Introducing Lambda expressions, the syntactic sugar of Java 8
Feb 18, 2021 pm 06:09 PM
Free learning recommendation: java basic tutorial
##1. Introduction to Lambda expressions
Lambda expression is a new feature of Java8 and one of the most worth learning new features in Java8. (Another new feature is flow programming.)
- A Lambda expression is, essentially, an
anonymous method
. You can use this anonymous method toimplement the methodsin the interface. - Function: Lambda expressions are usually used to
simplify interface implementation
. There are many ways to implement interfaces, such as: ① Design the implementation class of the interface, ② Use anonymous inner classes. But ③ using lambda expression is simpler than these two methods. - Requirements: lambda expressions,
can only implement functional interfaces
: That is, in an interface, there is only one abstract method that the implementation class must implement.
@FunctionalInterface annotation
, used before the interface, is used to determine whether the interface is a functional interface. If it is not a functional interface, an error will be reported. The functionality is similar to @Override.
2. Lambda expression syntax
lambda expression is essentially an anonymous method, so when writing lambda expressions, no need You don't care what the method name is, and you don't need to care about the return value type. You only need to care about two parts:Parameter list
,Method body.
- () Parameter part: The parameter list of the method must be consistent with the method parameter part in the implemented interface, including the number and type of parameters.
- {}Method body part: The implementation part of the method. If the method defined in the interface has a return value, pay attention to the return value when implementing it.
- -> : Separates the parameter part and the method body part.
Lambda表達(dá)式基礎(chǔ)語法:(參數(shù))?->{
方法體}
The following defines 6 types offunctional interfaces
with different parameters and return values, and uses lambda expressions to implement the methods in the interface:
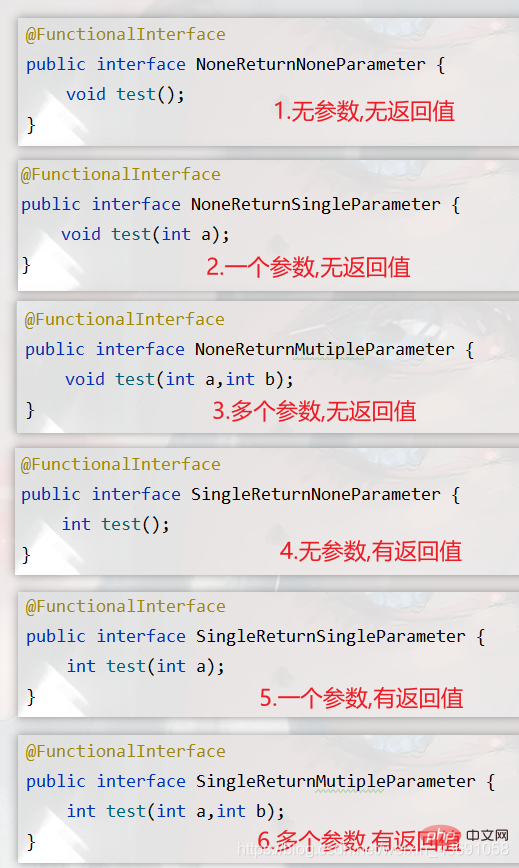
#The following is the lambda expression implementation for the above six functional interfaces.
/**
?*?@Description:
?*?@author?Guoqianliang
?*?@date?19:50?-?2021/2/15
?*/public?class?BasicSyntax?{
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????//?1.實(shí)現(xiàn)無參數(shù),無返回值的函數(shù)式接口
????????NoneReturnNoneParameter?lambda1?=?()?->?{
????????????System.out.println("這是無參,無返回值的方法");
????????};
????????lambda1.test();
????????//?2.實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)參數(shù),無返回值的函數(shù)式接口
????????NoneReturnSingleParameter?lambda2?=?(int?a)?->?{
????????????System.out.println("這是一個(gè)參數(shù),無返回值的方法,參數(shù)a:"?+?a);
????????};
????????lambda2.test(10);
????????//?3.實(shí)現(xiàn)多個(gè)參數(shù),無返回值的函數(shù)式接口
????????NoneReturnMutipleParameter?lambda3?=?(int?a,?int?b)?->?{
????????????System.out.println("這是多個(gè)參數(shù),無返回值的方法,參數(shù)a="?+?a?+?",b="?+?b);
????????};
????????lambda3.test(10,?20);
????????//?4.實(shí)現(xiàn)無參數(shù),有返回值有返回值的函數(shù)式接口
????????SingleReturnNoneParameter?lambda4?=?()?->?{
????????????System.out.println("這是無參數(shù),有返回值的方法,返回值是:");
????????????return?10;
????????};
????????System.out.println(lambda4.test());
????????//?5.實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)參數(shù),有返回值的函數(shù)式接口
????????SingleReturnSingleParameter?lambda5?=?(int?a)?->?{
????????????System.out.println("這是一個(gè)參數(shù),有返回值的方法,返回值是:");
????????????return?a;
????????};
????????System.out.println(lambda5.test(10));
????????//?6.實(shí)現(xiàn)多個(gè)參數(shù),有返回值的函數(shù)式接口
????????SingleReturnMutipleParameter?lambda6?=?(int?a,?int?b)?->?{
????????????System.out.println("這是多個(gè)參數(shù),有返回值的方法,返回值是:");
????????????return?a?+?b;
????????};
????????System.out.println(lambda6.test(1,?2));
????}}
Syntax simplification and advanced:
- The parameter type of the parameter list can be omitted.
