Ejb is denoted as Enterprise Java Bean Component, also called server-side software components; it will mainly be used as the applications’ business logic. The web containers used for runtime environments include the software components, computer security, servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and web services.EJb is the architecture style written in the Java programming languages running on the server-side of the computer network, so it has followed the client-server model in the applications. And also, ejb is the java bean technology to distribute the web components on the client-side it has the feature called reusable components in multiple web applications.
Start Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Syntax:
The basic syntax of the EJB model in java programming as follows.
import javax.ejb.*;
import java packages;
class classname
{
Main? method()
{
-----Some programming logics----
}
}
The above codes are basic steps for developing the application using ejb packages.
How to use EJB in Java Works?
- In EJB, the java bean class will use more than one annotation for the ejb specifications, which will be helpful for satisfying the user requirements based on the business purpose.EJB has a different set of versions and has followed the feature like JNDI(java naming directory interface). One of the resources in servers jndi is the directory service is used for locating or allocating the resource, like ejb, data source, and JMS queue services. The servers have a default scheme name for the jndi resources, but it should be overridden if we changed the configuration part’s name.
- EJB will work on java beans; it has two different types 1. Session beans and 2.Message Driven BeansSession beans. Session beans will be used for client-server interactions; it encapsulates the application’s business logic through programmatically by the client invocation will be done by either local machine or remote machine bean will be used by the client with the help of web services. Session beans will be three different categories 1. Stateless,2.Stateful and 3.Singleton.Stateless beans when the client use these type of beans there is no permanent state in web containers, so they are thread-safe performance wise very fast when compared to stateful beans. These beans are shared with multiple clients at the same time.
- Stateful beans can store the states in containers; once the client terminates the session, these states are also destroyed in the server. Singelton beans it has a single instance session for the entire lifecycle of that application; these beans also shared the states with multiple clients. These beans are thread-safe, so developers will use them more easily, and performance also fast compared to stateful beans.
- Message Driven Beans(MDB) is the type of bean that is used as the type of message asynchronous like JMS message listeners, but it will receive the message response as JMS messages instead of the events. We can map the messages using jndi services whenever the message receives the container calls the MDB beans using the onMessage() method for further process. The whole process of the MDB using the onMessage() method will be a single transaction. If suppose message process is a rollback, the receiver message again redelivered.
Examples to Implement EJB in Java
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Interface:
package JPAEJB;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface CustomerInterface {
void addBooks(String name);
List getBooks();
}
Implementation:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import JPAEJB.CustomerInterface;
@Stateless
public class CustomerClass implements CustomerInterface {
List<String>books;
public CustomerClass() {
books = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBooks(String name) {
books.add(name);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return books;
}
}
CustomerInterface:
import JPAEJB.CustomerInterface;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class CustomerInterfaceImplem {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties p;
InitialContext c;
{
p = new Properties();
try {
p.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
c = new InitialContext(p);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomerInterfaceImplem cust = new CustomerInterfaceImplem();
cust.testStatelessEjb();
}
private void show() {
System.out.println("Welcome to my domain");
System.out.print("Options \n1. Add the Books\n2. Exit \nEnter your Choice: ");
}
private void StatelessEjb() {
try {
intc = 1;
CustomerInterface cust =
(CustomerInterface)ctx.lookup("CustomerInterface/remote");
while (c != 2) {
String books;
show();
String str = brConsoleReader.readLine();
c = Integer.parseInt(str);
if (c == 1) {
books = brConsoleReader.readLine();
cust.addBooks(books);
}elseif (c == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<String>books1 = cust.getBooks();
System.out.println(books1.size());
for (inti = 0; i<books1.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + books1.get(i));
}
CustomerInterface cust1 =
(CustomerInterface)ctx.lookup("cust/remote");
List<String>books2 = cust.getBooks();
