 web3.0
web3.0
 What is NodeOps (NODE)? Is it worth investing? A comprehensive introduction to NodeOps (NODE) ??project
What is NodeOps (NODE)? Is it worth investing? A comprehensive introduction to NodeOps (NODE) ??project
What is NodeOps (NODE)? Is it worth investing? A comprehensive introduction to NodeOps (NODE) ??project
Jul 02, 2025 pm 06:54 PMTable of contents
- Brief facts: NodeOps (NODE) ??Overview
- What is NodeOps?
- How many NODE tokens are there?
- What is the function of NODE tokens?
- NodeOps' core products and services
- NodeOps (NODE) ??and Ethereum (ETH): A Two-Level Story
- The technology behind NodeOps
- Team and Origin
- Is NODE a potential quality investment? A balanced perspective
- Potential Advantages
- Risks and challenges to consider
- in conclusion
In a complex and rapidly evolving Web3 world, infrastructure that supports decentralized applications, blockchains, and AI is often as complex as the technology itself. For developers and protocols, managing this underlying “computing” layer can be a major obstacle to innovation. The NodeOps project is working on this challenge, positioning itself as the foundational layer of the next wave of decentralized development.
NodeOps aims to be the leading DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network) coordination protocol to simplify the management of cloud infrastructure. With its native token NODE as the economic core, the project provides a set of tools for node operators, developers and the entire protocol. This article provides an objective and educational overview of NodeOps, explaining its technology, purpose, and role in the broader Web3 ecosystem.

Brief facts: NodeOps (NODE) ??Overview
- Stock Code: NODE
- Chain: Ethereum
- Contract address: 0x2f714d7b9a035d4ce24af8d9b6091c07e37f43fb
- Circulation supply at the time of issuance: approximately 133.4 million
- Total supply at the time of creation: approximately 678.8 million (Note: This is dynamic supply, not hard upper limit)
- Main use cases: DePIN coordination protocol for verifiable, universal computing.
- Current market value: /
- Availability on Phemex: Not available yet (as of this writing).
What is NodeOps?
In short, NodeOps is a dedicated platform for managing the computer resources (i.e., "computing") needed to run blockchain and decentralized applications. Blockchain relies on computer networks (i.e. "nodes") to operate safely. Setting up and maintaining these nodes has high technical requirements and resource consuming, which has brought bottlenecks to many projects.
NodeOps strives to solve this problem by creating a permissionless, blockchain-free network to coordinate these resources. The mission of the project is to enhance the builder’s experience and allow developers to focus on innovation rather than complex operations.
The project provides a very apt metaphor: The NodeOps network is like a large, secure playground . Protocols and dApps are like "parents", bringing their "children" (nodes, applications) to play. These "parents" use "pocket money" (tokens) to rent "toys" (computing resources) from the playground's shop (NodeOps market). The "Guardian" (surveillance system) protects everything to ensure its safety and normal operation.
The entire NodeOps ecosystem is organized around four key pillars:
- NodeOps Network: DePIN coordinator for general purpose computing, protected by Active Verification Service (AVS).
- Core Service Suite: A collection of products for developers, node operators and users.
- NodeOps Foundation: a governance layer centered on NODE tokens to support the network.
- Partner ecosystem: computing providers and consumers that form the lifeblood of the network.
Through these pillars, NodeOps provides a platform designed to abstract the challenges of decentralized computing infrastructure.
How many NODE tokens are there?
NODE's token economics is designed to be dynamic and responsive to network activities, unlike a model with a fixed maximum supply.
In its Token Generation Event (TGE), the total supply at the time of creation was 678,833,730 NODE and the initial circulation supply was 133,390,828 NODE (approximately 19.65%).

The core characteristics of its economic model are dynamic coin minting and destruction mechanisms . The system is inspired by the popular "BME" framework in DePIN, directly linking the creation of new tokens to on-chain revenue. When users pay for service fees on the network, a portion of the NODE tokens they use are destroyed (permanently exited from circulation). After that, the system will mint the corresponding number of new tokens and allocate them according to the "destruction/mint ratio" to be distributed as rewards to the network participants. This ensures that token inflation is supported by real economic activity, creating a sustainable model where supply only expands based on real demand.
The initial allocation of Genesis supply is as follows:
1. Community and ecosystem (47.5%):
- Ecosystem Growth (30%): The largest allocation for contributor incentives, partnerships and marketing, TGE unlocks 10%, followed by 6 months of cliffs and 60 months of linear attribution.
- Airdrop (15.5%): Reward early supporters and community members, 80% of whom are unlocked in TGE.
