Border-radius — don’t ya just love it? It’s easily over-used, but done nicely and not too often, rounded corners can add a touch of class to pretty-much anything.
However certain color combinations can produce a somewhat jagged effect, even with the anti-aliasing that all browsers apply. In my experience, the offender is dark backgrounds with lighter borders, particularly against off-white backgrounds, and is particularly pronounced in Safari, though it’s there in all browsers.
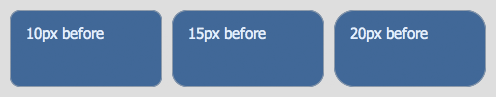
Here’s an image taken with Safari, that illustrates this with three different border radii:

Looks pretty good, but you can clearly see a slightly jagged effect to each corner. Now here’s those boxes again, this time with smoother corners:

And the difference? Simply split the colors between different elements — the outer element has the border and the specified border-radius, while the inner element has the background-color and a slightly smaller border-radius.
It’s a simple trick, and not a huge difference, but there definitely is a difference and a clear improvement, as you can see. I’m not entirely sure why it makes a difference, but I imagine it’s because of the way the anti-aliasing algorithms are applied; because each algorithm only deals with one color instead of two, or the way the now-separate anti-aliasings merge together; something.
If you’d like to poke around those examples in more detail, here are the live demos from which those screenshots were taken. But you can also see it right on this page — the categories tabs at the top, and the boxes down the right with dark-blue headers, all use this technique. I developed it while building these templates, because the jaggedness was bugging me!
And now they’re smooth as the proverbial baby’s bottom!
Photo credit: meltingnoise
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Smoother Rounded Corners in CSS
What is the significance of using smoother rounded corners in web design?
Smoother rounded corners play a crucial role in enhancing the aesthetics of a website. They make the design more appealing and user-friendly. Rounded corners are easier on the eyes as they guide the viewer’s attention towards the content. They also give a sense of professionalism and sophistication to the design. Moreover, smoother rounded corners can make elements like buttons and cards more clickable and interactive, improving the overall user experience.
How can I create smoother rounded corners using CSS?
CSS provides a property called ‘border-radius’ to create rounded corners. You can specify the radius of the corners to control their roundness. For smoother corners, you can use larger values. For example, ‘border-radius: 50%;’ will create a circle if applied to a square element. You can also specify different values for each corner to create unique shapes.
Can I use percentages with the border-radius property?
Yes, you can use percentages with the border-radius property. When you use a percentage, it’s based on the corresponding dimensions of the box. For instance, ‘border-radius: 50%;’ will create a circle if the element is a square. If the element is a rectangle, it will create an ellipse.
How does the border-radius property work with background images?
The border-radius property also affects background images. The image will be clipped to fit within the rounded corners. This can create a unique effect and can be used to highlight certain parts of an image.
What are the browser compatibility issues with the border-radius property?
The border-radius property is well supported in all modern browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. However, it may not work correctly in older versions of Internet Explorer. To ensure compatibility, you can use vendor prefixes like ‘-webkit-‘ for Chrome and Safari, and ‘-moz-‘ for Firefox.
Can I animate the border-radius property?
Yes, you can animate the border-radius property using CSS transitions or animations. This can create interesting effects, such as a button that changes shape when hovered over.
How can I create complex shapes with the border-radius property?
You can create complex shapes by specifying different values for each corner of the element. For example, ‘border-radius: 10px 20px 30px 40px;’ will give each corner a different radius. You can also use the ‘/’ syntax to specify horizontal and vertical radii for each corner, allowing for even more complex shapes.
What is the difference between ‘border-radius’ and ‘outline-radius’?
The ‘border-radius’ property affects the border of an element, while the ‘outline-radius’ property affects the outline. However, ‘outline-radius’ is not a standard CSS property and is not supported in most browsers.
Can I use the border-radius property with other CSS properties?
Yes, the border-radius property can be used in combination with other CSS properties to create unique effects. For example, you can use it with box-shadow to create a shadow that follows the shape of the rounded corners.
How can I create a smooth transition effect on hover using the border-radius property?
You can create a smooth transition effect on hover by using the ‘transition’ property in combination with ‘border-radius’. For example, ‘transition: border-radius 0.5s;’ will create a smooth transition over half a second when the border-radius changes.
The above is the detailed content of How To Get Smoother Rounded Corners. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to make an HTTP request in Node.js?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:18 AM
How to make an HTTP request in Node.js?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:18 AM
There are three common ways to initiate HTTP requests in Node.js: use built-in modules, axios, and node-fetch. 1. Use the built-in http/https module without dependencies, which is suitable for basic scenarios, but requires manual processing of data stitching and error monitoring, such as using https.get() to obtain data or send POST requests through .write(); 2.axios is a third-party library based on Promise. It has concise syntax and powerful functions, supports async/await, automatic JSON conversion, interceptor, etc. It is recommended to simplify asynchronous request operations; 3.node-fetch provides a style similar to browser fetch, based on Promise and simple syntax
 JavaScript Data Types: Primitive vs Reference
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:43 AM
JavaScript Data Types: Primitive vs Reference
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:43 AM
JavaScript data types are divided into primitive types and reference types. Primitive types include string, number, boolean, null, undefined, and symbol. The values are immutable and copies are copied when assigning values, so they do not affect each other; reference types such as objects, arrays and functions store memory addresses, and variables pointing to the same object will affect each other. Typeof and instanceof can be used to determine types, but pay attention to the historical issues of typeofnull. Understanding these two types of differences can help write more stable and reliable code.
