 Java
Java
 JavaInterview questions
JavaInterview questions
 Interviewer: How to solve Redis data skew, hot spots and other issues
Interviewer: How to solve Redis data skew, hot spots and other issues
Interviewer: How to solve Redis data skew, hot spots and other issues
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:43 PMAs a mainstream technology, Redis has many application scenarios. Many interviews with large, medium and small factories have listed it as a key inspection content
A few days ago, there was a interview with Planet Small When I was studying with my partner, I encountered the following questions and came to consult Brother Tom
Considering that these problems are relatively high-frequency and often encountered at work, I will write an article to explain them systematically
Problem description:
Question to you: When reviewing redis, I have some questions, please take a look:
If the redis cluster has data skew and uneven data distribution, how to solve it?
When processing hotKey, create multiple copies of the key, such as k-1, k-2..., How to make these copies write evenly? How to evenly access?
Redis uses hash slot to maintain the cluster. Similar to consistent hashing, full migration can be avoided. Why not just use consistent hashing?
Reply:
As a performance accelerator, distributed cache plays a very important role in system optimization character of. Compared with local cache, although it adds a network transmission and takes less than 1 millisecond, it has the advantage of centralized management and supports a very large storage capacity.
In the field of distributed cache, Redis is currently widely used. This framework is pure memory storage, single-threaded execution of commands, rich underlying data structures, and supports multiple dimensions. of data storage and retrieval.
Of course, when the amount of data is large, various problems will arise, such as: data skew, data hotspots, etc.
What is data skew?
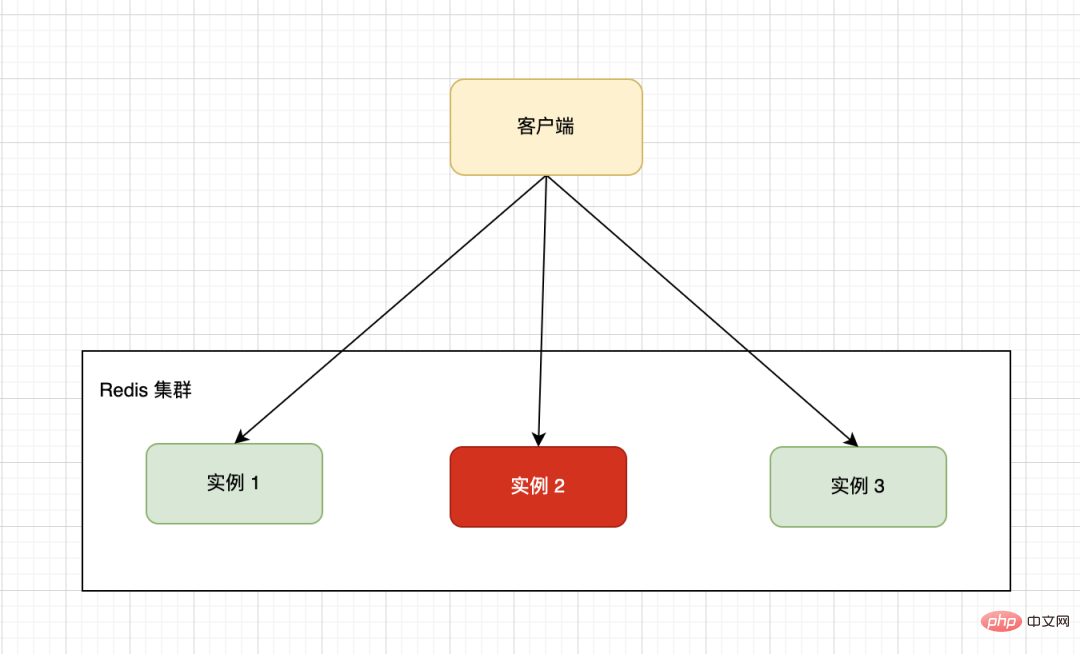
The hardware configuration of a single machine has an upper limit. Generally, we will use a distributed architecture to form a cluster of multiple machines. The cluster in the figure below is composed of three It consists of a single Redis machine. The client forwards read and write requests to specific instances through a certain routing strategy.
