The network configuration of CentOS 7 no longer uses the old ifconfig tool, but uses a more powerful systemd-networkd, which manages the network through configuration files. Configuration files ending in .network (for example, /etc/systemd/network/eth0.network) specify network settings using YAML format. Static IP configuration requires the specified address, gateway, and DNS, while dynamic IP configuration requires only one line of DHCP=yes. systemd-networkd supports a variety of complex configurations, including multiple IP addresses, VLANs, and Bonding. Need to pay attention to syntax errors

CentOS 7 Network Configuration: More than ifconfig
Many newbies will ask, how to configure the network in CentOS 7? The answer is more than just the simple ifconfig . That thing is outdated in modern Linux systems. Although it can still be used, it is just a tool and not the right way to configure the network. Only by understanding the deep principles can we deal with various strange network environments. After reading this article, you can not only configure the network, but also understand the mechanism behind it, and even write a simple network configuration tool yourself.
First, we need to figure out whether CentOS 7 uses NetworkManager or systemd-networkd to manage the network. NetworkManager is a graphical tool that is convenient for novices to get started, but it seems to be powerless for complex network scenarios; systemd-networkd is a command line tool that is more flexible and powerful, and suitable for advanced users. Generally, NetworkManager is the default, but this article mainly talks about systemd-networkd because it represents a more modern way of network management.
The core of systemd-networkd is the configuration file, located in /etc/systemd/network/ directory. Each configuration file corresponds to a network interface, and the file name usually ends with .network . The configuration file is written in YAML format and is very concise and easy to read. For example, configure a static IP address named eth0 :
<code class="yaml">[Match] Name=eth0 [Network] Address=192.168.1.100/24 Gateway=192.168.1.1 DNS=8.8.8.8</code>
This configuration is very simple. Match part specifies the matching interface name, and Network part specifies the IP address, gateway and DNS server. After saving the file, execute systemctl daemon-reload and systemctl restart network to take effect. Note that file names are important, and it determines how the system recognizes this configuration.
Of course, this is just a static IP configuration, and the dynamic IP (DHCP) configuration is also simple:
<code class="yaml">[Match] Name=eth0 [Network] DHCP=yes</code>
Just one line of DHCP=yes is done.
More advanced usage? Do you want to configure multiple IP addresses? no problem! VLAN? That's fine! Bonding? sure! systemd-networkd supports various complex network configurations. There are many options in the configuration file, so you can refer to the official documentation.
Here I want to focus on the possible pitfalls:
- Configuration file syntax error: YAML format is very sensitive to indentation, and an error in a space will cause configuration failure. Be sure to check the grammar carefully.
- Interface name: Be sure to confirm the interface name, don’t write it incorrectly. You can use
ip link showcommand to view the interface name. - Firewall: After configuring the network, don't forget to check whether the firewall allows access.
firewall-cmdcommand can be used to manage firewall. - SELinux: SELinux may also affect network configuration. If you encounter problems, you can temporarily shut down SELinux, but this is not recommended for production environments.
Performance optimization? For systemd-networkd itself, performance optimization is mainly reflected in the writing of configuration files, avoid unnecessary complex configurations, and keep the configuration files simple and easy to read. This is more effective than modifying kernel parameters.
Finally, remember that practice brings true knowledge. Only by doing more hands-on configuration and trying different configurations can you truly master the network configuration of CentOS 7. Don’t be afraid of making mistakes, making mistakes is part of learning. Network configuration is a complex topic, but as long as you master the basic principles and tools, you can easily deal with various challenges. I wish you a happy time!
The above is the detailed content of How to configure network in centos7. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Integrating Postman applications on CentOS can be achieved through a variety of methods. The following are the detailed steps and suggestions: Install Postman by downloading the installation package to download Postman's Linux version installation package: Visit Postman's official website and select the version suitable for Linux to download. Unzip the installation package: Use the following command to unzip the installation package to the specified directory, for example /opt: sudotar-xzfpostman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz-C/opt Please note that "postman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz" is replaced by the file name you actually downloaded. Create symbols
 The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The main difference between Java and other programming languages ??is its cross-platform feature of "writing at once, running everywhere". 1. The syntax of Java is close to C, but it removes pointer operations that are prone to errors, making it suitable for large enterprise applications. 2. Compared with Python, Java has more advantages in performance and large-scale data processing. The cross-platform advantage of Java stems from the Java virtual machine (JVM), which can run the same bytecode on different platforms, simplifying development and deployment, but be careful to avoid using platform-specific APIs to maintain cross-platformity.
