Stream flow
The previous article talked about a new feature of Java 8: Lambda expression. If you can use it skillfully in business, you can save money. There is a lot of code and it looks a lot neater. Then this article will introduce another new feature: Stream stream, don’t read it wrong! ! ! Not for playing games steam! !
1. What is a Stream:
Stream is a new concept proposed by Java 8. It is not an input and output Stream (it is not the same as the IO stream. Any relationship ha), but a tool that uses functional programming to operate on collection classes. In short, it is an operation of processing collection data in an internal iteration method. Internal iteration can give more control to the collection class. The functions of Stream and Iterator are similar, except that Iterator is an operation that processes collection data in the form of external iteration.
Of course Stream also has its own characteristics:
1. It is not a data structure and does not store data. It just defines a set of operations on the original data set
2. These operations are lazy, that is, whenever an element in the stream is accessed, this series of operations will be performed on this element
3. Because the data is not saved, each Stream Streams can only be used once.
Implementation diagram of Stream stream:
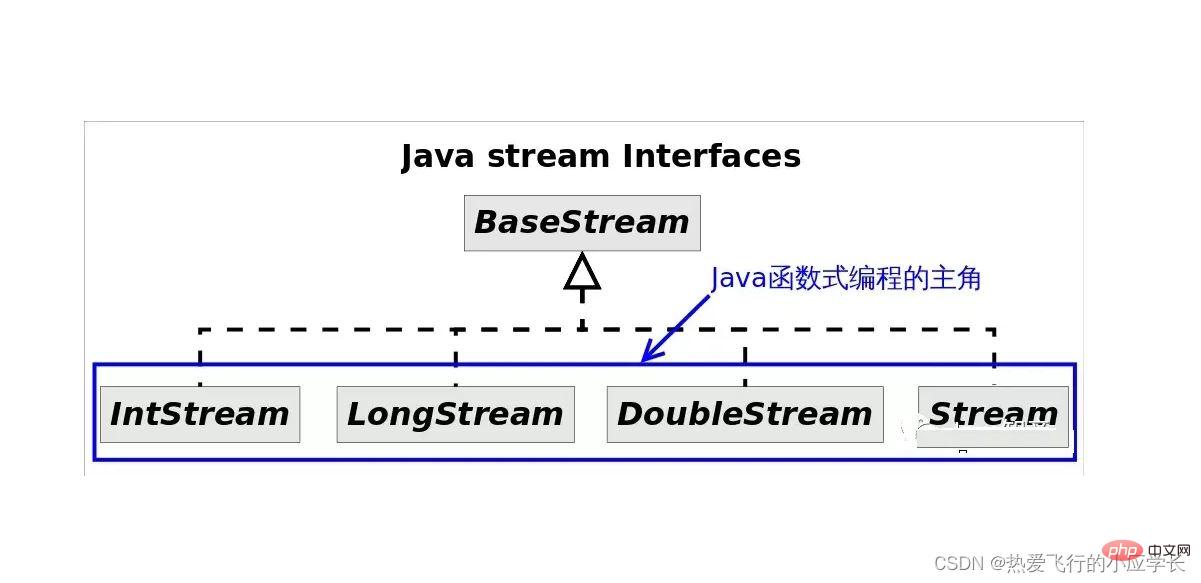
2. Create stream:
If you want to use Stream stream to To operate a collection, you need to convert the array or collection into a Stream first before you can operate
Official document of Stream:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/17/docs/api/java.base/java/util/stream/Stream.html
Let’s look at four first Method:
1.filter: Implement conditional filtering through lambda expressions
2.limit: Intercept the stream, intercept a section of the stream
3.skip: Skip Overflow
4.distinct: Remove duplicates
Create Stream:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String [] arr = {"東","南","西","北"};
//將數(shù)組轉(zhuǎn)換成Stream
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(arr);
stream = Stream.of(arr);
stream = Stream.of("東","南","西","北");
//將list集合轉(zhuǎn)換成stream
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa","cc","bb","aa","dd");
stream = list.stream();
//排序、去重、遍歷
list.stream().sorted().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
//用過Stream流操作完集合后還可以再轉(zhuǎn)換成一個新的集合
List<String> newList = list.stream().sorted().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(newList.toString());
}
}Output:
//The result after traversing and deduplicating:
aa
bb
cc
dd
//After using the Stream stream to operate the collection, it can be converted into a new one Collection
[aa, bb, cc, dd]
Operations of four methods: Person class:
Code comparison of this class Many, so don’t write the get/set method in it. Don’t forget it when you use it! !
