This article explores top-notch Notepad alternatives for Linux users. Notepad , while excellent on Windows, lacks a Linux version. This guide offers a diverse range of options to suit various needs and preferences.
Top Notepad Alternatives for Linux
Here's a curated selection of powerful text editors and IDEs readily available for Linux distributions:
1. Vim Editor
Vim, a highly configurable text editor, excels in handling diverse text types, including source code, configuration files, and scripts. Its terminal-based interface offers distinct modes: normal (navigation), insert (typing), and command (execution). Its extensive customization options, plugin support, and multi-level undo are key strengths.

2. Nano Editor
Nano, a user-friendly command-line editor, is often pre-installed on many Linux systems. It boasts features like syntax highlighting and convenient keybindings for tasks such as commenting/uncommenting lines. Installation instructions for various distributions are provided below.

Installation Commands:
# Debian/Ubuntu/Mint: sudo apt install nano # RHEL/CentOS/Fedora/Rocky/AlmaLinux: sudo yum install nano # Gentoo: sudo emerge -a sys-apps/nano # Alpine: sudo apk add nano # Arch: sudo pacman -S nano # OpenSUSE: sudo zypper install nano
3. GNU Emacs
GNU Emacs, a highly customizable and extensible editor, is renowned for its extensibility via Emacs Lisp. It supports numerous file formats and languages, offers a GUI option, and includes comprehensive documentation.

Installation is similar to Nano, using the appropriate package manager command for your distribution.
4. Gedit
Gedit, GNOME's default text editor, provides a clean, intuitive GUI. Features include file backups, text wrapping, line numbering, and remote file editing. Installation mirrors the previous examples.

5. Geany
Geany, a lightweight IDE, offers a speedy and efficient environment with minimal dependency on other packages. Its features include a built-in console, support for various programming languages, and code folding. Installation commands follow the same pattern as above.

6. GNOME Text Editor
GNOME Text Editor, the successor to gedit in GNOME 42 and later, maintains a user-friendly interface with built-in themes and syntax highlighting for various languages. Installation instructions are consistent with those previously shown.

7. Sublime Text
Sublime Text, a cross-platform, proprietary editor with a Python API, is praised for its clean interface, "Goto Anything" feature, and extensive plugin support. Further installation details can be found in separate documentation.

8. Kate
Kate (KDE Advanced Text Editor), integrated with KDE software, offers features such as code folding, extensible syntax highlighting, and automatic character encoding detection. Installation is consistent with the previously provided examples.

9. Notepadqq
Notepadqq, a direct Linux alternative to Notepad , prioritizes small program size and high execution speed, offering a user-friendly interface and plugin support. Installation commands follow the established pattern.

10. Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code (VS Code), a powerful and highly customizable cross-platform editor from Microsoft, features IntelliSense, built-in Git integration, and a debugger. Installation follows the same method as other editors.

11. SciTE
SciTE, a Scintilla-based editor, is known for its simple interface, syntax highlighting, and support for bidirectional text. Installation is consistent with previous examples.

12. CodeLobster
CodeLobster, a free IDE focused on PHP, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, provides a rich feature set comparable to many paid applications. Further details on installation can be found separately.

13. Lite XL
Lite XL, a lightweight and fast editor, is praised for its minimal interface and Lua-based extensibility. It's ideal for users seeking a snappy and resource-efficient editor.

14. Bluefish Editor
Bluefish, a powerful editor geared towards web developers, supports numerous languages and offers features like auto-completion, code folding, and remote file editing.

15. Micro Editor
Micro, a modern terminal-based editor, provides a user-friendly experience even for command-line newcomers. It supports plugins and offers features like syntax highlighting and split windows.

16. Phoenix Code (Recommended over Brackets)
Phoenix Code, a continuation of Brackets, is a front-end web development editor with Live Preview and inline editing capabilities. It's a strong choice for web developers seeking a modern, efficient workflow.