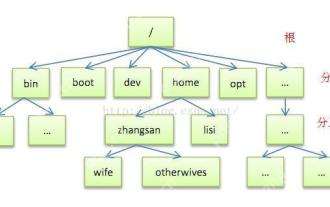 Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
[Common Directory Description] Directory/bin stores binary executable files (ls, cat, mkdir, etc.), and common commands are generally here. /etc stores system management and configuration files/home stores all user files. The root directory of the user's home directory is the basis of the user's home directory. For example, the home directory of the user user is /home/user. You can use ~user to represent /usr to store system applications. The more important directory /usr/local Local system administrator software installation directory (install system-level applications). This is the largest directory, and almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory. /usr/x11r6?Directory for storing x?window/usr/bin?Many
 Where is the pycharm interpreter?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Where is the pycharm interpreter?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Setting the location of the interpreter in PyCharm can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Open PyCharm, click the "File" menu, and select "Settings" or "Preferences". 2. Find and click "Project:[Your Project Name]" and select "PythonInterpreter". 3. Click "AddInterpreter", select "SystemInterpreter", browse to the Python installation directory, select the Python executable file, and click "OK". When setting up the interpreter, you need to pay attention to path correctness, version compatibility and the use of the virtual environment to ensure the smooth operation of the project.
 MySQL installation tutorial teach you step by step the detailed steps for installing and configuration of mySQL step by step
May 23, 2025 am 06:09 AM
MySQL installation tutorial teach you step by step the detailed steps for installing and configuration of mySQL step by step
May 23, 2025 am 06:09 AM
The installation and configuration of MySQL can be completed through the following steps: 1. Download the installation package suitable for the operating system from the official website. 2. Run the installer, select the "Developer Default" option and set the root user password. 3. After installation, configure environment variables to ensure that the bin directory of MySQL is in PATH. 4. When creating a user, follow the principle of minimum permissions and set a strong password. 5. Adjust the innodb_buffer_pool_size and max_connections parameters when optimizing performance. 6. Back up the database regularly and optimize query statements to improve performance.
 How to optimize HDFS configuration on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to optimize HDFS configuration on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Optimizing the performance of Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS) on CentOS systems can be achieved through a variety of methods, including adjusting system kernel parameters, optimizing HDFS configuration files, and improving hardware resources. The following are detailed optimization steps and suggestions: Adjust the system kernel parameters to increase the limit on the number of files opened by a single process: Use the ulimit-n65535 command to temporarily adjust. If it needs to take effect permanently, please edit the /etc/security/limits.conf and /etc/pam.d/login files. Optimize TCP parameters: Edit /etc/sysctl.conf file, add or modify the following content: net.ipv4.tcp_tw
 Comparison between Informix and MySQL on Linux
May 29, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Comparison between Informix and MySQL on Linux
May 29, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Informix and MySQL are both popular relational database management systems. They perform well in Linux environments and are widely used. The following is a comparison and analysis of the two on the Linux platform: Installing and configuring Informix: Deploying Informix on Linux requires downloading the corresponding installation files, and then completing the installation and configuration process according to the official documentation. MySQL: The installation process of MySQL is relatively simple, and can be easily installed through system package management tools (such as apt or yum), and there are a large number of tutorials and community support on the network for reference. Performance Informix: Informix has excellent performance and
 Experience in participating in VSCode offline technology exchange activities
May 29, 2025 pm 10:00 PM
Experience in participating in VSCode offline technology exchange activities
May 29, 2025 pm 10:00 PM
I have a lot of experience in participating in VSCode offline technology exchange activities, and my main gains include sharing of plug-in development, practical demonstrations and communication with other developers. 1. Sharing of plug-in development: I learned how to use VSCode's plug-in API to improve development efficiency, such as automatic formatting and static analysis plug-ins. 2. Practical demonstration: I learned how to use VSCode for remote development and realized its flexibility and scalability. 3. Communicate with developers: I have obtained skills to optimize VSCode startup speed, such as reducing the number of plug-ins loaded at startup and managing the plug-in loading order. In short, this event has benefited me a lot and I highly recommend those who are interested in VSCode to participate.