Due to the particularity of business data, according to the specified sharding rules, data may be unevenly distributed on different instances, and a large amount of data is concentrated on one or several machine nodes for calculation. , which leads to how loaded these nodes are, while other nodes are waiting idle, resulting in low overall efficiency.
What are the reasons for data skew?
1. There is a large key
For example, storing one or more String types bigKey data takes up a lot of memory.
Brother Tom has investigated this problem before. In order to save trouble during development, a colleague used JSON format to merge multiple business data into one value and only associated one key, which led to this The key-value pair capacity reaches several hundred M.
Frequent reading and writing of large keys consumes heavy memory resources and puts great pressure on network transmission, which in turn causes the request response to slow down and triggers an avalanche effect. In the end, the system A timeout alarm.
Solution:
The method is very simple, use <span style="font-size: 16px;">Break it into parts</span>The strategy of splitting a bigKey into multiple small keys and maintaining them independently will reduce the cost a lot. Of course, this disassembly also pays attention to some principles. It is necessary to consider both business scenarios and access scenarios, and put them closely together.
For example: there is an RPC interface that has an internal dependence on Redis. In the past, all the data could be obtained by accessing it once. Splitting will control the size of the single value and the number of accesses. After all, an increase in the number of calls will increase the overall interface response time.
Government agencies in Zhejiang are advocating optimizing the process, and running it once at most is the same principle.

2. Improper use of HashTag
Redis uses a single thread to execute commands, thus ensuring atomicity. When cluster deployment is adopted, in order to solve multi-key batch operations such as mset and lua scripts, and to ensure that different keys can be routed to the same Redis instance, the HashTag mechanism is introduced.
Usage is also very simple, use <span style="font-size: 16px;">{}</span> braces, specify the key to only calculate the string within the braces Hash, thereby inserting key-value pairs of different keys into the same hash slot.
For example:
192.168.0.1:6380> CLUSTER KEYSLOT testtag
(integer) 764
192.168.0.1:6380> CLUSTER KEYSLOT {testtag}
(integer) 764
192.168.0.1:6380> CLUSTER KEYSLOT mykey1{testtag}
(integer) 764
192.168.0.1:6380> CLUSTER KEYSLOT mykey2{testtag}
(integer) 764Check the business code and see if HashTag is introduced. , routing too many keys to one instance. Consider how to split based on specific scenarios.
Just like RocketMQ, in many cases our business needs can be met as long as the partitions are kept in order. In actual practice, we need to find this balance point, rather than solving problems for the sake of solving them.
3. Uneven distribution of slots
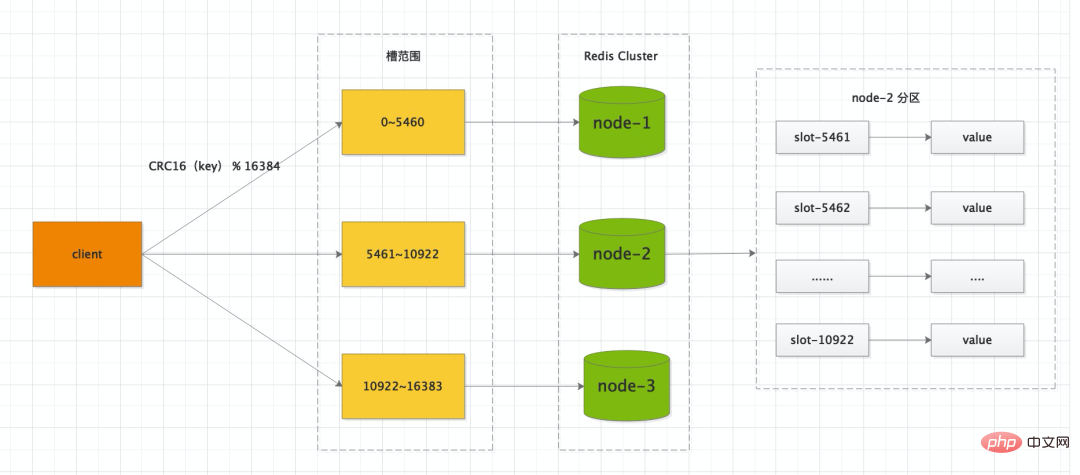
If the Redis Cluster deployment method is adopted, the database in the cluster is divided into 16384 slots (slot), each key in the database belongs to one of these 16384 slots, and each node in the cluster can handle 0 or up to 16384 slots.
