix dependency problem sudo apt --fix-broken install
These tips can help you solve common problems more smoothly when using Linux.
Performance optimization and best practices
In practical applications, how to optimize the performance of Linux system is a key issue. Let's look at some common optimization methods:
Use a lightweight desktop environment : If you are using Linux in your desktop environment, you can choose a lightweight desktop environment such as LXDE or Xfce to improve system performance.
Optimized startup time : By adjusting startup items and services, the system startup time can be significantly reduced. For example:
# List all startup services systemctl list-units --type=service --state=active # Disable unnecessary_service
- Monitor and optimize resource usage : Use tools such as
top,htoporglancesto monitor system resource usage and optimize as needed.
In addition, programming habits and best practices are also important aspects to improve Linux usage efficiency. For example, writing highly readable scripts, using version control systems, and regularly backing up data are all good Linux usage habits.
Overall, Linux's versatility makes it ideal for a variety of application scenarios. Whether you are a developer, system administrator, or technology enthusiast, Linux can provide you with powerful tools and environments. Hope this article helps you better understand and utilize the powerful features of Linux.
The above is the detailed content of What is the Linux best used for?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Integrating Postman applications on CentOS can be achieved through a variety of methods. The following are the detailed steps and suggestions: Install Postman by downloading the installation package to download Postman's Linux version installation package: Visit Postman's official website and select the version suitable for Linux to download. Unzip the installation package: Use the following command to unzip the installation package to the specified directory, for example /opt: sudotar-xzfpostman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz-C/opt Please note that "postman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz" is replaced by the file name you actually downloaded. Create symbols
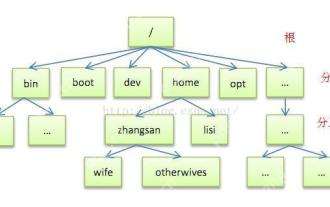 Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
[Common Directory Description] Directory/bin stores binary executable files (ls, cat, mkdir, etc.), and common commands are generally here. /etc stores system management and configuration files/home stores all user files. The root directory of the user's home directory is the basis of the user's home directory. For example, the home directory of the user user is /home/user. You can use ~user to represent /usr to store system applications. The more important directory /usr/local Local system administrator software installation directory (install system-level applications). This is the largest directory, and almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory. /usr/x11r6?Directory for storing x?window/usr/bin?Many
 Where is the pycharm interpreter?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Where is the pycharm interpreter?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Setting the location of the interpreter in PyCharm can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Open PyCharm, click the "File" menu, and select "Settings" or "Preferences". 2. Find and click "Project:[Your Project Name]" and select "PythonInterpreter". 3. Click "AddInterpreter", select "SystemInterpreter", browse to the Python installation directory, select the Python executable file, and click "OK". When setting up the interpreter, you need to pay attention to path correctness, version compatibility and the use of the virtual environment to ensure the smooth operation of the project.
 The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The main difference between Java and other programming languages ??is its cross-platform feature of "writing at once, running everywhere". 1. The syntax of Java is close to C, but it removes pointer operations that are prone to errors, making it suitable for large enterprise applications. 2. Compared with Python, Java has more advantages in performance and large-scale data processing. The cross-platform advantage of Java stems from the Java virtual machine (JVM), which can run the same bytecode on different platforms, simplifying development and deployment, but be careful to avoid using platform-specific APIs to maintain cross-platformity.
 After installing Nginx, the configuration file path and initial settings
May 16, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
After installing Nginx, the configuration file path and initial settings
May 16, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
Understanding Nginx's configuration file path and initial settings is very important because it is the first step in optimizing and managing a web server. 1) The configuration file path is usually /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. The syntax can be found and tested using the nginx-t command. 2) The initial settings include global settings (such as user, worker_processes) and HTTP settings (such as include, log_format). These settings allow customization and extension according to requirements. Incorrect configuration may lead to performance issues and security vulnerabilities.
 MySQL installation tutorial teach you step by step the detailed steps for installing and configuration of mySQL step by step
May 23, 2025 am 06:09 AM
MySQL installation tutorial teach you step by step the detailed steps for installing and configuration of mySQL step by step
May 23, 2025 am 06:09 AM
The installation and configuration of MySQL can be completed through the following steps: 1. Download the installation package suitable for the operating system from the official website. 2. Run the installer, select the "Developer Default" option and set the root user password. 3. After installation, configure environment variables to ensure that the bin directory of MySQL is in PATH. 4. When creating a user, follow the principle of minimum permissions and set a strong password. 5. Adjust the innodb_buffer_pool_size and max_connections parameters when optimizing performance. 6. Back up the database regularly and optimize query statements to improve performance.
 Comparison between Informix and MySQL on Linux
May 29, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Comparison between Informix and MySQL on Linux
May 29, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Informix and MySQL are both popular relational database management systems. They perform well in Linux environments and are widely used. The following is a comparison and analysis of the two on the Linux platform: Installing and configuring Informix: Deploying Informix on Linux requires downloading the corresponding installation files, and then completing the installation and configuration process according to the official documentation. MySQL: The installation process of MySQL is relatively simple, and can be easily installed through system package management tools (such as apt or yum), and there are a large number of tutorials and community support on the network for reference. Performance Informix: Informix has excellent performance and
 Experience in participating in VSCode offline technology exchange activities
May 29, 2025 pm 10:00 PM
Experience in participating in VSCode offline technology exchange activities
May 29, 2025 pm 10:00 PM
I have a lot of experience in participating in VSCode offline technology exchange activities, and my main gains include sharing of plug-in development, practical demonstrations and communication with other developers. 1. Sharing of plug-in development: I learned how to use VSCode's plug-in API to improve development efficiency, such as automatic formatting and static analysis plug-ins. 2. Practical demonstration: I learned how to use VSCode for remote development and realized its flexibility and scalability. 3. Communicate with developers: I have obtained skills to optimize VSCode startup speed, such as reducing the number of plug-ins loaded at startup and managing the plug-in loading order. In short, this event has benefited me a lot and I highly recommend those who are interested in VSCode to participate.