- IDO (2%): Used for initial public sale, 100% unlocked after completion.
2. Protocol incentives (15%): Provides a core reward system for computing providers and stakeholders.
3. Initial Contributor (15%): For the core team, there is a 12-month cliff period and a 60-month vest period to coordinate long-term interests.
4. Early supporters (22.5%): For investors who provide seed funds, there are 12-month cliff periods and 36-month vest periods.

This structured distribution and dynamic supply model is designed to balance initial growth incentives with long-term economic stability, directly linking NODE prices and supply to the utility of the platform.
What is the function of NODE tokens?
NODE tokens are an indispensable part of the platform's functions, and their functions are far more than simple speculation. Its design makes it the main economic engine of the NodeOps network. The core use cases of NODE can be understood through the following four main functions:
- Service Access (Destroy and Generate Points): All services on the NodeOps platform are denominated in US dollars. When a user accesses the service, he or she needs to destroy an equal amount of NODE token and receive non-transferable points. This directly links platform usage to token demand.
- Computation Binding: In order to contribute resources to the network, the computing provider must "bind" or stake NODE tokens. This sets an economic threshold for participation, ensuring that providers are involved and aligned with the healthy development of the network.
- Ensure network security (verified computing): NodeOps integrates with AVS ecosystems such as EigenLayer. This allows NODE to be restaked, providing economic security for computing workloads. If a provider fails to meet performance or integrity standards, its pledged tokens may be "cut" or forfeited as a penalty.
- Governance: NODE holders can participate in agreement governance and vote on key parameters such as destruction/casting ratios, reward policies, and other operational decisions that affect the future of the network.
NodeOps' core products and services
NODE's utility is achieved through its product suite:
- Agent Terminal: Developer sandbox for building and deploying AI solutions.
- NodeOps Cloud: A market for verifiable computing without permission.
- NodeOps console: A raw node-as-a-service (NaaS) dashboard for no-code node deployment.
- Security Center: An artificial intelligence tool for scanning code and application sequence vulnerabilities.
- Staking Hub: A platform that allows users to pool their tokens to meet the minimum requirements for running validator nodes.
- NodeOps Enterprise: B2B service for enterprise-level RPC and validator nodes.
For those who wish to trade NODE , understanding this deep utility is key to assessing its role in the market.
NodeOps (NODE) ??and Ethereum (ETH): A Two-Level Story
Comparing NodeOps with industry giants like Ethereum is not because they are direct competitors, but because it clearly demonstrates the unique symbiotic relationship between them. Understanding this difference is key to understanding the position of NodeOps in Web3 architecture.
| feature | NodeOps (NODE) | Ethereum (ETH) |
| Main use cases | The DePIN coordination layer for deploying and managing distributed computing resources. | A universal, decentralized smart contract platform for building DApps. |
| technology | Active Verification Service (AVS) built on EigenLayer, leveraging the security of Ethereum. | The foundation of the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism is the 1st layer blockchain. |
| Role in ecosystem | Infrastructure Service Layer: Provides "picks and shovels" for the operation of other chains and services. | Settlement and Application Layer: The basic “digital jurisdiction” for DApp execution and transaction completion. |
| Token utility | Calculate service costs, binding/staking to protect NodeOps networks, and governance costs. | Gas fees for transactions, pledges that ensure the security of the entire network, and core value storage. |
| Target audience | Blockchain developers, new protocols, AI projects, and professional node operators. | DApp developers, end users of DeFi/NFT, and investors in the basic layer of Web3. |
The key to comparing NodeOps with Ethereum is that they run at different and complementary levels of the technology stack. NodeOps is not an attempt to become the new Ethereum; rather, it is a professional service that utilizes Ethereum security to provide the necessary infrastructure to the multi-chain world.
The technology behind NodeOps
NodeOps is built on advanced technologies designed for security and scalability. Its core innovation lies in its position as an active verification service (AVS) on EigenLayer . EigenLayer is a protocol on Ethereum that introduces a "restaking" mechanism that allows the use of staking ETH to protect the security of other applications.

By running as AVS, NodeOps allows new blockchain projects to leverage this shared security pool without building their own security pool from scratch. NodeOps AVS is a decentralized operator network focused on deploying and managing nodes. This process is guaranteed by restaking ETH and pledged NODE tokens, thus building a powerful dual security model. This framework positions NodeOps as a "layer 0" infrastructure solution, providing basic services to a variety of other networks.