You can manually migrate a relatively large slot to a slightly idle machine to ensure the uniformity of storage and access.
What are cache hotspots?
Cache hotspot means that most or even all business requests hit the same cached data, which puts huge pressure on the cache server, even exceeding the capacity of a single machine. The load limit is exceeded, causing server downtime.
solution:
1. Copy multiple copies
#We can spell sequential numbers after the key, such as key#01, key#02. . . Multiple copies of key#10, these processed keys are located on multiple cache nodes.
Every time the client accesses, it only needs to splice a random number with the upper limit of the number of shards based on the original key, and route the request to the instance node that cannot be routed.
Note: Cache generally sets expiration time. In order to avoid centralized cache failure, we try not to have the same cache expiration time. We can add a random number based on the preset.
As for the uniformity of data routing, this is guaranteed by the Hash algorithm.
2. Local memory cache
Cache hotspot data in the client's local memory and set an expiration time. For each read request, it will first check whether the data exists in the local cache. If it exists, it will be returned directly. If it does not exist, it will then access the distributed cache server.
The local memory cache completely "liberates" the cache server and does not put any pressure on the cache server.
Disadvantages: It is a bit troublesome to sense the latest cached data in real time, and data inconsistency may occur. We can set a relatively short expiration time and use passive updates. Of course, you can also use a monitoring mechanism to update the local cache in a timely manner if it senses that the data has changed.
Redis Cluster Why not use consistent Hash?
Redis Cluster cluster has 16384 hash slots , each <span style="font-size: 16px;">key</span> passes <span style="font-size: 16px;">CRC16</span> after verification. ##16384<span style="font-size: 16px;"></span>Take a mold to determine which slot to place. Each node in the cluster is responsible for a part of the hash slot. For example, if the current cluster has 3 nodes, then node-1<span style="font-size: 16px;"></span> contains numbers 0 to 5460. Hash slots, node-2<span style="font-size: 16px;"></span> Contains hash slots 5461 to 10922, node-3<span style="font-size: 16px;"></span> Contains hash slots 10922 to 16383.
The consistent hashing algorithm is essentially a modulo algorithm. Different from taking the modulo based on the number of servers, the consistent hashing modulo a fixed value 2^32.