This comprehensive list provides a solid foundation for selecting the ideal Notepad replacement tailored to your specific coding preferences and Linux distribution. Remember to consult individual editor documentation for detailed installation and usage instructions.
The above is the detailed content of Top 16 Notepad Replacements for Linux in 2025. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1794
1794
 16
16
 1739
1739
 56
56
 1590
1590
 29
29
 1467
1467
 72
72
 267
267
 587
587
 Install LXC (Linux Containers) in RHEL, Rocky & AlmaLinux
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:25 AM
Install LXC (Linux Containers) in RHEL, Rocky & AlmaLinux
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:25 AM
LXD is described as the next-generation container and virtual machine manager that offers an immersive for Linux systems running inside containers or as virtual machines. It provides images for an inordinate number of Linux distributions with support
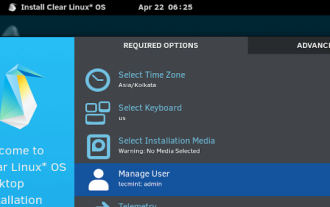 Clear Linux Distro - Optimized for Performance and Security
Jul 02, 2025 am 09:49 AM
Clear Linux Distro - Optimized for Performance and Security
Jul 02, 2025 am 09:49 AM
Clear Linux OS is the ideal operating system for people – ahem system admins – who want to have a minimal, secure, and reliable Linux distribution. It is optimized for the Intel architecture, which means that running Clear Linux OS on AMD sys
 7 Ways to Speed Up Firefox Browser in Linux Desktop
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:18 AM
7 Ways to Speed Up Firefox Browser in Linux Desktop
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:18 AM
Firefox browser is the default browser for most modern Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Mint, and Fedora. Initially, its performance might be impressive, however, with the passage of time, you might notice that your browser is not as fast and resp
 How to create a self-signed SSL certificate using OpenSSL?
Jul 03, 2025 am 12:30 AM
How to create a self-signed SSL certificate using OpenSSL?
Jul 03, 2025 am 12:30 AM
The key steps for creating a self-signed SSL certificate are as follows: 1. Generate the private key, use the command opensslgenrsa-outselfsigned.key2048 to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key file, optional parameter -aes256 to achieve password protection; 2. Create a certificate request (CSR), run opensslreq-new-keyselfsigned.key-outselfsigned.csr and fill in the relevant information, especially the "CommonName" field; 3. Generate the certificate by self-signed, and use opensslx509-req-days365-inselfsigned.csr-signk
 How to Hide Files and Directories in Linux
Jun 26, 2025 am 09:13 AM
How to Hide Files and Directories in Linux
Jun 26, 2025 am 09:13 AM
Do you sometimes share your Linux desktop with family, friends, or coworkers? If so, you may want to hide some personal files and folders. The challenge is figuring out how to conceal these files on a Linux system.In this guide, we will walk through
 How to extract a .tar.gz or .zip file?
Jul 02, 2025 am 12:52 AM
How to extract a .tar.gz or .zip file?
Jul 02, 2025 am 12:52 AM
Decompress the .zip file on Windows, you can right-click to select "Extract All", while the .tar.gz file needs to use tools such as 7-Zip or WinRAR; on macOS and Linux, the .zip file can be double-clicked or unzip commanded, and the .tar.gz file can be decompressed by tar command or double-clicked directly. The specific steps are: 1. Windows processing.zip file: right-click → "Extract All"; 2. Windows processing.tar.gz file: Install third-party tools → right-click to decompress; 3. macOS/Linux processing.zip file: double-click or run unzipfilename.zip; 4. macOS/Linux processing.tar
 How to Burn CD/DVD in Linux Using Brasero
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Burn CD/DVD in Linux Using Brasero
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:26 AM
Frankly speaking, I cannot recall the last time I used a PC with a CD/DVD drive. This is thanks to the ever-evolving tech industry which has seen optical disks replaced by USB drives and other smaller and compact storage media that offer more storage
 How would you debug a server that is slow or has high memory usage?
Jul 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How would you debug a server that is slow or has high memory usage?
Jul 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
If you find that the server is running slowly or the memory usage is too high, you should check the cause before operating. First, you need to check the system resource usage, use top, htop, free-h, iostat, ss-antp and other commands to check CPU, memory, disk I/O and network connections; secondly, analyze specific process problems, and track the behavior of high-occupancy processes through tools such as ps, jstack, strace; then check logs and monitoring data, view OOM records, exception requests, slow queries and other clues; finally, targeted processing is carried out based on common reasons such as memory leaks, connection pool exhaustion, cache failure storms, and timing task conflicts, optimize code logic, set up a timeout retry mechanism, add current limit fuses, and regularly pressure measurement and evaluation resources.