System.out.println(books2.size());
for (inti = 0; i<books2.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + books2.get(i));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null) {
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
Sample Output:
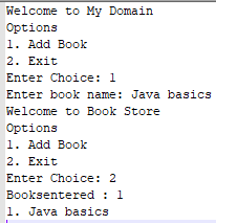
Example #2
EJB in Web Services:
package JPAEJB;
import java.util.List;
import Customers.CustomerInterfaceImplem;
public class Ejbclients{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(CustomerInterface cust:getBooks()) {
System.out.println(cust.getBooks());
}
}
private static List
<CustomerInterface> getBooks() {
CustomerInterfaceImplem s =
new CustomerInterfaceImplem();
CustomerInterface c =
s.getCustomerInterfacePort();
return c.getBooks();
}
}
Example #3
EJB Security:
import javax.ejb.*
@Stateless
@DeclareRoles({"customer""books"})
public class CustSecurity implements CustomerInterface {
@RolesAllowed({"books"})
public void delete(CustomerInterface cust) {
System.out.println("customer delete the books");
}
@PermitAll
public void showBooks(CustomerInterface cust) {
System.out.println("customer viewed the books");
}
@DenyAll
public void deleteAll() {
System.out.println("customer delete all the books in libraries");
}
}
Security XML:
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE sun-ejb-jar PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Application Server 9.0 EJB 3.0//EN""http://www.sun.com/software/appserver/dtds/sun-ejb-jar_3_0-0.dtd"> <ejb-jar> <security-role-mapping> <role-name>customer</role-name> <group-name>customer-groups</group-name> </security-role-mapping> <security-role-mapping> <role-name>Books</role-name> <group-name>Books-group</group-name> </security-role-mapping> <enterprise-beans/> </ejb-jar>
Explanation: The above three examples are the same output we used different features of the ejb first example we use the customer will add and delete the books using jndi(java naming directory interface) second example we use the web service for customer done the operations through web final example we used the additional security.
Conclusion
Generally, EJB act as an interface outside of business logic applications; it has the? browser compatibility feature security-wise more when compared to other business logic frameworks. It also maintains the system-level transactions.
The above is the detailed content of EJB in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How Java ClassLoaders Work Internally
Jul 06, 2025 am 02:53 AM
How Java ClassLoaders Work Internally
Jul 06, 2025 am 02:53 AM
Java's class loading mechanism is implemented through ClassLoader, and its core workflow is divided into three stages: loading, linking and initialization. During the loading phase, ClassLoader dynamically reads the bytecode of the class and creates Class objects; links include verifying the correctness of the class, allocating memory to static variables, and parsing symbol references; initialization performs static code blocks and static variable assignments. Class loading adopts the parent delegation model, and prioritizes the parent class loader to find classes, and try Bootstrap, Extension, and ApplicationClassLoader in turn to ensure that the core class library is safe and avoids duplicate loading. Developers can customize ClassLoader, such as URLClassL
 Asynchronous Programming Techniques in Modern Java
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:24 AM
Asynchronous Programming Techniques in Modern Java
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:24 AM
Java supports asynchronous programming including the use of CompletableFuture, responsive streams (such as ProjectReactor), and virtual threads in Java19. 1.CompletableFuture improves code readability and maintenance through chain calls, and supports task orchestration and exception handling; 2. ProjectReactor provides Mono and Flux types to implement responsive programming, with backpressure mechanism and rich operators; 3. Virtual threads reduce concurrency costs, are suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, and are lighter and easier to expand than traditional platform threads. Each method has applicable scenarios, and appropriate tools should be selected according to your needs and mixed models should be avoided to maintain simplicity
 Understanding Java NIO and Its Advantages
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Understanding Java NIO and Its Advantages
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:55 AM
JavaNIO is a new IOAPI introduced by Java 1.4. 1) is aimed at buffers and channels, 2) contains Buffer, Channel and Selector core components, 3) supports non-blocking mode, and 4) handles concurrent connections more efficiently than traditional IO. Its advantages are reflected in: 1) Non-blocking IO reduces thread overhead, 2) Buffer improves data transmission efficiency, 3) Selector realizes multiplexing, and 4) Memory mapping speeds up file reading and writing. Note when using: 1) The flip/clear operation of the Buffer is easy to be confused, 2) Incomplete data needs to be processed manually without blocking, 3) Selector registration must be canceled in time, 4) NIO is not suitable for all scenarios.