The result of the modulus must be Integers in the interval [0, 2^32-1], The first node found clockwise from the mapped position on the circle is the node where the key is stored
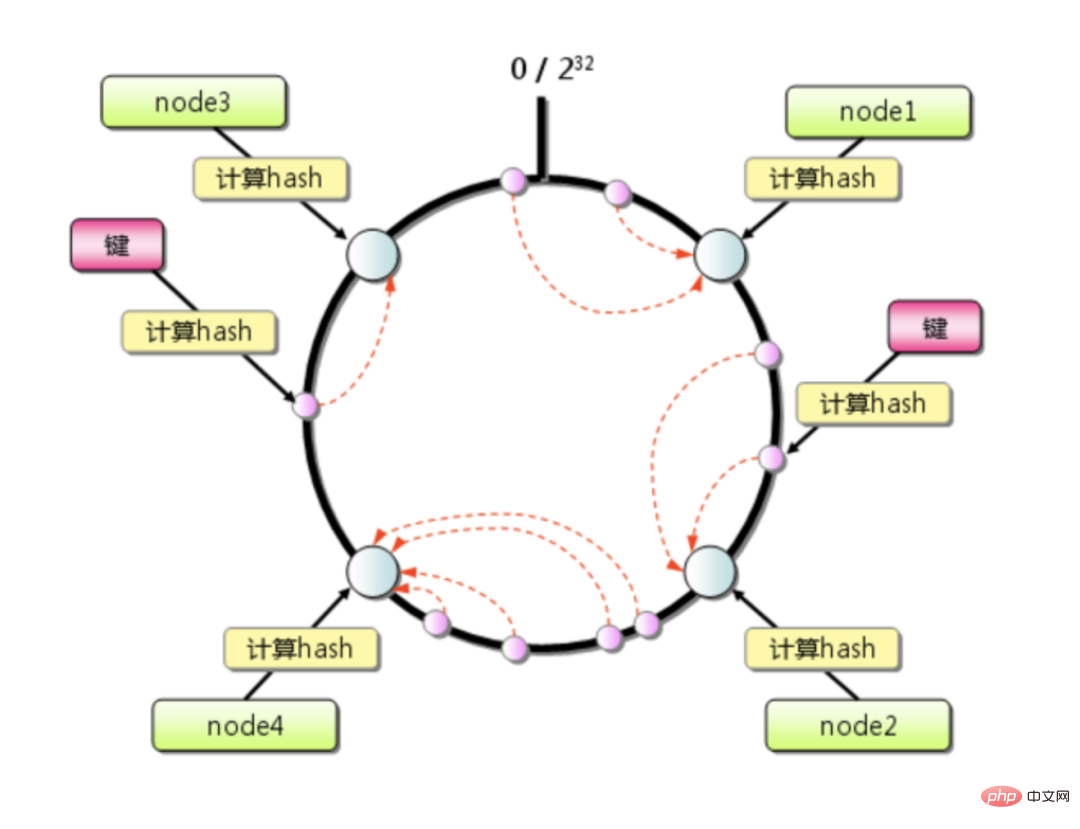
The consistent hash algorithm greatly alleviates the cache failure problem caused by expansion or shrinkage, and only affects the small section of keys that this node is responsible for. If there are not many machines in the cluster, and the load level of a single machine is usually very high, the pressure caused by the downtime of a certain node can easily trigger an avalanche effect.
##For example:
Redis There are a total of 4 machines in the cluster. Assuming that the data is distributed evenly, each machine will bear a quarter of the traffic. If a machine suddenly hangs up, the next machine in the clockwise direction will bear the extra quarter of the traffic. , it is still a bit scary to end up bearing one-half of the traffic.
But if CRC16<span style="font-size: 16px;"></span> is calculated and combined with the binding relationship between the slot and the instance, whether Whether expanding or shrinking, you only need to smoothly migrate the data of the corresponding node's key, broadcast and store the new slot mapping relationship, without causing cache failure, and the flexibility is very high.
In addition, if there are differences in server node configurations, we can customize the slot numbers assigned to different nodes and adjust the load capabilities of different nodes, which is very convenient.
The above is the detailed content of Interviewer: How to solve Redis data skew, hot spots and other issues. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
There are three common methods to traverse Map in Java: 1. Use entrySet to obtain keys and values at the same time, which is suitable for most scenarios; 2. Use keySet or values to traverse keys or values respectively; 3. Use Java8's forEach to simplify the code structure. entrySet returns a Set set containing all key-value pairs, and each loop gets the Map.Entry object, suitable for frequent access to keys and values; if only keys or values are required, you can call keySet() or values() respectively, or you can get the value through map.get(key) when traversing the keys; Java 8 can use forEach((key,value)->
 Java Optional example
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Java Optional example
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Optional can clearly express intentions and reduce code noise for null judgments. 1. Optional.ofNullable is a common way to deal with null objects. For example, when taking values ??from maps, orElse can be used to provide default values, so that the logic is clearer and concise; 2. Use chain calls maps to achieve nested values ??to safely avoid NPE, and automatically terminate if any link is null and return the default value; 3. Filter can be used for conditional filtering, and subsequent operations will continue to be performed only if the conditions are met, otherwise it will jump directly to orElse, which is suitable for lightweight business judgment; 4. It is not recommended to overuse Optional, such as basic types or simple logic, which will increase complexity, and some scenarios will directly return to nu.