 JavaScript time object, someone builds an eactexe, faster website on Google Chrome, etc.
Jul 08, 2025 pm 02:27 PM
JavaScript time object, someone builds an eactexe, faster website on Google Chrome, etc.
Jul 08, 2025 pm 02:27 PM
Hello, JavaScript developers! Welcome to this week's JavaScript news! This week we will focus on: Oracle's trademark dispute with Deno, new JavaScript time objects are supported by browsers, Google Chrome updates, and some powerful developer tools. Let's get started! Oracle's trademark dispute with Deno Oracle's attempt to register a "JavaScript" trademark has caused controversy. Ryan Dahl, the creator of Node.js and Deno, has filed a petition to cancel the trademark, and he believes that JavaScript is an open standard and should not be used by Oracle
 Handling Promises: Chaining, Error Handling, and Promise Combinators in JavaScript
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:40 AM
Handling Promises: Chaining, Error Handling, and Promise Combinators in JavaScript
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:40 AM
Promise is the core mechanism for handling asynchronous operations in JavaScript. Understanding chain calls, error handling and combiners is the key to mastering their applications. 1. The chain call returns a new Promise through .then() to realize asynchronous process concatenation. Each .then() receives the previous result and can return a value or a Promise; 2. Error handling should use .catch() to catch exceptions to avoid silent failures, and can return the default value in catch to continue the process; 3. Combinators such as Promise.all() (successfully successful only after all success), Promise.race() (the first completion is returned) and Promise.allSettled() (waiting for all completions)
 What is the cache API and how is it used with Service Workers?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:43 AM
What is the cache API and how is it used with Service Workers?
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:43 AM
CacheAPI is a tool provided by the browser to cache network requests, which is often used in conjunction with ServiceWorker to improve website performance and offline experience. 1. It allows developers to manually store resources such as scripts, style sheets, pictures, etc.; 2. It can match cache responses according to requests; 3. It supports deleting specific caches or clearing the entire cache; 4. It can implement cache priority or network priority strategies through ServiceWorker listening to fetch events; 5. It is often used for offline support, speed up repeated access speed, preloading key resources and background update content; 6. When using it, you need to pay attention to cache version control, storage restrictions and the difference from HTTP caching mechanism.
 JS roundup: a deep dive into the JavaScript event loop
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:24 AM
JS roundup: a deep dive into the JavaScript event loop
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:24 AM
JavaScript's event loop manages asynchronous operations by coordinating call stacks, WebAPIs, and task queues. 1. The call stack executes synchronous code, and when encountering asynchronous tasks, it is handed over to WebAPI for processing; 2. After the WebAPI completes the task in the background, it puts the callback into the corresponding queue (macro task or micro task); 3. The event loop checks whether the call stack is empty. If it is empty, the callback is taken out from the queue and pushed into the call stack for execution; 4. Micro tasks (such as Promise.then) take precedence over macro tasks (such as setTimeout); 5. Understanding the event loop helps to avoid blocking the main thread and optimize the code execution order.
 Understanding Event Bubbling and Capturing in JavaScript DOM events
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:36 AM
Understanding Event Bubbling and Capturing in JavaScript DOM events
Jul 08, 2025 am 02:36 AM
Event bubbles propagate from the target element outward to the ancestor node, while event capture propagates from the outer layer inward to the target element. 1. Event bubbles: After clicking the child element, the event triggers the listener of the parent element upwards in turn. For example, after clicking the button, it outputs Childclicked first, and then Parentclicked. 2. Event capture: Set the third parameter to true, so that the listener is executed in the capture stage, such as triggering the capture listener of the parent element before clicking the button. 3. Practical uses include unified management of child element events, interception preprocessing and performance optimization. 4. The DOM event stream is divided into three stages: capture, target and bubble, and the default listener is executed in the bubble stage.
 A JS roundup of higher-order functions beyond map and filter
Jul 10, 2025 am 11:41 AM
A JS roundup of higher-order functions beyond map and filter
Jul 10, 2025 am 11:41 AM
In JavaScript arrays, in addition to map and filter, there are other powerful and infrequently used methods. 1. Reduce can not only sum, but also count, group, flatten arrays, and build new structures; 2. Find and findIndex are used to find individual elements or indexes; 3.some and everything are used to determine whether conditions exist or all meet; 4.sort can be sorted but will change the original array; 5. Pay attention to copying the array when using it to avoid side effects. These methods make the code more concise and efficient.






