This chapter focuses on the interfaces and classes under the java.lang.reflect package

When the program uses a certain class, if the class has not been loaded into the memory, then the system will load, connect, There are three steps to initialize the class. When loading a class, it means reading the class file into the memory and creating a java.lang.class object for it. That is to say, when any class is used in the program , the system will create a java.lang.Class object for it. (Almost all classes are instances of java.lang.Class);



 so the JVM is initialized first Always the java.long.Object class.
so the JVM is initialized first Always the java.long.Object class.
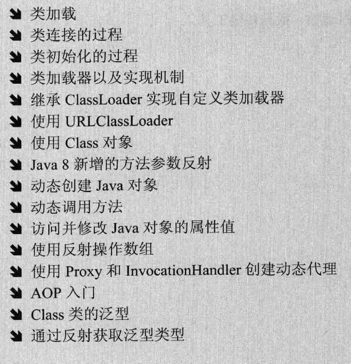
In Java, a class is identified by its fully qualified class name (including package name and class name); but in JVM, a class is identified by its fully qualified class name and class loader. Its unique identifier.
 Print root class loader:
Print root class loader:
public class BootstrapTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 獲取根類加載器所加載的全部URL數(shù)組
for (URL url : sun.misc.Launcher.getBootstrapClassPath().getURLs()) {
// 遍歷、輸出根類加載器加載的全部URL
System.out.println(url.toExternalForm());
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------
file:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_51.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/resources.jar
file:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_51.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/rt.jar
file:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_51.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jsse.jar
file:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_51.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jce.jar
file:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_51.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/charsets.jar
file:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_51.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jfr.jarExtended class loader, this can be added to your own jar package, which is quite fun.
 System class loader: This is what we usually use Define the parent loader of the class
System class loader: This is what we usually use Define the parent loader of the class


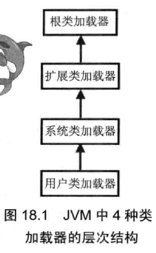 Developers need to implement a custom class loader by inheriting ClassLoader.
Developers need to implement a custom class loader by inheriting ClassLoader.
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// 獲取系統(tǒng)類加載器
ClassLoader systemLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println("系統(tǒng)類加載器:" + systemLoader);
/*
獲取系統(tǒng)類加載器的加載路徑——通常由CLASSPATH環(huán)境變量指定
如果操作系統(tǒng)沒有指定CLASSPATH環(huán)境變量,默認以當前路徑作為
系統(tǒng)類加載器的加載路徑
*/
Enumeration<URL> em1 = systemLoader.getResources("");
while(em1.hasMoreElements())
{
System.out.println(em1.nextElement());
}
// 獲取系統(tǒng)類加載器的父類加載器:得到擴展類加載器
ClassLoader extensionLader = systemLoader.getParent();
System.out.println("擴展類加載器:" + extensionLader);
System.out.println("擴展類加載器的加載路徑:"
+ System.getProperty("java.ext.dirs"));
System.out.println("擴展類加載器的parent: "
+ extensionLader.getParent());
}
 Example of custom class loader :
Example of custom class loader :
Since the URLClassLoader of java8.0.51 rewrites the following method in the ClassLoader class,
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}So, we haven’t figured out the reason yet. If we rewrite findClass(String name) ourselves, the result is that the program will first Call the findClass method in URLClassLoader. If this method cannot find the class, it will call the findClass(String name) we wrote ourselves.
For example, if we want to dynamically load a certain class (if this class exists in the memory, then fetch it from the memory ;If it does not exist in the memory, then load the java file of that class and compile it (I am not sure whether to check whether there is a class file first, looking at the source code and my own test results, it is not checked)).
Example
public class Hello
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("tes22t2");
for (String arg : args)
{
System.out.println("運行Hello的參數(shù):" + arg);
}
}
}import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.net.URL;
import java.security.CodeSigner;
import java.security.CodeSource;
import java.util.jar.Manifest;
import sun.misc.Resource;
import sun.misc.URLClassPath;
import com.sun.xml.internal.bind.annotation.OverrideAnnotationOf;
/**
* Description:
* <br/>網(wǎng)站: <a href="http://www.crazyit.org">瘋狂Java聯(lián)盟</a>
* <br/>Copyright (C), 2001-2016, Yeeku.H.Lee
* <br/>This program is protected by copyright laws.