 How to fix java.io.NotSerializableException?
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:07 AM
How to fix java.io.NotSerializableException?
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:07 AM
The core workaround for encountering java.io.NotSerializableException is to ensure that all classes that need to be serialized implement the Serializable interface and check the serialization support of nested objects. 1. Add implementsSerializable to the main class; 2. Ensure that the corresponding classes of custom fields in the class also implement Serializable; 3. Use transient to mark fields that do not need to be serialized; 4. Check the non-serialized types in collections or nested objects; 5. Check which class does not implement the interface; 6. Consider replacement design for classes that cannot be modified, such as saving key data or using serializable intermediate structures; 7. Consider modifying
 Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
In Java, Comparable is used to define default sorting rules internally, and Comparator is used to define multiple sorting logic externally. 1.Comparable is an interface implemented by the class itself. It defines the natural order by rewriting the compareTo() method. It is suitable for classes with fixed and most commonly used sorting methods, such as String or Integer. 2. Comparator is an externally defined functional interface, implemented through the compare() method, suitable for situations where multiple sorting methods are required for the same class, the class source code cannot be modified, or the sorting logic is often changed. The difference between the two is that Comparable can only define a sorting logic and needs to modify the class itself, while Compar
 How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
To deal with character encoding problems in Java, the key is to clearly specify the encoding used at each step. 1. Always specify encoding when reading and writing text, use InputStreamReader and OutputStreamWriter and pass in an explicit character set to avoid relying on system default encoding. 2. Make sure both ends are consistent when processing strings on the network boundary, set the correct Content-Type header and explicitly specify the encoding with the library. 3. Use String.getBytes() and newString(byte[]) with caution, and always manually specify StandardCharsets.UTF_8 to avoid data corruption caused by platform differences. In short, by
 How to parse JSON in Java?
Jul 11, 2025 am 02:18 AM
How to parse JSON in Java?
Jul 11, 2025 am 02:18 AM
There are three common ways to parse JSON in Java: use Jackson, Gson, or org.json. 1. Jackson is suitable for most projects, with good performance and comprehensive functions, and supports conversion and annotation mapping between objects and JSON strings; 2. Gson is more suitable for Android projects or lightweight needs, and is simple to use but slightly inferior in handling complex structures and high-performance scenarios; 3.org.json is suitable for simple tasks or small scripts, and is not recommended for large projects because of its lack of flexibility and type safety. The choice should be decided based on actual needs.
 Java method references explained
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:59 AM
Java method references explained
Jul 12, 2025 am 02:59 AM
Method reference is a way to simplify the writing of Lambda expressions in Java, making the code more concise. It is not a new syntax, but a shortcut to Lambda expressions introduced by Java 8, suitable for the context of functional interfaces. The core is to use existing methods directly as implementations of functional interfaces. For example, System.out::println is equivalent to s->System.out.println(s). There are four main forms of method reference: 1. Static method reference (ClassName::staticMethodName); 2. Instance method reference (binding to a specific object, instance::methodName); 3.
 Outlook shortcut for new email
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:25 AM
Outlook shortcut for new email
Jul 11, 2025 am 03:25 AM
How to quickly create new emails in Outlook is as follows: 1. The desktop version uses the shortcut key Ctrl Shift M to directly pop up a new email window; 2. The web version can create new emails in one-click by creating a bookmark containing JavaScript (such as javascript:document.querySelector("divrole='button'").click()); 3. Use browser plug-ins (such as Vimium, CrxMouseGestures) to trigger the "New Mail" button; 4. Windows users can also select "New Mail" by right-clicking the Outlook icon of the taskbar





