What is the PATH environment variable and how do you modify it?
Jun 25, 2025 am 12:14 AMThe PATH environment variable tells the operating system where to look for executable programs when running commands from the terminal. 1. It contains a list of directories separated by colons (on Unix-like systems) or semicolons (on Windows). 2. When you enter a command, the system searches these directories in order to locate the executable. 3. If the executable isn't found in any of the listed directories, the command fails unless a full path is provided. 4. You can view your current PATH by using echo $PATH (Unix-like) or echo %PATH% (Windows). 5. To temporarily add a directory to PATH, use export PATH="/your/custom/path:$PATH" (bash/zsh) or set -x PATH /your/custom/path $PATH (fish). 6. For permanent changes, edit your shell configuration file (e.g., .bashrc, .zshrc), add the export line, and reload the configuration with source ~/.zshrc (or equivalent). This allows custom tools to be accessed globally or override default system commands as needed.

The PATH environment variable is basically a list of directories that your operating system uses to find executable programs. When you type a command in the terminal or run a program from the command line, the system looks through the directories listed in PATH, in order, to find the executable file it needs. If it's not in PATH, you either have to type the full path to the program or the system won't recognize the command.
What does PATH do exactly?
Think of PATH like a set of shortcuts for your command line. It tells the system where to look for commands without you having to specify the full location every time. For example, when you type python or git, the system checks each directory in your PATH until it finds an executable named python or git.
Each entry in PATH is a directory path — things like /usr/local/bin or /usr/bin. These are standard locations where many applications install their command-line tools. If you install something custom and want to run it from anywhere, adding its bin directory to PATH makes that possible.
Some common cases where you might need to modify PATH:
- You installed a tool manually and want to use it globally.
- You're using version managers (like
nvmfor Node.js) that rely on modifying PATH temporarily. - You want to override a default system command with a newer version you installed yourself.
How to view your current PATH
To see what your PATH currently contains, just open a terminal and type:
echo $PATH
You’ll get a long string separated by colons (:). Each segment is a directory. On most systems, the output will look something like this:
/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin
If you’re on Windows, you can check PATH by opening Command Prompt and typing:
echo %PATH%
It works similarly, except directories are separated by semicolons (;) instead of colons.
How to add a directory to PATH temporarily
If you just want to test something out or make a change that lasts for one session, you can add a directory to PATH directly in the terminal. The syntax depends on your shell.
For bash/zsh:
export PATH="/your/custom/path:$PATH"
For fish shell:
set -x PATH /your/custom/path $PATH
This will prepend the new directory to your PATH, meaning it checks there first. Keep in mind: these changes go away once you close the terminal window.
How to make PATH changes permanent
To keep your changes across sessions, you need to edit your shell configuration file. Which file depends on your shell and OS setup.
Common files include:
.bashrcor.bash_profilefor bash.zshrcfor zsh.profileor.bash_profileon macOS if using bash as default
Open the appropriate file in a text editor, then add the same export PATH=... line you used earlier. For example:
export PATH="/opt/myapp/bin:$PATH"
Save the file and reload your shell config:
source ~/.zshrc # or .bashrc, depending on your shell
After that, your new PATH should stick around even after restarting your terminal.
That’s basically how PATH works and how to manage it — not too complicated, but super useful once you understand how it affects your workflow.
The above is the detailed content of What is the PATH environment variable and how do you modify it?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Details on how to turn on environment variable settings on Windows 11
Dec 30, 2023 pm 06:07 PM
Details on how to turn on environment variable settings on Windows 11
Dec 30, 2023 pm 06:07 PM
The environment variable function is an essential tool for running the configuration program in the system. However, in the latest win11 system, there are still many users who do not know how to set it up. Here is a detailed introduction to the location of the win11 environment variable opening. Come and join us. Learn to operate it. Where are the win11 environment variables: 1. First enter "win+R" to open the run box. 2. Then enter the command: controlsystem. 3. In the system information interface that opens, select "Advanced System Settings" from the left menu. 4. Then select the "Environment Variables" option at the bottom of the "System Properties" window that opens. 5. Finally, in the opened environment variables, you can make relevant settings according to your needs.
