 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 Unlocking the Secrets of Writing Custom Linux Kernel Drivers for Smooth Hardware Integration
Unlocking the Secrets of Writing Custom Linux Kernel Drivers for Smooth Hardware Integration
Unlocking the Secrets of Writing Custom Linux Kernel Drivers for Smooth Hardware Integration
Mar 06, 2025 am 11:08 AM
Introduction: Bridging the Gap Between Linux and Hardware
Linux kernel drivers are essential for communication between the operating system and hardware components. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of creating custom Linux kernel drivers, covering everything from environment setup to advanced debugging techniques. Mastering this skill allows developers to integrate new hardware, optimize performance, and achieve granular system control.
Prerequisites: Essential Knowledge and Skills
Before embarking on kernel driver development, you'll need a solid foundation in:
- Linux Fundamentals: A working knowledge of Linux commands, file systems, and system architecture is crucial.
- C Programming: Kernel drivers are primarily written in C, requiring proficiency in low-level programming concepts, memory management, and system calls.
- Kernel Development Concepts: Understanding kernel space, user space, and kernel modules is fundamental.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
A well-configured development environment is paramount:
- Choose a Distribution: Ubuntu, Fedora, and Debian are popular choices.
-
Install Essential Tools: Use your distribution's package manager (e.g.,
apt-geton Ubuntu) to installbuild-essential,make, andlinux-headers-$(uname -r). -
Obtain Kernel Source Code: Download the source code matching your kernel version from the official Linux kernel website or your distribution's repository (e.g.,
sudo apt-get install linux-sourceon Ubuntu). Extract the archive and navigate to the source directory. - Configure Your Workspace: Organize your project files effectively. Using Git for version control is highly recommended.
Understanding Kernel Driver Components
Kernel drivers interact with hardware and provide a kernel interface. Key components include:
- Driver Types: Character devices (serial ports, input devices), block devices (hard drives, SSDs), and network devices (Ethernet, Wi-Fi).
- Driver Structure: Includes initialization, exit functions, and a file operations structure defining how the driver handles file I/O (open, read, write, close).
A Simple "Hello, World!" Kernel Driver
This example demonstrates a basic driver:
-
Create
hello_world.c: This file will contain the driver code (see the original article for the code snippet). - Create a Makefile: This file automates the compilation process (see the original article for the Makefile).
-
Compile and Load: Use
maketo compile andsudo insmod hello_world.koto load the module. Check the kernel log (dmesg | tail) for output. -
Unload: Use
sudo rmmod hello_worldto remove the module.
Interacting with Hardware: Advanced Techniques
Interacting with hardware involves understanding I/O methods:
- Memory-Mapped I/O: Accessing device registers through memory addresses.
- Port I/O: Reading and writing data through specific I/O ports.
Functions like ioremap, ioread8, iowrite8, request_irq, free_irq are used for register access and interrupt handling (see the original article for code examples).
Implementing Device-Specific Features
Custom drivers require device-specific features:
- Device Initialization: Configure registers, set up DMA, initialize structures.
-
File Operations: Implement
open,read,write, andreleasefunctions. - Error Handling: Implement robust error handling for memory allocation failures, hardware malfunctions, etc.
Debugging and Testing
Effective debugging is crucial:
-
Printk: Use
printkfor logging messages at various levels (KERN_INFO, KERN_ERR). -
Kernel Logs: Examine kernel logs using
dmesg. -
Debugging Tools: Use tools like
gdbandftrace. - Testing: Thorough testing with various scenarios is essential.
Advanced Topics and Best Practices
Advanced topics include concurrency and synchronization (using spinlocks, mutexes, semaphores), power management, and device trees. Best practices emphasize code quality, performance optimization, and security considerations.
Conclusion: Mastering Kernel Driver Development
Developing custom Linux kernel drivers is a challenging but rewarding process. This guide provides a strong foundation for creating efficient and robust drivers, enabling greater control over hardware and system resources.
