 Database
Database
 Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial
 Use the mysql_query() function to execute SQL statements (PHP method 3 for operating MySQL database)
Use the mysql_query() function to execute SQL statements (PHP method 3 for operating MySQL database)
Use the mysql_query() function to execute SQL statements (PHP method 3 for operating MySQL database)
Apr 20, 2017 pm 01:48 PM
How PHP operates MySQL database-functions that execute SQL statements
In our daily PHP development work, when we want to When getting data from the database, after PHP connects to the database, the next step is to select the database. Then to operate the database table, we need to use SQL statements!
Recommended related mysql video tutorials: "mysql tutorial"
In the previous two articles "How to operate MySQL database with PHP - how to choose Database file ", "How to operate MySQL database with PHP - using the mysql_connect() function to connect to the database" introduces how to connect to the database and select the database, so today we will introduce how to execute SQL statements.
To operate on tables in the database, we usually use the mysql_query() function to execute SQL statements. The syntax format of this function is as follows:
mysql_query(string query[,resource link_identifier])
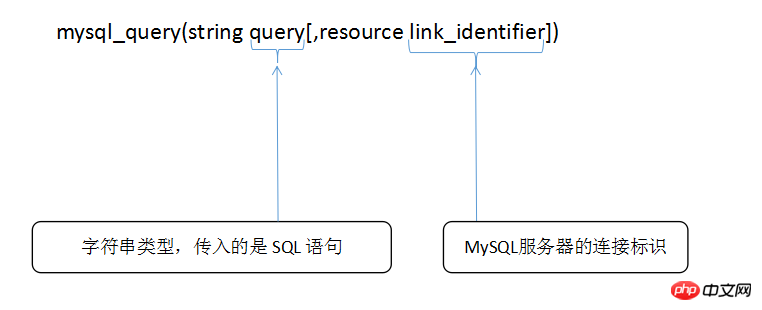
mysql_query() function is a special function of the instruction. All SQL statements are executed through it and the result set is returned.
Note:
The SQL statement executed in the mysql_query function should not end with a semicolon ";".
mysql_query() returns a resource identifier only for SELECT, SHOW, EXPLAIN or DESCRIBE statements, or FALSE if the query was executed incorrectly.
For other types of SQL statements, mysql_query() returns TRUE when executed successfully and FALSE when an error occurs.
A non-FALSE return value means the query is valid and can be executed by the server. This does not say anything about the number of rows affected or returned. It's possible that a query executed successfully but did not affect or return any rows.
Note:
The mysql_unbuffered_query() function sends a SQL query statement to MySQL, but does not obtain and cache the result set. It does not automatically obtain and cache the result set like the mysql_query() function. On the one hand, this will save considerable memory when processing large result sets. On the other hand, the result set can be operated immediately after obtaining the first row. , without waiting for the entire SQL statement to be executed.
The following uses the table tb_nember in the database as an example to illustrate the usage of common SQL statements.
For example, the code to execute a SQL statement to add member records is as follows:
$result = mysql_query("insert into tb_nember values('tm','111','tm@tmsoft')",$link);For example, the code to execute a SQL statement to modify members is as follows:
$result = mysql_query("update tb_nember set user= '純凈水',pwd ='1025'where user = 'tm'",$link);For example, to execute a The code of the SQL statement to delete member records is as follows:
$result = mysql_query("delete from tb_nember where user = '純凈水'",$link);For example, the code to execute a SQL statement to query member records is as follows:
$result = mysql_query("select * from tb_nember",$link);For example, to execute an SQL statement to display the structure of the member information table The code is as follows:
$result = mysql_query("DESC tb_nember");Instructions:
Before executing the SQL statements listed above, you need to connect to the MySQL server and select The database and its implementation methods have been introduced in detail in the previous articles. Friends who don’t know can check it out. I won’t go into details here!
The above creates SQL statements through each instance and assigns them to the variable $result. PHP provides some functions to process the query result $result, such as mysql_fetch_array() function, mysql_fetch_object() function and mysql_fetch_row() function, etc. In order to let everyone understand these functions, we will start with the mysql_fetch_array() function below. , read specifically "How to operate MySQL database with PHP - use the mysql_fetch_array() function to obtain information in the array result set"!