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String country;
private char sex;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "信息表:{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", country='" + country + '\'' +
", sex=" + sex +
'}';
}
//這里節(jié)省的get/set代碼
//重寫toString() 和 equals 和 hashcode 方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o){
if(this == o)
return true;
if(o == null || getClass() != o.getClass())
return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
if(country != null){
if(this.country.equals(person.country)){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode(){
return Objects.hash(country);
}
}Test class:
Combined with lambda expression to write
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> perosnList = new ArrayList<>();
perosnList.add(new Person("王一", 30, "中國", 'M'));
perosnList.add(new Person("張三", 19, "美國", 'F'));
perosnList.add(new Person("李四", 29, "日本", 'F'));
perosnList.add(new Person("小美", 74, "英國", 'M'));
perosnList.add(new Person("熊二", 15, "意大利", 'F'));
perosnList.add(new Person("熊大", 66, "韓國", 'F'));
//返回年齡大于20歲的學(xué)生集合
System.out.println("返回年齡大于20歲的學(xué)生集合");
perosnList.stream().filter(p -> p.getAge() > 20).forEach(System.out::println);
//返回年齡大于50歲的學(xué)生集合
System.out.println("返回年齡大于50歲的集合");
List<Person> list = perosnList.stream().filter(p -> p.getAge() > 50).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
//返回年齡大于20歲的中國學(xué)生
System.out.println("返回年齡大于20歲的中國人");
perosnList.stream().filter(p -> p.getAge() > 20).filter(p -> p.getCountry().equals("韓國")).forEach(System.out::println);
//年齡大于20 中國 性別M
System.out.println("返回年齡大于20 中國 性別M");
perosnList.stream().filter(p -> p.getAge() > 20 && p.getCountry().equals("中國") && p.getSex() == 'M').forEach(System.out::println);
}
}Look at the result:
Return the collection of students older than 20 years old
Information table: {name='Wang Yi', age=30, country='China', sex=M}
Information table: {name='李思', age=29, country='Japan', sex=F}
Information table: {name='Xiaomei', age=74, country='UK', sex=M}
Information table: {name='Xiong Da', age=66, country='Korea', sex=F}
Return the collection of people older than 50 years old
[Information table: {name='小Beauty', age=74, country='UK', sex=M}, information table: {name='Xiong Da', age=66, country='South Korea', sex=F}]
Return age greater than 20-year-old Chinese
Information table: {name='Xiong Da', age=66, country='South Korea', sex=F}
Return age greater than 20 China GenderM
Information table: { name='Wang Yi', age=30, country='China', sex=M}
Summary:
Using Stream can be easily operated Arrays or collections can be combined with Lambda expressions to make an expression neat and clear. In fact, since it is a new feature exited by Java, it must be useful.
3. Stream map mapping stream
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//map的作用是迭代取到每個list元素,再通過map里面的函數(shù)進(jìn)行相應(yīng)的操作
List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("a","bb","ccc","dddd");
//通過map取到每個集合元素的長度并返回
Stream<Integer> stream = list1.stream().map(p->p.length());
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------");
List<String> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add("周杰倫.tom");
userList.add("尼古拉斯.趙四");
userList.add("牛頓.巴基斯");
userList.add("趙少華.思密達(dá)");
List<String> uList = userList.stream().map(p->p.substring(p.indexOf(".")+1,
p.length())).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(uList.toString());
}
}Output:
1
2
3
4
----------------
[tom, Zhao Si, Bakis, Smecta]
4. Stream search and There is also a
anyMatch(Predicate predicate) method in the matching Stream:
Returns whether any element in this stream matches the provided word
Demo:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("周杰倫","王力宏","孫燕姿","林俊杰");
boolean flag1 = list.stream().anyMatch(ele->ele.contains("燕"));
System.out.println("有沒有名字包含燕的同學(xué):"+flag1);
//判斷開頭:
boolean flag2 = list.stream().anyMatch(ele->ele.startsWith("王"));
System.out.println("有沒有名字開頭是王的同學(xué):"+flag2);
//判斷結(jié)尾:
boolean flag3 = list.stream().anyMatch(ele->ele.endsWith("杰"));
System.out.println("有沒有名字結(jié)尾是杰的同學(xué):"+flag3);
// anyMatch是匹配所有的,要滿足條件
boolean flag4 = list.stream().anyMatch(ele->ele.length()>2);
System.out.println("所有同學(xué)的名字都是兩個字以上的嗎"+flag4);
boolean flag5 = list.stream().anyMatch(ele->ele.startsWith("王"));
System.out.println("所有同學(xué)的名字都有王嗎?"+flag5);
//noneMatch
boolean flag6 = list.stream().noneMatch(ele->ele.contains("燕"));
System.out.println("集合中都沒有包含'燕'這個字嗎"+flag5);
}
}Output:
Are there any students whose names contain Yan: true
Are there any students whose names start with Wang: true
Are there any students whose names end with Jie: true
Do all students’ names have more than two characters? true
All students’ names have Wang ? true
The collection does not contain the word 'Yan' true
Using the method in anyMatch() can easily match the information of this stream.