 How to configure python environment variables in Win11? Tips for adding environment variables in win11python
Feb 29, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
How to configure python environment variables in Win11? Tips for adding environment variables in win11python
Feb 29, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
Win11 system is the latest Windows operating system, and users may encounter some configuration problems when using it. Among them, configuring Python environment variables is a common requirement because it allows users to easily use Python commands from any location. This article will introduce how to configure Python environment variables in Win11 system so that users can use the Python programming language more conveniently. 1. [Right-click] this computer on the desktop, and select [Properties] in the menu item that opens; 2. Then, under related links, find and click [Advanced System Settings]; 3. In the system properties window, click [Environment] at the bottom Variables]; 4. In the environment variables window, under system variables, select [Path], and then click
 Windows 10 environment variable setting tutorial
Jul 15, 2023 pm 06:09 PM
Windows 10 environment variable setting tutorial
Jul 15, 2023 pm 06:09 PM
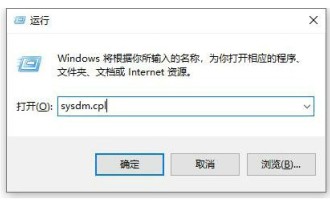
Environment variables are an important setting in the operating system, but some Windows 10 users still don’t know how to set environment variables. In fact, the method is very simple. Open the run window, call up the system characteristics window through the sysdm.cpl command, and then switch to the advanced tab. You will see a button for environment variables. Click this button to enter the setting of environment variables. interface, and then just set it up according to actual needs. How to set environment variables in Windows 10: 1. First open the run window on the computer, then enter sysdm.cpl in the window and press Enter. 2. Select Advanced in the system properties interface, and then click Environment Variables. 3. Here we can see the variables displayed, and we can create a new one on a single machine.
 Steps to set the PATH environment variable of the Linux system
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:40 PM
Steps to set the PATH environment variable of the Linux system
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:40 PM
How to set the PATH environment variable in Linux systems In Linux systems, the PATH environment variable is used to specify the path where the system searches for executable files on the command line. Correctly setting the PATH environment variable allows us to execute system commands and custom commands at any location. This article will introduce how to set the PATH environment variable in a Linux system and provide detailed code examples. View the current PATH environment variable. Execute the following command in the terminal to view the current PATH environment variable: echo$P
 How to configure Tomcat environment variables
Oct 26, 2023 am 10:41 AM
How to configure Tomcat environment variables
Oct 26, 2023 am 10:41 AM
To configure Tomcat environment variables, you need to add the CATALINA_HOME variable to the system and add the Tomcat installation path to the PATH variable. The steps in Windows are to first download and install Tomcat, open the system properties window, open the environment variable settings, add the Tomcat environment variable, modify the Path variable and verify the configuration. The steps in Linux are to first download and install Tomcat, open a terminal window, edit the bashrc file, add Tomcat environment variables, etc.
 How to set conda environment variables
Dec 05, 2023 pm 01:42 PM
How to set conda environment variables
Dec 05, 2023 pm 01:42 PM
Conda environment variable setting steps: 1. Find the installation path of conda; 2. Open the "System Properties" dialog box; 3. In the "System Properties" dialog box, select the "Advanced" tab, and then click the "Environment Variables" button; 4. In the "Environment Variables" dialog box, find the "System Variables" section, and then scroll to the "Path" variable; 5. Click the "New" button, and then paste the conda installation path; 6. Click "OK" to save the changes; 7. Verify whether the setting is successful.
 How to solve the problem that Java environment variable configuration does not take effect
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:57 PM
How to solve the problem that Java environment variable configuration does not take effect
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:57 PM
How to solve the problem that Java environment variables do not take effect after configuration. During the Java development process, we often need to configure Java environment variables to ensure the normal operation of the program. However, sometimes we encounter some strange problems. Even if the Java environment variables are configured correctly, we find that the program does not run as configured. This is actually a common problem, and this article will introduce some solutions and provide specific code examples. The root cause of the problem is that the configuration of Java environment variables does not take effect correctly. Here are some common
 Practical tips to effectively solve Tomcat environment variable configuration failure
Dec 28, 2023 am 10:32 AM
Practical tips to effectively solve Tomcat environment variable configuration failure
Dec 28, 2023 am 10:32 AM
Practical tips to solve the problem of unsuccessful configuration of Tomcat environment variables Summary: Tomcat is a very popular Java application server, but sometimes we may encounter some problems when configuring environment variables. This article will introduce several practical techniques to solve the problem of unsuccessful Tomcat environment variable configuration, and give specific code examples. Introduction: Tomcat is an open source web server used to run JavaWeb applications. However, when configuring Tomcat environment variables, you may sometimes encounter