Team and Origin
The credibility of a project usually depends on its founding team. NodeOps was co-founded by Naman Kabra and Shivam Tuteja , who have a background in software engineering and focus on solving infrastructure-level problems in the field of encryption.
The project has a strong momentum after receiving a $5 million seed round . This round of financing was led by well-known cryptocurrency native venture capital firm Borderless Capital , Wormhole , and other strategic investors. This funding and strategic support provides NodeOps with the resources needed to achieve its ambitious roadmap.
Is NODE a potential quality investment? A balanced perspective
This section explores the potential advantages and disadvantages of NodeOps, but must be viewed from the perspective of the high risk and high reward nature of early crypto projects.
Potential Advantages
DePIN and Infrastructure Layout: NodeOps operates in the DePIN field, providing the necessary "picks and shovels" infrastructure. Its success is closely related to the overall growth of the Web3 industry, not the success of a single application.
Integration with EigenLayer: As AVS on EigenLayer, NodeOps is at the center of a strong restaking narrative that may benefit from its growth and capital flows.
Clear revenue model: Destruction/mint mechanisms and service fees create direct links between platform use and token economy, providing a clear pathway to sustainable income.
Diverse product suite: A range of services from artificial intelligence development to node deployment meets a variety of needs in the Web3 field and creates multiple approaches to adoption.
Risks and challenges to consider
- Execution Risk: The project’s vision is ambitious, but its success is not inevitable. It depends heavily on the team’s ability to execute its complex roadmap, maintain security, and attract a large number of computing providers and consumers.
- Fierce competition: The node-as-a-service and DePIN markets are fiercely competitive. NodeOps faces challenges both from established centralized players and from other emerging decentralized solutions. Whether it can maintain its competitive advantage is still uncertain.
- Technology dependency: The success of this project is closely related to the security and ongoing application of EigenLayer. Any unforeseen vulnerability or failure in the underlying restaking agreement can have a serious negative chain impact on all AVSs, including NodeOps.
- Extreme market fluctuations: Like all altcoins (especially newly issued altcoins), NODE prices are prone to drastic fluctuations. Its value may be severely affected by the overall trend of the cryptocurrency market and may experience substantial fluctuations in the short term. Investors must be prepared to deal with huge losses.
in conclusion
NodeOps (NODE) ??is a technology-focused project designed to solve a fundamental problem in the Web3 field: the complexity of decentralized infrastructure management. By creating the DePIN coordination layer, which has a well-established token economic model and a clear product suite, it is building the basic services for developers and protocols.
Although the project is still in its early stages and faces inherent risks of pioneering technology, its strategic positioning in DePIN and its restaking narrative make it an important project worthy of attention. For anyone interested in the underlying infrastructure that drives the future of decentralized applications, it is crucial to understand projects like NodeOps. However, any potential interest must be balanced with a clear understanding of the significant risks involved. As the ecosystem matures, information on how to buy NODE on platforms like Phemex will become richer, reflecting its growth and market influence. You can follow NODE's news to keep up with its latest developments.
Here is the article about what is NodeOps (NODE)? Is it worth investing? This is the article about the comprehensive introduction of the NodeOps (NODE) ??project. For more related NodeOps (NODE) ??content, please search for previous articles on this site or continue to browse the related articles below. I hope everyone will support this site in the future!
The above is the detailed content of What is NodeOps (NODE)? Is it worth investing? A comprehensive introduction to NodeOps (NODE) ??project. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Binance official app download latest link Binance exchange app installation portal
Aug 04, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
Binance official app download latest link Binance exchange app installation portal
Aug 04, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
Binance is a world-renowned digital asset trading platform, providing users with secure, stable and rich cryptocurrency trading services. Its app is simple to design and powerful, supporting a variety of transaction types and asset management tools.
 Binance official app latest official website entrance Binance exchange app download address
Aug 04, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Binance official app latest official website entrance Binance exchange app download address
Aug 04, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Binance is one of the world's well-known digital asset trading platforms, providing users with safe, stable and convenient cryptocurrency trading services. Through the Binance App, you can view market conditions, buy, sell and asset management anytime, anywhere.