The above is the detailed content of Unlocking the Secrets of Writing Custom Linux Kernel Drivers for Smooth Hardware Integration. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1794
1794
 16
16
 1739
1739
 56
56
 1590
1590
 29
29
 1467
1467
 72
72
 267
267
 587
587
 Install LXC (Linux Containers) in RHEL, Rocky & AlmaLinux
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:25 AM
Install LXC (Linux Containers) in RHEL, Rocky & AlmaLinux
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:25 AM
LXD is described as the next-generation container and virtual machine manager that offers an immersive for Linux systems running inside containers or as virtual machines. It provides images for an inordinate number of Linux distributions with support
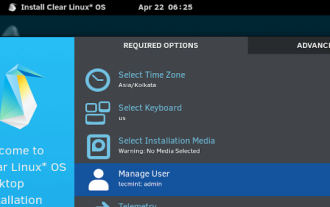 Clear Linux Distro - Optimized for Performance and Security
Jul 02, 2025 am 09:49 AM
Clear Linux Distro - Optimized for Performance and Security
Jul 02, 2025 am 09:49 AM
Clear Linux OS is the ideal operating system for people – ahem system admins – who want to have a minimal, secure, and reliable Linux distribution. It is optimized for the Intel architecture, which means that running Clear Linux OS on AMD sys
 7 Ways to Speed Up Firefox Browser in Linux Desktop
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:18 AM
7 Ways to Speed Up Firefox Browser in Linux Desktop
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:18 AM
Firefox browser is the default browser for most modern Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Mint, and Fedora. Initially, its performance might be impressive, however, with the passage of time, you might notice that your browser is not as fast and resp
 How to create a self-signed SSL certificate using OpenSSL?
Jul 03, 2025 am 12:30 AM
How to create a self-signed SSL certificate using OpenSSL?
Jul 03, 2025 am 12:30 AM
The key steps for creating a self-signed SSL certificate are as follows: 1. Generate the private key, use the command opensslgenrsa-outselfsigned.key2048 to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key file, optional parameter -aes256 to achieve password protection; 2. Create a certificate request (CSR), run opensslreq-new-keyselfsigned.key-outselfsigned.csr and fill in the relevant information, especially the "CommonName" field; 3. Generate the certificate by self-signed, and use opensslx509-req-days365-inselfsigned.csr-signk
 How to Hide Files and Directories in Linux
Jun 26, 2025 am 09:13 AM
How to Hide Files and Directories in Linux
Jun 26, 2025 am 09:13 AM
Do you sometimes share your Linux desktop with family, friends, or coworkers? If so, you may want to hide some personal files and folders. The challenge is figuring out how to conceal these files on a Linux system.In this guide, we will walk through
 How to extract a .tar.gz or .zip file?
Jul 02, 2025 am 12:52 AM
How to extract a .tar.gz or .zip file?
Jul 02, 2025 am 12:52 AM
Decompress the .zip file on Windows, you can right-click to select "Extract All", while the .tar.gz file needs to use tools such as 7-Zip or WinRAR; on macOS and Linux, the .zip file can be double-clicked or unzip commanded, and the .tar.gz file can be decompressed by tar command or double-clicked directly. The specific steps are: 1. Windows processing.zip file: right-click → "Extract All"; 2. Windows processing.tar.gz file: Install third-party tools → right-click to decompress; 3. macOS/Linux processing.zip file: double-click or run unzipfilename.zip; 4. macOS/Linux processing.tar
 How to Burn CD/DVD in Linux Using Brasero
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Burn CD/DVD in Linux Using Brasero
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:26 AM
Frankly speaking, I cannot recall the last time I used a PC with a CD/DVD drive. This is thanks to the ever-evolving tech industry which has seen optical disks replaced by USB drives and other smaller and compact storage media that offer more storage
 How would you debug a server that is slow or has high memory usage?
Jul 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How would you debug a server that is slow or has high memory usage?
Jul 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
If you find that the server is running slowly or the memory usage is too high, you should check the cause before operating. First, you need to check the system resource usage, use top, htop, free-h, iostat, ss-antp and other commands to check CPU, memory, disk I/O and network connections; secondly, analyze specific process problems, and track the behavior of high-occupancy processes through tools such as ps, jstack, strace; then check logs and monitoring data, view OOM records, exception requests, slow queries and other clues; finally, targeted processing is carried out based on common reasons such as memory leaks, connection pool exhaustion, cache failure storms, and timing task conflicts, optimize code logic, set up a timeout retry mechanism, add current limit fuses, and regularly pressure measurement and evaluation resources.