* <br/>Program Name:
* <br/>Date:
* @author Yeeku.H.Lee kongyeeku@163.com
* @version 1.0
*/
public class CompileClassLoader extends ClassLoader
{
// 讀取一個文件的內(nèi)容
private byte[] getBytes(String filename)
throws IOException
{
File file = new File(filename);
long len = file.length();
byte[] raw = new byte[(int)len];
try(
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file))
{
// 一次讀取class文件的全部二進制數(shù)據(jù)
int r = fin.read(raw);
if(r != len)
throw new IOException("無法讀取全部文件:"
+ r + " != " + len);
return raw;
}
}
// 定義編譯指定Java文件的方法
private boolean compile(String javaFile)
throws IOException
{
System.out.println("CompileClassLoader:正在編譯 "
+ javaFile + "...");
// 調(diào)用系統(tǒng)的javac命令
Process p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("javac " + javaFile);
try
{
// 其他線程都等待這個線程完成
p.waitFor();
}
catch(InterruptedException ie)
{
System.out.println(ie);
}
// 獲取javac線程的退出值
int ret = p.exitValue();
// 返回編譯是否成功
return ret == 0;
}
// 重寫ClassLoader的findClass方法
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String tmpName)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
System.out.println(tmpName);
Class clazz = null;
// 將包路徑中的點(.)替換成斜線(/);
String className = tmpName.replace("." , "/").replace("1" , "");
// 這里因為我是在eclipse里編輯的,而java文件統(tǒng)一放到src里,class文件統(tǒng)一放到了bin里, 所以我需要加前綴,
String javaFilename = "src/"+className + ".java";
String classFilename = "bin/"+className + ".class";
File javaFile = new File(javaFilename);
System.out.println(javaFile.getAbsolutePath());
File classFile = new File(classFilename);
// 當指定Java源文件存在,且class文件不存在、或者Java源文件
// 的修改時間比class文件修改時間更晚,重新編譯
if(javaFile.exists() && (!classFile.exists()
|| javaFile.lastModified() > classFile.lastModified()))
{
try
{
// 如果編譯失敗,或者該Class文件不存在
if(!compile(javaFilename) || !classFile.exists())
{
throw new ClassNotFoundException(
"ClassNotFoundExcetpion:" + javaFilename);
}
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 如果class文件存在,系統(tǒng)負責將該文件轉(zhuǎn)換成Class對象
if (classFile.exists())
{
try
{
// 將class文件的二進制數(shù)據(jù)讀入數(shù)組
byte[] raw = getBytes(classFilename);
// 調(diào)用ClassLoader的defineClass方法將二進制數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)換成Class對象
clazz = defineClass(className,raw,0,raw.length);
}
catch(IOException ie)
{
ie.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 如果clazz為null,表明加載失敗,則拋出異常
if(clazz == null)
{
throw new ClassNotFoundException(className);
}
return clazz;
}
// 定義一個主方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// 如果運行該程序時沒有參數(shù),即沒有目標類
args = new String[]{"Hello","java瘋狂講義w"};
// 第一個參數(shù)是需要運行的類
String progClass = args[0];
// 剩下的參數(shù)將作為運行目標類時的參數(shù),
// 將這些參數(shù)復制到一個新數(shù)組中
String[] progArgs = new String[args.length-1];
System.arraycopy(args , 1 , progArgs
, 0 , progArgs.length);
CompileClassLoader ccl = new CompileClassLoader();
// 加載需要運行的類
Class<?> clazz = ccl.loadClass(progClass);
// 獲取需要運行的類的主方法
Method main = clazz.getMethod("main" , (new String[0]).getClass());
Object[] argsArray = {progArgs};
main.invoke(null,argsArray);
}
}Output The result is
tes22t2 運行Hello的參數(shù):java瘋狂講義w
The break point is visible, and our custom findClass(String tmpName) method is not called.
當我們把
args = new String[]{"Hello","java瘋狂講義w"};
改為
args = new String[]{"Hello1","java瘋狂講義w"};
時,由于URLClassLoader并沒有找到被加載的類Hello1,所以最后會調(diào)用我們自定義的findClass方法.
