Creating a network location is a practical feature on a Mac, suitable for users who frequently switch network environments. The core steps are: open "System Settings" or "System Preferences" to enter the "Network" section, click "Edit Location" in the "Position" drop-down menu, add a new location and name it through the " " sign; then select the location to configure the corresponding Wi-Fi or Ethernet network service parameters, such as connecting to a specific wireless network, specifying DNS, or setting a static IP address; finally, you can quickly switch different network locations through the top menu bar. The configuration of each location does not affect each other, and certain network services can be disabled as needed, suitable for various scenarios such as home, company, and business trips. It is recommended to specify the purpose when naming it for identification and switch when the network is idle to avoid connection interruptions.

Creating a network location is actually a very practical feature on Mac, especially suitable for users who often switch different network environments. By setting different network locations, you can quickly switch network configurations such as Wi-Fi and Ethernet without having to manually adjust them every time.

What is a network location?
The "network location" of a Mac can be understood as a set of preset network configurations. For example, if you use static IP in your company and automatically assign addresses at home using DHCP, you can create two network locations for these two scenarios. When switching, you can automatically apply the corresponding network settings.
How to create a new network location
This is the most core step in the entire process:

- Open System Settings or System Preferences and enter the Network section
- Find the "Location" drop-down menu in the lower left corner
- Click "Edit Location", then click " " to add a new location, and give an easily recognizable name, such as "Office" or "School"
- After creation is completed, select this new location and configure the corresponding network service (such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet)
Once created, you can quickly switch through the shortcuts in the top menu bar.
How to configure parameters of different network services
Each network location can have completely different settings. For example:

- Select to connect to a specific wireless network and specify DNS in "Wi-Fi"
- Setting a static IP address and subnet mask in Ethernet
- You can also disable certain network services that you do not use, such as Bluetooth PAN or infrequently used VPNs
These settings will only take effect on the network location you currently selected and other locations will not be affected.
Practical tips and tips
- Try to clarify the purpose when naming each location, such as "home-automatic acquisition" and "company-fixed IP" so that you can understand it at a glance
- If you travel frequently, you can create a corresponding location at each location and configure the proxy or DNS in advance to save time
- Switching network locations will affect all network connections, so it is best to operate when the network is idle to avoid interrupting ongoing tasks.
If you are a technician or often need to debug network problems, this feature is even more worth using.
Basically all of this is it. Although it seems that there are a lot of steps, it is very fast to operate, and once it is set up, it can save a lot of trouble.
The above is the detailed content of How to create a network location on Mac. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to Remove Old Devices from Apple ID on Mac
Jul 07, 2025 am 09:08 AM
How to Remove Old Devices from Apple ID on Mac
Jul 07, 2025 am 09:08 AM
If you've owned multiple Apple devices over the years, you might find yourself in a situation where some of those older Macs, iPhones, iPads, or other Apple hardware have been sold, given away, or traded. No matter how they left your possession, it's
 How to Play Fortnite on Mac with FnMacAssistant & Sideloadly
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:21 AM
How to Play Fortnite on Mac with FnMacAssistant & Sideloadly
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:21 AM
Fortnite is once again available for iPhone and iPad users, bringing joy to many gamers. However, there's still no official version for Mac (at least not yet). Despite that, Apple Silicon Mac owners aren’t completely out of luck—you can run the iOS/i
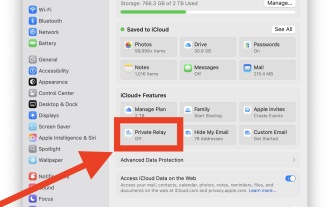 How to Enable iCloud Private Relay on Mac
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:36 AM
How to Enable iCloud Private Relay on Mac
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:36 AM
iCloud Private Relay is an excellent privacy feature included with the iCloud subscription, designed to safeguard your online activity and browsing by masking your IP address (using a temporary one) and encrypting DNS lookups. This prevents third pa
 How to Allow Apps During Downtime on Mac
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:03 AM
How to Allow Apps During Downtime on Mac
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:03 AM
Are you using Screen Time to manage your or your child’s Mac usage? If yes, you likely already know that it allows you to set app limits, schedule downtime on the Mac, and more. Additionally, you can also choose specific apps that remain accessible a
 How to Make MacOS Sequoia Feel Faster: Tips to Speed Up Slow MacOS
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:28 AM
How to Make MacOS Sequoia Feel Faster: Tips to Speed Up Slow MacOS
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:28 AM
macOS Sequoia is a solid operating system that brings some impressive features like iPhone Mirroring, and while performance is excellent for many users, not everyone experiences the same level of speed. If you're finding macOS Sequoia slower than pre
 How to See All Links Shared in Messages on iPhone & iPad
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:31 AM
How to See All Links Shared in Messages on iPhone & iPad
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:31 AM
If you frequently use iMessage, then you've likely shared numerous web links in your chats — maybe an article, a video, a tweet, a song, or anything else. Locating these links later can be quite frustrating, but thankfully there's a simpler method th
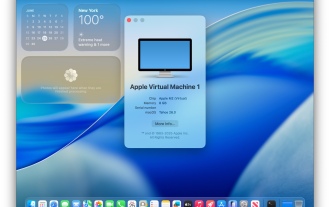 Create a MacOS Tahoe 26 Beta VM with Three Commands in Terminal Using tart
Jul 06, 2025 am 09:28 AM
Create a MacOS Tahoe 26 Beta VM with Three Commands in Terminal Using tart
Jul 06, 2025 am 09:28 AM
Advanced Mac users familiar with the command line can swiftly set up a MacOS Tahoe 26 beta virtual machine by entering a few commands into Terminal, using tart. Tart is a command-line utility for managing virtual machines and offers one of the quicke
 WindowServer Quit Unexpectedly: How to Fix It on Mac Air/Pro?
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:17 AM
WindowServer Quit Unexpectedly: How to Fix It on Mac Air/Pro?
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:17 AM
What is WindowServer and why is it importantWindowServer is a core macOS process that manages how apps and windows appear on screen. It handles GUI rendering, controls internal and external displays, and enables all vis