- If there is and is only one parameter in the parameter list, the parentheses can be omitted.
- If there is only one statement in the method body, the curly braces can be omitted. (Note: If this statement is a return statement, the return keyword must also be omitted after omitting the braces)
3. Function reference
Lambda expressions are to simplify the interface. In lambda expressions, more complex logic should not appear. If the logic that needs to be processed is relatively complex, a separate method will generally be written. Just reference this method directly in the lambda expression. That is,refers to an existing method so that it can replace the lambda expression to complete the implementation of the interface.
1. Static method reference
Syntax:Class::Static method
Do not add parentheses after the quoted method.
- The referenced method, parameters (number, type) and return value must be consistent with those defined in the interface.
/** ?*?@Description:?方法引用 ?*?@author?Guoqianliang ?*?@date?0:26?-?2021/2/16 ?*/public?class?Lambda1?{ ????private?static?interface?Calculate?{ ????????int?calculate(int?a,?int?b); ????} ????private?static?int?calculate(int?x,?int?y)?{ ????????if?(x?>?y)?{ ????????????return?x?-?y; ????????}?else?if?(x?
2. Non-static method reference
Syntax:Object::Non-static method
Do not add parentheses after the quoted method.
- The referenced method, parameters (number, type) and return value must be consistent with those defined in the interface.
/** ?*?@Description:?方法引用 ?*?@author?Guoqianliang ?*?@date?0:26?-?2021/2/16 ?*/public?class?Lambda1?{ ????private?static?interface?Calculate?{ ????????int?calculate(int?a,?int?b); ????} ????//?非靜態(tài)方法 ????private?int?calculate2(int?a,?int?b)?{ ????????if?(a?!=?b)?{ ????????????return?a?-?b; ????????} ????????return?a?+?b; ????} ????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{ ????????//?非靜態(tài)方法引用 ????????Calculate?calculate2?=?new?Lambda1()::calculate2; ????????System.out.println(calculate.calculate(10,?20)); ????}}
3. Constructor method reference
Syntax:Class name::new
You can distinguish between different constructor methods through the parameters of the methods in the interface.
- If a method defined in a functional interface is just to get an object of a class. At this point, you can use the reference to the constructor method to simplify the implementation of this method.
/** ?*?@Description:?構(gòu)造方法引用 ?*?@author?Guoqianliang ?*?@date?11:20?-?2021/2/16 ?*/public?class?Lambda2?{ ????@FunctionalInterface ????private?interface?GetPersonWithNoneParameter?{ ????????Person?get(); ????} ????@FunctionalInterface ????private?interface?GetPersonWithSingleParameter?{ ????????Person?get(String?name); ????} ????@FunctionalInterface ????private?interface?GetPersonWithMutipleParameter?{ ????????Person?get(String?name,?int?age); ????} ????private?static?class?Person?{ ????????String?name; ????????int?age; ????????public?Person()?{ ????????????System.out.println("Person類的無參構(gòu)造方法執(zhí)行了"); ????????} ????????public?Person(String?name)?{ ????????????this.name?=?name; ????????????System.out.println("Person類的有參構(gòu)造方法執(zhí)行了"); ????????} ????????public?Person(String?name,?int?age)?{ ????????????this.name?=?name; ????????????this.age?=?age; ????????????System.out.println("Person類的兩個(gè)參數(shù)的構(gòu)造方法執(zhí)行了"); ????????} ????} ????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{ ????????//?1.使用lambda表達(dá)式,實(shí)現(xiàn)GetPersonWithNoneParameter接口 ????????GetPersonWithNoneParameter?getPerson?=?Person::new; ????????//?2.使用lambda表達(dá)式,實(shí)現(xiàn)GetPersonWithSingleParameter接口 ????????GetPersonWithSingleParameter?getPerson2?=?Person::new; ????????//?3.使用lambda表達(dá)式,實(shí)現(xiàn)GetPersonWithMutipleParameter接口 ????????GetPersonWithMutipleParameter?getPerson3?=?Person::new; ????????System.out.println(getPerson.get()); ????????System.out.println(getPerson2.get("樹先生")); ????????System.out.println(getPerson3.get("你好",?23)); ????}}
4. Special references to object methods
When using lambda expressions to implement certain interfaces, if in the lambda expression Contains an object. In the method body, directly using this object to call one of its methods can complete the overall logic.