The above is the detailed content of Use the mysql_query() function to execute SQL statements (PHP method 3 for operating MySQL database). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Using std::chrono in C
Jul 15, 2025 am 01:30 AM
Using std::chrono in C
Jul 15, 2025 am 01:30 AM
std::chrono is used in C to process time, including obtaining the current time, measuring execution time, operation time point and duration, and formatting analysis time. 1. Use std::chrono::system_clock::now() to obtain the current time, which can be converted into a readable string, but the system clock may not be monotonous; 2. Use std::chrono::steady_clock to measure the execution time to ensure monotony, and convert it into milliseconds, seconds and other units through duration_cast; 3. Time point (time_point) and duration (duration) can be interoperable, but attention should be paid to unit compatibility and clock epoch (epoch)
 How does PHP handle Environment Variables?
Jul 14, 2025 am 03:01 AM
How does PHP handle Environment Variables?
Jul 14, 2025 am 03:01 AM
ToaccessenvironmentvariablesinPHP,usegetenv()orthe$_ENVsuperglobal.1.getenv('VAR_NAME')retrievesaspecificvariable.2.$_ENV['VAR_NAME']accessesvariablesifvariables_orderinphp.iniincludes"E".SetvariablesviaCLIwithVAR=valuephpscript.php,inApach
 Why We Comment: A PHP Guide
Jul 15, 2025 am 02:48 AM
Why We Comment: A PHP Guide
Jul 15, 2025 am 02:48 AM
PHPhasthreecommentstyles://,#forsingle-lineand/.../formulti-line.Usecommentstoexplainwhycodeexists,notwhatitdoes.MarkTODO/FIXMEitemsanddisablecodetemporarilyduringdebugging.Avoidover-commentingsimplelogic.Writeconcise,grammaticallycorrectcommentsandu
 mysql common table expression (cte) example
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:28 AM
mysql common table expression (cte) example
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:28 AM
CTE is a temporary result set in MySQL used to simplify complex queries. It can be referenced multiple times in the current query, improving code readability and maintenance. For example, when looking for the latest orders for each user in the orders table, you can first obtain the latest order date for each user through the CTE, and then associate it with the original table to obtain the complete record. Compared with subqueries, the CTE structure is clearer and the logic is easier to debug. Usage tips include explicit alias, concatenating multiple CTEs, and processing tree data with recursive CTEs. Mastering CTE can make SQL more elegant and efficient.
 PHP header redirect not working
Jul 14, 2025 am 01:59 AM
PHP header redirect not working
Jul 14, 2025 am 01:59 AM
Reasons and solutions for the header function jump failure: 1. There is output before the header, and all pre-outputs need to be checked and removed or ob_start() buffer is used; 2. The failure to add exit causes subsequent code interference, and exit or die should be added immediately after the jump; 3. The path error should be used to ensure correctness by using absolute paths or dynamic splicing; 4. Server configuration or cache interference can be tried to clear the cache or replace the environment test.
 PHP prepared statement get result
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:12 AM
PHP prepared statement get result
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:12 AM
The method of using preprocessing statements to obtain database query results in PHP varies from extension. 1. When using mysqli, you can obtain the associative array through get_result() and fetch_assoc(), which is suitable for modern environments; 2. You can also use bind_result() to bind variables, which is suitable for situations where there are few fields and fixed structures, and it is good compatibility but there are many fields when there are many fields; 3. When using PDO, you can obtain the associative array through fetch (PDO::FETCH_ASSOC), or use fetchAll() to obtain all data at once, so the interface is unified and the error handling is clearer; in addition, you need to pay attention to parameter type matching, execution of execute(), timely release of resources and enable error reports.
 PHP check if a string starts with a specific string
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:44 AM
PHP check if a string starts with a specific string
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:44 AM
In PHP, you can use a variety of methods to determine whether a string starts with a specific string: 1. Use strncmp() to compare the first n characters. If 0 is returned, the beginning matches and is not case sensitive; 2. Use strpos() to check whether the substring position is 0, which is case sensitive. Stripos() can be used instead to achieve case insensitive; 3. You can encapsulate the startsWith() or str_starts_with() function to improve reusability; in addition, it is necessary to note that empty strings return true by default, encoding compatibility and performance differences, strncmp() is usually more efficient.
 Choosing appropriate data types for columns in MySQL tables
Jul 15, 2025 am 02:25 AM
Choosing appropriate data types for columns in MySQL tables
Jul 15, 2025 am 02:25 AM
WhensettingupMySQLtables,choosingtherightdatatypesiscrucialforefficiencyandscalability.1)Understandthedataeachcolumnwillstore—numbers,text,dates,orflags—andchooseaccordingly.2)UseCHARforfixed-lengthdatalikecountrycodesandVARCHARforvariable-lengthdata