當然,更規(guī)范的是把
Class<?> clazz = ccl.loadClass(progClass);
改為
Class<?> clazz = ccl.findClass(progClass);Output result:
Hello1/Users/liuxin/work/workspace2/learnJava/src/Hello.java tes22t2 運行Hello的參數(shù):java瘋狂講義w
Here we can see that if you want to dynamically load a class, you don’t need to overwrite it yourself. To write the findClass method, just need the following code:
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.net.URL;
import java.security.CodeSigner;
import java.security.CodeSource;
import java.util.jar.Manifest;
import sun.misc.Resource;
import sun.misc.URLClassPath;
import com.sun.xml.internal.bind.annotation.OverrideAnnotationOf;
public class CompileClassLoader extends ClassLoader
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// 如果運行該程序時沒有參數(shù),即沒有目標類
args = new String[]{"Hello","java瘋狂講義w"};
// 第一個參數(shù)是需要運行的類
String progClass = args[0];
// 剩下的參數(shù)將作為運行目標類時的參數(shù),
// 將這些參數(shù)復制到一個新數(shù)組中
String[] progArgs = new String[args.length-1];
System.arraycopy(args , 1 , progArgs
, 0 , progArgs.length);
CompileClassLoader ccl = new CompileClassLoader();
// 加載需要運行的類
Class<?> clazz = ccl.loadClass(progClass);
// 獲取需要運行的類的主方法
Method main = clazz.getMethod("main" , (new String[0]).getClass());
Object[] argsArray = {progArgs};
main.invoke(null,argsArray);
}
}
----------------輸出結(jié)果--------------------
tes22t2
運行Hello的參數(shù):java瘋狂講義w18.2.4 URLClassLoader class
java provides a URLClassLoader implementation class for ClassLoader, which is also the parent class of the system class loader and extension class loader (the parent here Class refers to the inheritance relationship between classes). URLClassLoader is powerful and can obtain binary files from local or remote hosts to load classes.
Here is an example
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.net.*;
/**
* Description:
* <br/>網(wǎng)站: <a href="http://www.crazyit.org">瘋狂Java聯(lián)盟</a>
* <br/>Copyright (C), 2001-2016, Yeeku.H.Lee
* <br/>This program is protected by copyright laws.
* <br/>Program Name:
* <br/>Date:
* @author Yeeku.H.Lee kongyeeku@163.com
* @version 1.0
*/
public class URLClassLoaderTest
{
private static Connection conn;
// 定義一個獲取數(shù)據(jù)庫連接方法
public static Connection getConn(String url ,
String user , String pass) throws Exception
{
if (conn == null)
{
// 創(chuàng)建一個URL數(shù)組
URL[] urls = {new URL(
"file:mysql-connector-java-5.1.30-bin.jar")};
// 以默認的ClassLoader作為父ClassLoader,創(chuàng)建URLClassLoader
URLClassLoader myClassLoader = new URLClassLoader(urls);
// 加載MySQL的JDBC驅(qū)動,并創(chuàng)建默認實例
Driver driver = (Driver)myClassLoader.
loadClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").newInstance();
// 創(chuàng)建一個設(shè)置JDBC連接屬性的Properties對象
Properties props = new Properties();
// 至少需要為該對象傳入user和password兩個屬性
props.setProperty("user" , user);
props.setProperty("password" , pass);
// 調(diào)用Driver對象的connect方法來取得數(shù)據(jù)庫連接
conn = driver.connect(url , props);
}
return conn;
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
Connection temconn = getConn("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"
, "root" , "password");
try{
String sql = "INSERT INTO `mybatis`.`users` (`NAME`, `age`) VALUES ('java8', '2')";
java.sql.PreparedStatement stmt = temconn.prepareStatement(sql);
stmt.execute();
stmt.close();
String sql2 = "select * from `mybatis`.`users`";
java.sql.PreparedStatement stmt2 = temconn.prepareStatement(sql2);
ResultSet rs = stmt2.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData m=rs.getMetaData();
//顯示列,表格的表頭
int columns=m.getColumnCount();
for(int i=1;i<=columns;i++)
{
System.out.print(m.getColumnName(i));
System.out.print("\t\t");
}
System.out.println();
//顯示表格內(nèi)容
while(rs.next())
{
for(int i=1;i<=columns;i++)
{
System.out.print(rs.getString(i));
System.out.print("\t\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
stmt2.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
temconn.close();
}
}
}So the previous dynamically loaded class can be used with URLClassLoader Rewritten as follows: (In order to understand the path, Hello.java was put into the learnJava package)
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
args = new String[]{"learnJava.Hello","java瘋狂講義w"};
String progClass = args[0];
String[] progArgs = new String[args.length-1];
System.arraycopy(args , 1 , progArgs, 0 , progArgs.length);
URL[] urls = {new URL("file:")};
Class<?> clazz = (new URLClassLoader(urls)).loadClass(progClass);
// 獲取需要運行的類的主方法
Method main = clazz.getMethod("main" , (new String[0]).getClass());
Object[] argsArray = {progArgs};
main.invoke(null,argsArray);
} 18.3 View class information through reflection
18.3 View class information through reflection
When will reflection be used?