 Best Practices for Using Enums in Java
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:35 AM
Best Practices for Using Enums in Java
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:35 AM
In Java, enums are suitable for representing fixed constant sets. Best practices include: 1. Use enum to represent fixed state or options to improve type safety and readability; 2. Add properties and methods to enums to enhance flexibility, such as defining fields, constructors, helper methods, etc.; 3. Use EnumMap and EnumSet to improve performance and type safety because they are more efficient based on arrays; 4. Avoid abuse of enums, such as dynamic values, frequent changes or complex logic scenarios, which should be replaced by other methods. Correct use of enum can improve code quality and reduce errors, but you need to pay attention to its applicable boundaries.
 How to handle exceptions properly in Java?
Jul 06, 2025 am 02:43 AM
How to handle exceptions properly in Java?
Jul 06, 2025 am 02:43 AM
The key to handling exceptions in Java is to catch them, handle them clearly, and not cover up problems. First, we must catch specific exception types as needed, avoid general catches, and prioritize checkedexceptions. Runtime exceptions should be judged in advance; second, we must use the log framework to record exceptions, and retry, rollback or throw based on the type; third, we must use the finally block to release resources, and recommend try-with-resources; fourth, we must reasonably define custom exceptions, inherit RuntimeException or Exception, and carry context information for easy debugging.
 What is an anonymous inner class?
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:18 AM
What is an anonymous inner class?
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:18 AM
Anonymous internal classes are used in Java to create subclasses or implement interfaces on the fly, and are often used to override methods to achieve specific purposes, such as event handling in GUI applications. Its syntax form is a new interface or class that directly defines the class body, and requires that the accessed local variables must be final or equivalent immutable. Although they are convenient, they should not be overused. Especially when the logic is complex, they can be replaced by Java8's Lambda expressions.
 What is a Singleton design pattern in Java?
Jul 09, 2025 am 01:32 AM
What is a Singleton design pattern in Java?
Jul 09, 2025 am 01:32 AM
Singleton design pattern in Java ensures that a class has only one instance and provides a global access point through private constructors and static methods, which is suitable for controlling access to shared resources. Implementation methods include: 1. Lazy loading, that is, the instance is created only when the first request is requested, which is suitable for situations where resource consumption is high and not necessarily required; 2. Thread-safe processing, ensuring that only one instance is created in a multi-threaded environment through synchronization methods or double check locking, and reducing performance impact; 3. Hungry loading, which directly initializes the instance during class loading, is suitable for lightweight objects or scenarios that can be initialized in advance; 4. Enumeration implementation, using Java enumeration to naturally support serialization, thread safety and prevent reflective attacks, is a recommended concise and reliable method. Different implementation methods can be selected according to specific needs
 Windows automatic repair loop fix
Jul 07, 2025 am 01:31 AM
Windows automatic repair loop fix
Jul 07, 2025 am 01:31 AM
Use the installation media to enter the recovery environment; 2. Run the bootrec command to repair the boot records; 3. Check for disk errors and repair system files; 4. Disable automatic repair as a temporary means. The Windows automatic repair loop is usually caused by system files corruption, hard disk errors or boot configuration abnormalities. The solution includes troubleshooting by installing the USB flash drive into the recovery environment, using bootrec to repair MBR and BCD, running chkdsk and DISM/sfc to repair disk and system files. If it is invalid, the automatic repair function can be temporarily disabled, but the root cause needs to be checked later to ensure that the hard disk and boot structure are normal.






