Detailed introduction to java reflection mechanism
Nov 25, 2019 pm 02:48 PM
This article is introduced in the Introduction to Java Programming column to introduce the reflection mechanism in Java in detail, hoping to help students who do not understand this mechanism.
java reflection
The mechanism is in the running state. For any class, all properties and methods (including private ones) of this class can be known; for any object , can call any of its methods and properties; this function of dynamically obtaining information and dynamically calling object methods is called Java's reflection mechanism.
Purpose:
Determine the class to which any object belongs at runtime.
Construct an object of any class at runtime.
Judge the member variables and methods of any class at runtime.
Call the method of any object at runtime.
Generate dynamic proxy.
Reflection related classes
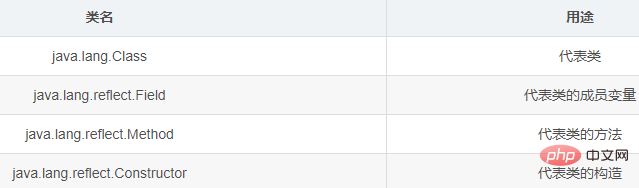
class class
obtained in Java program Class objects usually have the following three methods:
1. Use the forName(String clazzName) static method of the Class class. This method requires passing in a string parameter, the value of which is the fully qualified name of a class (the complete package name must be added).
2. Call the class attribute of a certain class to obtain the Class object corresponding to the class.
3. Call the getClass() method of an object. This method is a method in the java.lang.Object class.
Field
Field[] allFields = class2.getDeclaredFields();//獲取class對(duì)象的所有屬性
Field[] publicFields = class2.getFields();//獲取class對(duì)象的public屬性
Field ageField = class2.getDeclaredField("age");//獲取class指定屬性,可以獲得私有屬性
Field desField = class2.getField("des");//獲取class指定的public屬性Method
Method[] methods = class2.getDeclaredMethods();//獲取class對(duì)象的所有聲明方法
Method[] allMethods = class2.getMethods();//獲取class對(duì)象的所有public方法 包括父類的方法
Method method = class2.getMethod("info", String.class);//返回次Class對(duì)象對(duì)應(yīng)類的、帶指定形參列表的public方法
Method declaredMethod = class2.getDeclaredMethod("info", String.class);//返回次Class對(duì)象對(duì)應(yīng)類的、
帶指定形參列表的方法Constructor
Constructor<?>[] allConstructors = class2.getDeclaredConstructors();//獲取class對(duì)象的所有聲明構(gòu)造函數(shù) Constructor<?>[] publicConstructors = class2.getConstructors();//獲取class對(duì)象public構(gòu)造函數(shù) Constructor<?> constructor = class2.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);//獲取指定聲明構(gòu)造函數(shù) Constructor publicConstructor = class2.getConstructor(String.class);//獲取指定聲明的public構(gòu)造函數(shù)
Generating instance objects through reflection
1. Use the newInstance() method of the Class object to create an instance of the corresponding class of the Class object. This method requires that the corresponding class of the Class object has a default constructor, and when the newInstance() method is executed, the default constructor is actually used to create an instance of the class.
2. First use the Class object to obtain the specified Constructor object, and then call the newInstance() method of the Constructor object to create an instance of the corresponding class of the Class object. This way you can choose to use a specified constructor to create the instance.
Calling method
1. Obtain the specified method through the getMethods() method or getMethod() method of the Class object and return the Method array or object.
2. Call the Object invoke(Object obj, Object… args) method in the Method object. The first parameter corresponds to the instance object calling the method, and the second parameter corresponds to the parameters of the method.
Example code:
What is reflection?
package am;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
import javax.activation.FileDataSource;
/**
* 反射是什么:
* java中的反射:就是在類的加載過程中,發(fā)現(xiàn)類的屬性和方法構(gòu)造方法等信息??梢垣@得類的屬性值,可以調(diào)用類的方法。
*
*
* 反射獲得類的對(duì)象。
*
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 通過反射,獲取類的對(duì)象。
Object obj = create("am.Foo");;
Foo foo = (Foo)obj;
System.out.println(foo.a);
double dou = foo.show(12, "hello");
System.out.println(dou);
System.out.println("======================================");
// 獲得類的屬性
showField(obj);
System.out.println("======================================");
double a = (double)getFieldValue(obj, "b");
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println("========================================");
// 通過反射調(diào)用方法。
Object ob = getMethodValue(obj,"show",new Class[]{int.class,String.class},new Object[]{23,"abc"});
double douValue = (double)ob;
System.out.println(douValue);
}
//通過反射調(diào)用方法,哪個(gè)對(duì)象,什么名稱,參數(shù)類型,參數(shù)值
public static Object getMethodValue(Object obj,String method,Class[] paramType,Object[] param)
throws Exception{
Class cla = obj.getClass();
Method me = cla.getDeclaredMethod(method, paramType);
Object o = me.invoke(obj, param);
return o;
}
// 獲取類的屬性值:
public static Object getFieldValue(Object obj,String name)throws Exception{
Class cla = obj.getClass();// 獲取字節(jié)碼對(duì)象。
Field field = cla.getDeclaredField(name);// 通過屬性的名稱。獲取當(dāng)前屬性。
Object result = field.get(obj);
return result;
}
// 通過反射,可以獲得類的屬性信息以及方法信息。
public static void showField(Object obj){
// java中對(duì)屬性類。 Field 方法類:Method
Class cla = obj.getClass();
System.out.println("獲取類名:"+cla.getName());
System.out.println("======================================");
// 獲取類的屬性:
Field[] fields = cla.getDeclaredFields();// 獲取公開的屬性。
for(Field field : fields){