 From To obtain information in Class, the methods are divided into the following categories:
From To obtain information in Class, the methods are divided into the following categories:
1. Get the constructor
2. Get the method
3. Get the attributes
The above three categories of methods, each category is divided into 4 methods, for example: ( Single, multiple) * (by permission, regardless of permission)
 4. Get annotations, this is too many:
4. Get annotations, this is too many:
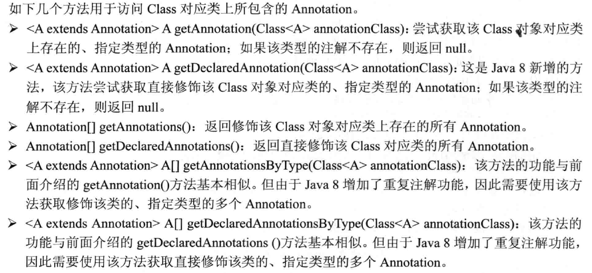 5. Get internal classes
5. Get internal classes
Class[] getDeclaredClasses():返回該Class對象對應類包含的全部內(nèi)部類
6.獲取外部類
Class[] getDeclaringClasse():返回該Class對象對應類所在的外部類
7.獲取接口
Class[] getInterfaces():返回該Class對象對應類所實現(xiàn)的全部接口
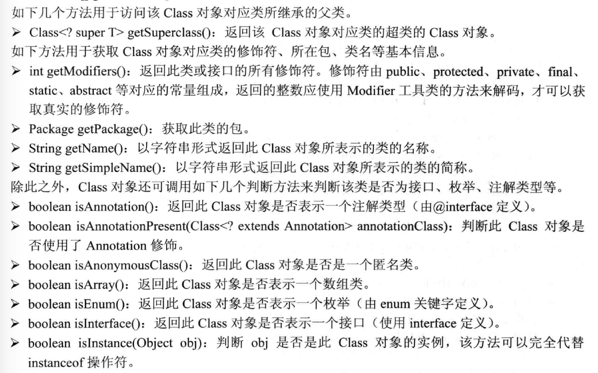
8.其他的如下:
例子:
// 定義可重復注解
@Repeatable(Annos.class)
@interface Anno {}
@Retention(value=RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Annos {
Anno[] value();
}
// 使用4個注解修飾該類
@SuppressWarnings(value="unchecked")
@Deprecated
// 使用重復注解修飾該類
@Anno
@Anno
public class ClassTest
{
// 為該類定義一個私有的構(gòu)造器
private ClassTest()
{
}
// 定義一個有參數(shù)的構(gòu)造器
public ClassTest(String name)
{
System.out.println("執(zhí)行有參數(shù)的構(gòu)造器");
}
// 定義一個無參數(shù)的info方法
public void info()
{
System.out.println("執(zhí)行無參數(shù)的info方法");
}
// 定義一個有參數(shù)的info方法
public void info(String str)
{
System.out.println("執(zhí)行有參數(shù)的info方法"
+ ",其str參數(shù)值:" + str);
}
// 定義一個測試用的內(nèi)部類
class Inner
{
}
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
// 下面代碼可以獲取ClassTest對應的Class
Class<?> clazz = ClassTest.class;
// 獲取該Class對象所對應類的全部構(gòu)造器
Constructor[] ctors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
System.out.println("ClassTest的全部構(gòu)造器如下:");
for (Constructor c : ctors)
{
System.out.println(c);
}
// 獲取該Class對象所對應類的全部public構(gòu)造器
Constructor[] publicCtors = clazz.getConstructors();
System.out.println("ClassTest的全部public構(gòu)造器如下:");
for (Constructor c : publicCtors)
{
System.out.println(c);
}
// 獲取該Class對象所對應類的全部public方法
Method[] mtds = clazz.getMethods();
System.out.println("ClassTest的全部public方法如下:");
for (Method md : mtds)
{
System.out.println(md);
}
// 獲取該Class對象所對應類的指定方法
System.out.println("ClassTest里帶一個字符串參數(shù)的info()方法為:"
+ clazz.getMethod("info" , String.class));
// 獲取該Class對象所對應類的上的全部注解
Annotation[] anns = clazz.getAnnotations();
System.out.println("ClassTest的全部Annotation如下:");
for (Annotation an : anns)
{
System.out.println(an);