The above is the detailed content of Analyze Stream flow instances in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
There are three common methods to traverse Map in Java: 1. Use entrySet to obtain keys and values at the same time, which is suitable for most scenarios; 2. Use keySet or values to traverse keys or values respectively; 3. Use Java8's forEach to simplify the code structure. entrySet returns a Set set containing all key-value pairs, and each loop gets the Map.Entry object, suitable for frequent access to keys and values; if only keys or values are required, you can call keySet() or values() respectively, or you can get the value through map.get(key) when traversing the keys; Java 8 can use forEach((key,value)->
 Java Optional example
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Java Optional example
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Optional can clearly express intentions and reduce code noise for null judgments. 1. Optional.ofNullable is a common way to deal with null objects. For example, when taking values ??from maps, orElse can be used to provide default values, so that the logic is clearer and concise; 2. Use chain calls maps to achieve nested values ??to safely avoid NPE, and automatically terminate if any link is null and return the default value; 3. Filter can be used for conditional filtering, and subsequent operations will continue to be performed only if the conditions are met, otherwise it will jump directly to orElse, which is suitable for lightweight business judgment; 4. It is not recommended to overuse Optional, such as basic types or simple logic, which will increase complexity, and some scenarios will directly return to nu.
 Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
In Java, Comparable is used to define default sorting rules internally, and Comparator is used to define multiple sorting logic externally. 1.Comparable is an interface implemented by the class itself. It defines the natural order by rewriting the compareTo() method. It is suitable for classes with fixed and most commonly used sorting methods, such as String or Integer. 2. Comparator is an externally defined functional interface, implemented through the compare() method, suitable for situations where multiple sorting methods are required for the same class, the class source code cannot be modified, or the sorting logic is often changed. The difference between the two is that Comparable can only define a sorting logic and needs to modify the class itself, while Compar
 How to fix java.io.NotSerializableException?
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:07 AM
How to fix java.io.NotSerializableException?
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:07 AM
The core workaround for encountering java.io.NotSerializableException is to ensure that all classes that need to be serialized implement the Serializable interface and check the serialization support of nested objects. 1. Add implementsSerializable to the main class; 2. Ensure that the corresponding classes of custom fields in the class also implement Serializable; 3. Use transient to mark fields that do not need to be serialized; 4. Check the non-serialized types in collections or nested objects; 5. Check which class does not implement the interface; 6. Consider replacement design for classes that cannot be modified, such as saving key data or using serializable intermediate structures; 7. Consider modifying
 How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
To deal with character encoding problems in Java, the key is to clearly specify the encoding used at each step. 1. Always specify encoding when reading and writing text, use InputStreamReader and OutputStreamWriter and pass in an explicit character set to avoid relying on system default encoding. 2. Make sure both ends are consistent when processing strings on the network boundary, set the correct Content-Type header and explicitly specify the encoding with the library. 3. Use String.getBytes() and newString(byte[]) with caution, and always manually specify StandardCharsets.UTF_8 to avoid data corruption caused by platform differences. In short, by
 Java method references explained
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:59 AM
Java method references explained
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:59 AM
Method reference is a way to simplify the writing of Lambda expressions in Java, making the code more concise. It is not a new syntax, but a shortcut to Lambda expressions introduced by Java 8, suitable for the context of functional interfaces. The core is to use existing methods directly as implementations of functional interfaces. For example, System.out::println is equivalent to s->System.out.println(s). There are four main forms of method reference: 1. Static method reference (ClassName::staticMethodName); 2. Instance method reference (binding to a specific object, instance::methodName); 3.
 How to parse JSON in Java?
Jul 11, 2025 am 02:18 AM
How to parse JSON in Java?
Jul 11, 2025 am 02:18 AM
There are three common ways to parse JSON in Java: use Jackson, Gson, or org.json. 1. Jackson is suitable for most projects, with good performance and comprehensive functions, and supports conversion and annotation mapping between objects and JSON strings; 2. Gson is more suitable for Android projects or lightweight needs, and is simple to use but slightly inferior in handling complex structures and high-performance scenarios; 3.org.json is suitable for simple tasks or small scripts, and is not recommended for large projects because of its lack of flexibility and type safety. The choice should be decided based on actual needs.
 Outlook shortcut for new email
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:25 AM
Outlook shortcut for new email
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:25 AM
How to quickly create new emails in Outlook is as follows: 1. The desktop version uses the shortcut key Ctrl Shift M to directly pop up a new email window; 2. The web version can create new emails in one-click by creating a bookmark containing JavaScript (such as javascript:document.querySelector("divrole='button'").click()); 3. Use browser plug-ins (such as Vimium, CrxMouseGestures) to trigger the "New Mail" button; 4. Windows users can also select "New Mail" by right-clicking the Outlook icon of the taskbar