/**
?*?@Description:?對象方法的特殊應(yīng)用
?*?@author?Guoqianliang
?*?@date?11:54?-?2021/2/16
?*/public?class?Lambda3?{
????@FunctionalInterface
????private?interface?MyInterface?{
????????//?String?get(Person?person);
????????void?set(Person?person,?String?name);
????}
????private?static?class?Person?{
????????private?String?name;
????????public?void?setName(String?name)?{
????????????this.name?=?name;
????????}
????????public?String?getName()?{
????????????return?name;
????????}
????}
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????Person?p1?=?new?Person();
????????p1.setName("小明");//????????邏輯實(shí)現(xiàn)只是為了獲取到對象的名字//????????MyInterface?lambda2?=?Person::getName;//????????System.out.println(lambda2.get(p1));
????????
????????//?邏輯實(shí)現(xiàn)只是為了給對象的某些屬性進(jìn)行賦值
????????MyInterface?lambda1?=?(x,?n)?->?x.setName(n);
????????MyInterface?lambda2?=?Person::setName;
????????lambda2.set(p1,?"李華");
????????System.out.println(p1.getName());
????}}
4. Issues to note with Lambda expressions
Iflocal variables
are used, they will be declared by default As a constant, the value cannot change./** ?*?@Description: ?*?@author?Guoqianliang ?*?@date?13:05?-?2021/2/16 ?*/public?class?Lambda4?{ ????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{ ????????//?1.定義一個(gè)局部變量 ????????int?x?=?10; ????????//?2.使用lambda表達(dá)式實(shí)現(xiàn)接口 ????????LambdaTest?lambda?=?()?->?{ ????????????System.out.println("x="?+?x); ????????}; ????????//?3.?無法修改常量x ????????//?x=20; ????}}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface?LambdaTest?{ ????void?test();}
Related learning recommendations: java basics
The above is the detailed content of Introducing Lambda expressions, the syntactic sugar of Java 8. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How do lambda expressions handle exceptions in C++?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:42 PM
How do lambda expressions handle exceptions in C++?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:42 PM
In C++, there are two ways to handle exceptions using Lambda expressions: catch the exception using a try-catch block, and handle or rethrow the exception in the catch block. Using a wrapper function of type std::function, its try_emplace method can catch exceptions in Lambda expressions.
 What is the meaning of closure in C++ lambda expression?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
What is the meaning of closure in C++ lambda expression?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
In C++, a closure is a lambda expression that can access external variables. To create a closure, capture the outer variable in the lambda expression. Closures provide advantages such as reusability, information hiding, and delayed evaluation. They are useful in real-world situations such as event handlers, where the closure can still access the outer variables even if they are destroyed.
 What are the advantages of using C++ lambda expressions for multi-threaded programming?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
What are the advantages of using C++ lambda expressions for multi-threaded programming?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
The advantages of lambda expressions in C++ multi-threaded programming include simplicity, flexibility, ease of parameter passing, and parallelism. Practical case: Use lambda expressions to create multi-threads and print thread IDs in different threads, demonstrating the simplicity and ease of use of this method.
 How to calculate date one year ago or one year later in Java 8?
Apr 26, 2023 am 09:22 AM
How to calculate date one year ago or one year later in Java 8?
Apr 26, 2023 am 09:22 AM
Java8 calculates the date one year ago or one year later using the minus() method to calculate the date one year ago packagecom.shxt.demo02;importjava.time.LocalDate;importjava.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;publicclassDemo09{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args ){LocalDatetoday=LocalDate.now();LocalDatepreviousYear=today.minus(1,ChronoUni
 How to implement closure in C++ Lambda expression?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
How to implement closure in C++ Lambda expression?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
C++ Lambda expressions support closures, which save function scope variables and make them accessible to functions. The syntax is [capture-list](parameters)->return-type{function-body}. capture-list defines the variables to capture. You can use [=] to capture all local variables by value, [&] to capture all local variables by reference, or [variable1, variable2,...] to capture specific variables. Lambda expressions can only access captured variables but cannot modify the original value.
 C++ function call Lambda expression: callback optimization for parameter passing and return value
May 03, 2024 pm 12:12 PM
C++ function call Lambda expression: callback optimization for parameter passing and return value
May 03, 2024 pm 12:12 PM
In C++, you can use Lambda expressions as function parameters to achieve the flexibility of callback functions. Specifically: Parameter passing: wrap the Lambda expression through std::function and pass it to the function in the form of a function pointer. Return value processing: Specify the return value type when declaring the callback function pointer using std::function. Practical case: Optimize callbacks in GUI event processing, avoid creating unnecessary objects or function pointers, and improve code simplicity and maintainability.
 How does a C++ lambda expression capture external variables?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 04:39 PM
How does a C++ lambda expression capture external variables?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 04:39 PM
There are three ways to capture lambda expressions of external variables in C++: Capture by value: Create a copy of the variable. Capture by reference: Get a variable reference. Capture by value and reference simultaneously: Allows capturing of multiple variables, either by value or by reference.
 How to perform lazy evaluation using C++ lambda expressions?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
How to perform lazy evaluation using C++ lambda expressions?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
How to perform lazy evaluation using C++ lambda expressions? Use lambda expressions to create lazily evaluated function objects. Delayed computation defers execution until needed. Calculate results only when needed, improving performance.