}
System.out.println("該Class元素上的@SuppressWarnings注解為:"
+ Arrays.toString(clazz.getAnnotationsByType(SuppressWarnings.class)));
System.out.println("該Class元素上的@Anno注解為:"
+ Arrays.toString(clazz.getAnnotationsByType(Anno.class)));
// 獲取該Class對象所對應類的全部內(nèi)部類
Class<?>[] inners = clazz.getDeclaredClasses();
System.out.println("ClassTest的全部內(nèi)部類如下:");
for (Class c : inners)
{
System.out.println(c);
}
// 使用Class.forName方法加載ClassTest的Inner內(nèi)部類
Class inClazz = Class.forName("ClassTest$Inner");
// 通過getDeclaringClass()訪問該類所在的外部類
System.out.println("inClazz對應類的外部類為:" +
inClazz.getDeclaringClass());
System.out.println("ClassTest的包為:" + clazz.getPackage());
System.out.println("ClassTest的父類為:" + clazz.getSuperclass());
}
}18.3.3 java8 新增的方法參數(shù)反射

關(guān)于反射方法的參數(shù)的名字,這個比較麻煩,如下的例子

class Test
{
public void replace(String str, List<String> list){}
}
public class MethodParameterTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
// 獲取Tesy的類
Class<Test> clazz = Test.class;
// 獲取Test類的帶兩個參數(shù)的replace()方法
Method replace = clazz.getMethod("replace"
, String.class, List.class);
// 獲取指定方法的參數(shù)個數(shù)
System.out.println("replace方法參數(shù)個數(shù):" + replace.getParameterCount());
// 獲取replace的所有參數(shù)信息
Parameter[] parameters = replace.getParameters();
System.out.println((new File("")).getAbsolutePath());
int index = 1;
// 遍歷所有參數(shù)
for (Parameter p : parameters)
{
if (p.isNamePresent())
{
System.out.println("---第" + index++ + "個參數(shù)信息---");
System.out.println("參數(shù)名:" + p.getName());
System.out.println("形參類型:" + p.getType());
System.out.println("泛型類型:" + p.getParameterizedType());
}
}
}
}所以,上面這個例子在用eclipse編譯時,總是找不到參數(shù)名.沒找到設(shè)置的地方,只能用javac編譯
編譯命令如下: javac -parameters -encoding GBK -d . MethodParameterTest.java 因為瘋狂java講義里的源碼都是GBK編碼,而一般的電腦默認utf-8,所以需要指定編碼方式 運行: java MethodParameterTest ----------------------結(jié)果-------------------------- replace方法參數(shù)個數(shù):2 /Users/liuxin/work/workspace2/learnJava/src ---第1個參數(shù)信息--- 參數(shù)名:str 形參類型:class java.lang.String 泛型類型:class java.lang.String ---第2個參數(shù)信息--- 參數(shù)名:list 形參類型:interface java.util.List 泛型類型:java.util.List<java.lang.String>
18.4 使用反射生成并操作對象


例子:這個個別地方?jīng)]理解,但是這是一個反射的典型應用,需要好好理解
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
/**
* Description:
* <br/>網(wǎng)站: <a href="http://www.crazyit.org">瘋狂Java聯(lián)盟</a>
* <br/>Copyright (C), 2001-2016, Yeeku.H.Lee
* <br/>This program is protected by copyright laws.