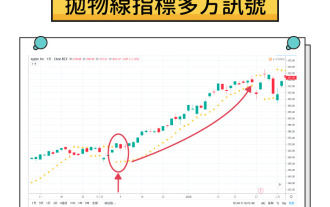 What is a parabolic SAR indicator? How does SAR indicator work? Comprehensive introduction to SAR indicators
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
What is a parabolic SAR indicator? How does SAR indicator work? Comprehensive introduction to SAR indicators
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
Contents Understand the mechanism of parabola SAR The working principle of parabola SAR calculation method and acceleration factor visual representation on trading charts Application of parabola SAR in cryptocurrency markets1. Identify potential trend reversal 2. Determine the best entry and exit points3. Set dynamic stop loss order case study: hypothetical ETH trading scenario Parabola SAR trading signals and interpretation Based on parabola SAR trading execution Combining parabola SAR with other indicators1. Use moving averages to confirm trend 2. Relative strength indicator (RSI) for momentum analysis3. Bollinger bands for volatility analysis Advantages of parabola SAR and limitations Advantages of parabola SAR
 Cardano (ADA Coin) price forecast: 2025, 2026 and beyond
Aug 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Cardano (ADA Coin) price forecast: 2025, 2026 and beyond
Aug 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Directory What is Cardano? Key Features of Cardano How does Cardano work? Why Cardano deserves to consider price and market performance history 2025 ADA forecast 2025, 2026 and 2027 Price forecasts 2040 and 2030 ADA price forecast Factors affecting ADA costs Chart analysis and technical outlook Cardano Forecast Table: Key points summary As an important force in the cryptocurrency industry, Cardano (ADA) provides cutting-edge blockchain solutions with a focus on sustainability, scalability and security. Cardano is co-founder of Ethereum.
 Solana (SOL Coin) Price Forecast: 2025-2030 and Future Outlook
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Solana (SOL Coin) Price Forecast: 2025-2030 and Future Outlook
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Table of Contents Solana's Price History and Important Market Data Important Data in Solana Price Chart: 2025 Solana Price Forecast: Optimistic 2026 Solana Price Forecast: Maintain Trend 2026 Solana Price Forecast: 2030 Solana Long-term Price Forecast: Top Blockchain? What affects the forecast of sun prices? Scalability and Solana: Competitive Advantages Should you invest in Solana in the next few years? Conclusion: Solana's price prospects Conclusion: Solana has its excellent scalability, low transaction costs and high efficiency
 Blockchain browser: a must-have tool for querying digital currency transaction information
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Blockchain browser: a must-have tool for querying digital currency transaction information
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Blockchain browser is a necessary tool for querying digital currency transaction information. It provides a visual interface for blockchain data, so that users can query transaction hash, block height, address balance and other information; its working principle includes data synchronization, parsing, indexing and user interface display; core functions cover querying transaction details, block information, address balance, token data and network status; when using it, you need to obtain TxID and select the corresponding blockchain browser such as Etherscan or Blockchain.com to search; query address information to view balance and transaction history by entering the address; mainstream browsers include Bitcoin's Blockchain.com, Ethereum's Etherscan.io, B
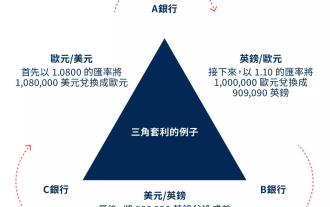 A detailed explanation of triangle arbitrage in the cryptocurrency market
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
A detailed explanation of triangle arbitrage in the cryptocurrency market
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Table of Contents Triangle Arbitrage Introduction Cryptocurrency Triangle Arbitrage Mechanism Challenges: Identifying Opportunities Risks, Ethics and Regulatory Considerations Conclusion Triangle Arbitrage Introduction Triangle Arbitrage is a trading strategy aimed at capturing the temporary price mismatch between the three related assets, thereby achieving nearly risk-free returns. This strategy forms a closed loop by conducting continuous trading between three related trading pairs (such as BTC/ETH, ETH/USDT, USDT/BTC), and takes advantage of temporary imbalance in the exchange rate to make profits. Its essence comes from the basic principle of arbitrage, that is, price correction is carried out when market efficiency is insufficient, while the triangle form increases the complexity of operations through multiple steps of trading. Cryptocurrencies provide more frequent opportunities for triangle arbitrage compared to traditional forex markets. Forex market due to
 What is open position in cryptocurrency? Comprehensive Guide to Open Positions
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
What is open position in cryptocurrency? Comprehensive Guide to Open Positions
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
Directory What is open position? Understand the importance of open positions in cryptocurrencies Where can I find open positions data? The role of open positions in market trends Comparison of open positions and trading volume Definition: Their indicative significance: Relationship: Market trend: Limitations of open positions Summary Thinking of common questions about open positions in cryptocurrencies 1. How to use open positions to confirm market trends? 2. What is the difference between open position volume and trading volume? 3. Is it always better to have higher open positions? 4. What is the role of open positions in evaluating market liquidity? 5. How to distinguish