* <br/>Program Name:
* <br/>Date:
* @author Yeeku.H.Lee kongyeeku@163.com
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ExtendedObjectPoolFactory
{
// 定義一個對象池,前面是對象名,后面是實際對象
private Map<String ,Object> objectPool = new HashMap<>();
private Properties config = new Properties();
// 從指定屬性文件中初始化Properties對象
public void init(String fileName)
{
// File tmpFi = new File(fileName);
// System.out.println(tmpFi.getAbsolutePath());
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName))
{
config.load(fis);
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("讀取" + fileName + "異常");
}
}
// 定義一個創(chuàng)建對象的方法,
// 該方法只要傳入一個字符串類名,程序可以根據(jù)該類名生成Java對象
private Object createObject(String clazzName)
throws InstantiationException
, IllegalAccessException , ClassNotFoundException
{
// 根據(jù)字符串來獲取對應的Class對象
Class<?> clazz =Class.forName(clazzName);
// 使用clazz對應類的默認構(gòu)造器創(chuàng)建實例
return clazz.newInstance();
}
// 該方法根據(jù)指定文件來初始化對象池,
// 它會根據(jù)配置文件來創(chuàng)建對象
public void initPool()throws InstantiationException
,IllegalAccessException , ClassNotFoundException
{
for (String name : config.stringPropertyNames())
{
// 每取出一對key-value對,如果key中不包含百分號(%)
// 這就標明是根據(jù)value來創(chuàng)建一個對象
// 調(diào)用createObject創(chuàng)建對象,并將對象添加到對象池中
if (!name.contains("%"))
{
objectPool.put(name ,
createObject(config.getProperty(name)));
}
}
}
// 該方法將會根據(jù)屬性文件來調(diào)用指定對象的setter方法
public void initProperty()throws InvocationTargetException
,IllegalAccessException,NoSuchMethodException
{
for (String name : config.stringPropertyNames())
{
// 每取出一對key-value對,如果key中包含百分號(%)
// 即可認為該key用于控制調(diào)用對象的setter方法設(shè)置值,
// %前半為對象名字,后半控制setter方法名
if (name.contains("%"))
{
// 將配置文件中key按%分割
String[] objAndProp = name.split("%");
// 取出調(diào)用setter方法的參數(shù)值
Object target = getObject(objAndProp[0]);
// 獲取setter方法名:set + "首字母大寫" + 剩下部分
String mtdName = "set" +
objAndProp[1].substring(0 , 1).toUpperCase()
+ objAndProp[1].substring(1);
// 通過target的getClass()獲取它實現(xiàn)類所對應的Class對象
Class<?> targetClass = target.getClass();
// 獲取希望調(diào)用的setter方法
Method mtd = targetClass.getMethod(mtdName , String.class);
// 通過Method的invoke方法執(zhí)行setter方法,
// 將config.getProperty(name)的值作為調(diào)用setter的方法的參數(shù)
mtd.invoke(target , config.getProperty(name));
}
}
}
public Object getObject(String name)
{
// 從objectPool中取出指定name對應的對象。
return objectPool.get(name);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
ExtendedObjectPoolFactory epf = new ExtendedObjectPoolFactory();
epf.init("src/extObj.txt");
epf.initPool();
epf.initProperty();
System.out.println(epf.getObject("a"));
}
}例子二:使用指定的構(gòu)造器來構(gòu)造對象.
public class CreateJFrame
{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
// 獲取JFrame對應的Class對象
Class<?> jframeClazz = Class.forName("javax.swing.JFrame");
// 獲取JFrame中帶一個字符串參數(shù)的構(gòu)造器
Constructor ctor = jframeClazz
.getConstructor(String.class);
// 調(diào)用Constructor的newInstance方法創(chuàng)建對象
Object obj = ctor.newInstance("測試窗口");
// 輸出JFrame對象
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
18.4.3 訪問成員變量值

例子:
class Person
{
private String name;
private int age;
public String toString()
{
return "Person[name:" + name +
" , age:" + age + " ]";
}
}
public class FieldTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
// 創(chuàng)建一個Person對象
Person p = new Person();
// 獲取Person類對應的Class對象
Class<Person> personClazz = Person.class;
// 獲取Person的名為name的成員變量
// 使用getDeclaredField()方法表明可獲取各種訪問控制符的成員變量
Field nameField = personClazz.getDeclaredField("name");
// 設(shè)置通過反射訪問該成員變量時取消訪問權(quán)限檢查
nameField.setAccessible(true);
// 調(diào)用set()方法為p對象的name成員變量設(shè)置值
nameField.set(p , "Yeeku.H.Lee");
// 獲取Person類名為age的成員變量
Field ageField = personClazz.getDeclaredField("age");
// 設(shè)置通過反射訪問該成員變量時取消訪問權(quán)限檢查
ageField.setAccessible(true);
// 調(diào)用setInt()方法為p對象的age成員變量設(shè)置值
ageField.setInt(p , 30);
System.out.println(p);
}
}用java.lang.reflect包下的Array類操作數(shù)組

例子:
public class ArrayTest1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
// 創(chuàng)建一個元素類型為String ,長度為10的數(shù)組
Object arr = Array.newInstance(String.class, 10);
// 依次為arr數(shù)組中index為5、6的元素賦值
Array.set(arr, 5, "瘋狂Java講義");
Array.set(arr, 6, "輕量級Java EE企業(yè)應用實戰(zhàn)");
// 依次取出arr數(shù)組中index為5、6的元素的值
Object book1 = Array.get(arr , 5);
Object book2 = Array.get(arr , 6);
// 輸出arr數(shù)組中index為5、6的元素
System.out.println(book1);
System.out.println(book2);
}
catch (Throwable e)
{
System.err.println(e);
}
}
}操作多維數(shù)組的例子:
public class ArrayTest2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
/*
創(chuàng)建一個三維數(shù)組。
根據(jù)前面介紹數(shù)組時講的:三維數(shù)組也是一維數(shù)組,
是數(shù)組元素是二維數(shù)組的一維數(shù)組,
因此可以認為arr是長度為3的一維數(shù)組
*/
Object arr = Array.newInstance(String.class, 3, 4, 10);
// 獲取arr數(shù)組中index為2的元素,該元素應該是二維數(shù)組
Object arrObj = Array.get(arr, 2);
// 使用Array為二維數(shù)組的數(shù)組元素賦值。二維數(shù)組的數(shù)組元素是一維數(shù)組,
// 所以傳入Array的set()方法的第三個參數(shù)是一維數(shù)組。
Array.set(arrObj , 2 , new String[]
{
"瘋狂Java講義",
"輕量級Java EE企業(yè)應用實戰(zhàn)"
});
// 獲取arrObj數(shù)組中index為3的元素,該元素應該是一維數(shù)組。
Object anArr = Array.get(arrObj, 3);
Array.set(anArr , 8 , "瘋狂Android講義");
// 將arr強制類型轉(zhuǎn)換為三維數(shù)組
String[][][] cast = (String[][][])arr;
// 獲取cast三維數(shù)組中指定元素的值
System.out.println(cast[2][3][8]);
System.out.println(cast[2][2][0]);
System.out.println(cast[2][2][1]);
}
}18.5 使用反射生成JDK動態(tài)代理
在java的java.lang.reflect包下提供了一個Proxy類和一個InvocationHandler接口,通過使用這個類和接口,可生成JDK動態(tài)代理或動態(tài)代理對象.

動態(tài)代理的例子:
interface Person
{
void walk();
void sayHello(String name);
}
class MyInvokationHandler implements InvocationHandler
{
/*
執(zhí)行動態(tài)代理對象的所有方法時,都會被替換成執(zhí)行如下的invoke方法
其中:
proxy:代表動態(tài)代理對象
method:代表正在執(zhí)行的方法
args:代表調(diào)用目標方法時傳入的實參。
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
{
System.out.println("----正在執(zhí)行的方法:" + method);
if (args != null)
{
System.out.println("下面是執(zhí)行該方法時傳入的實參為:");
for (Object val : args)
{
System.out.println(val);
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("調(diào)用該方法沒有實參!");
}
return null;
}
}
public class ProxyTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
// 創(chuàng)建一個InvocationHandler對象
InvocationHandler handler = new MyInvokationHandler();
// 使用指定的InvocationHandler來生成一個動態(tài)代理對象
Person p = (Person)Proxy.newProxyInstance(Person.class.getClassLoader()
, new Class[]{Person.class}, handler);
// 調(diào)用動態(tài)代理對象的walk()和sayHello()方法
p.walk();
p.sayHello("孫悟空");
}
}18.5.2 動態(tài)代理和AOP
一個AOP的實現(xiàn)例子:
public interface Dog
{
// info方法聲明
void info();
// run方法聲明
void run();
}public class GunDog implements Dog
{
// 實現(xiàn)info()方法,僅僅打印一個字符串
public void info()
{
System.out.println("我是一只獵狗");
}
// 實現(xiàn)run()方法,僅僅打印一個字符串
public void run()
{
System.out.println("我奔跑迅速");
}
}public class DogUtil
{
// 第一個攔截器方法
public void method1()
{
System.out.println("=====模擬第一個通用方法=====");
}
// 第二個攔截器方法
public void method2()
{
System.out.println("=====模擬通用方法二=====");
}
}public class MyInvokationHandler implements InvocationHandler
{
// 需要被代理的對象
private Object target;
public void setTarget(Object target)
{
this.target = target;
}
// 執(zhí)行動態(tài)代理對象的所有方法時,都會被替換成執(zhí)行如下的invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Exception
{
DogUtil du = new DogUtil();
// 執(zhí)行DogUtil對象中的method1。
du.method1();
// 以target作為主調(diào)來執(zhí)行method方法
Object result = method.invoke(target , args);
// 執(zhí)行DogUtil對象中的method2。
du.method2();
return result;
}
}public class MyProxyFactory
{
// 為指定target生成動態(tài)代理對象
public static Object getProxy(Object target)
throws Exception
{
// 創(chuàng)建一個MyInvokationHandler對象
MyInvokationHandler handler =
new MyInvokationHandler();
// 為MyInvokationHandler設(shè)置target對象
handler.setTarget(target);
// 創(chuàng)建、并返回一個動態(tài)代理
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader()
, target.getClass().getInterfaces() , handler);
}
}public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
// 創(chuàng)建一個原始的GunDog對象,作為target
Dog target = new GunDog();
// 以指定的target來創(chuàng)建動態(tài)代理
Dog dog = (Dog)MyProxyFactory.getProxy(target);
dog.info();
dog.run();
}
}--------------結(jié)果----------------- =====模擬第一個通用方法===== 我是一只獵狗 =====模擬通用方法二===== =====模擬第一個通用方法===== 我奔跑迅速 =====模擬通用方法二=====
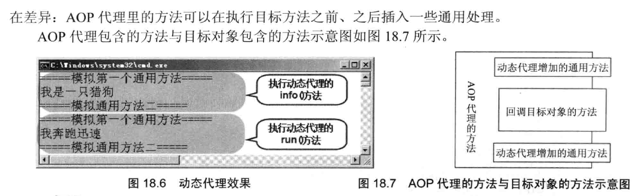
18.6 反射和泛型
例子1:泛型工廠類
public class CrazyitObjectFactory2
{
public static <T> T getInstance(Class<T> cls)
{
try
{
return cls.newInstance();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 獲取實例后無須類型轉(zhuǎn)換
Date d = CrazyitObjectFactory2.getInstance(Date.class);
JFrame f = CrazyitObjectFactory2.getInstance(JFrame.class);
}
}例子2:使用反射來獲取泛型信息
public class GenericTest
{
private Map<String , Integer> score;
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
Class<GenericTest> clazz = GenericTest.class;
Field f = clazz.getDeclaredField("score");
// 直接使用getType()取出的類型只對普通類型的成員變量有效
Class<?> a = f.getType();
// 下面將看到僅輸出java.util.Map
System.out.println("score的類型是:" + a);
// 獲得成員變量f的泛型類型
Type gType = f.getGenericType();
// 如果gType類型是ParameterizedType對象
if(gType instanceof ParameterizedType)
{
// 強制類型轉(zhuǎn)換
ParameterizedType pType = (ParameterizedType)gType;
// 獲取原始類型
Type rType = pType.getRawType();
System.out.println("原始類型是:" + rType);
// 取得泛型類型的泛型參數(shù)
Type[] tArgs = pType.getActualTypeArguments();
System.out.println("泛型信息是:");
for (int i = 0; i < tArgs.length; i++)
{
System.out.println("第" + i + "個泛型類型是:" + tArgs[i]);
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("獲取泛型類型出錯!");
}
}
}
Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)