System.out.println("獲取類的屬性類型"+field.getType());
System.out.println("獲取類的屬性名稱:"+field.getName());
}
System.out.println("======================================");
// 獲取類的方法。
Method[] methods = cla.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods){
System.out.println("獲取方法的返回值類型:"+method.getReturnType());
System.out.println("獲取方法名稱:"+method.getName());
System.out.println("獲取方法的參數(shù)類型。"+Arrays.toString(method.getParameterTypes()));
}
System.out.println("=======================================");
// 獲取類的構(gòu)造方法:
Constructor[] cons = cla.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor con : cons){
System.out.println("構(gòu)造方法的名字:"+con.getName());
System.out.println("構(gòu)造方法參數(shù)類型:"+Arrays.toString(con.getParameterTypes()));
}
}
// 如何反射類的實(shí)例。
public static Object create(String name) throws Exception{
// 反射的方法。Class.forName();
Class cla = Class.forName(name);
// 如何獲得Object類型對(duì)象。
Object obj = cla.newInstance();
return obj;
}
}
// 模擬類。
class Foo{
int a = 10;
double b = 20;
public double show(int p,String str){
System.out.println("調(diào)用方法傳入的值是:"+str);
return a+b+p;
}
public Foo(){
}
public Foo(int a,int b){
}
}More related learning video recommendations: java video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to java reflection mechanism. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
To correctly handle JDBC transactions, you must first turn off the automatic commit mode, then perform multiple operations, and finally commit or rollback according to the results; 1. Call conn.setAutoCommit(false) to start the transaction; 2. Execute multiple SQL operations, such as INSERT and UPDATE; 3. Call conn.commit() if all operations are successful, and call conn.rollback() if an exception occurs to ensure data consistency; at the same time, try-with-resources should be used to manage resources, properly handle exceptions and close connections to avoid connection leakage; in addition, it is recommended to use connection pools and set save points to achieve partial rollback, and keep transactions as short as possible to improve performance.
 How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
Use classes in the java.time package to replace the old Date and Calendar classes; 2. Get the current date and time through LocalDate, LocalDateTime and LocalTime; 3. Create a specific date and time using the of() method; 4. Use the plus/minus method to immutably increase and decrease the time; 5. Use ZonedDateTime and ZoneId to process the time zone; 6. Format and parse date strings through DateTimeFormatter; 7. Use Instant to be compatible with the old date types when necessary; date processing in modern Java should give priority to using java.timeAPI, which provides clear, immutable and linear
 Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Pre-formanceTartuptimeMoryusage, Quarkusandmicronautleadduetocompile-Timeprocessingandgraalvsupport, Withquarkusoftenperforminglightbetterine ServerLess scenarios.2.Thyvelopecosyste,
 Understanding Network Ports and Firewalls
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:40 AM
Understanding Network Ports and Firewalls
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:40 AM
Networkportsandfirewallsworktogethertoenablecommunicationwhileensuringsecurity.1.Networkportsarevirtualendpointsnumbered0–65535,withwell-knownportslike80(HTTP),443(HTTPS),22(SSH),and25(SMTP)identifyingspecificservices.2.PortsoperateoverTCP(reliable,c
 How does garbage collection work in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 01:55 PM
How does garbage collection work in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 01:55 PM
Java's garbage collection (GC) is a mechanism that automatically manages memory, which reduces the risk of memory leakage by reclaiming unreachable objects. 1.GC judges the accessibility of the object from the root object (such as stack variables, active threads, static fields, etc.), and unreachable objects are marked as garbage. 2. Based on the mark-clearing algorithm, mark all reachable objects and clear unmarked objects. 3. Adopt a generational collection strategy: the new generation (Eden, S0, S1) frequently executes MinorGC; the elderly performs less but takes longer to perform MajorGC; Metaspace stores class metadata. 4. JVM provides a variety of GC devices: SerialGC is suitable for small applications; ParallelGC improves throughput; CMS reduces
 Using HTML `input` Types for User Data
Aug 03, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Using HTML `input` Types for User Data
Aug 03, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Choosing the right HTMLinput type can improve data accuracy, enhance user experience, and improve usability. 1. Select the corresponding input types according to the data type, such as text, email, tel, number and date, which can automatically checksum and adapt to the keyboard; 2. Use HTML5 to add new types such as url, color, range and search, which can provide a more intuitive interaction method; 3. Use placeholder and required attributes to improve the efficiency and accuracy of form filling, but it should be noted that placeholder cannot replace label.
 Comparing Java Build Tools: Maven vs. Gradle
Aug 03, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Comparing Java Build Tools: Maven vs. Gradle
Aug 03, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Gradleisthebetterchoiceformostnewprojectsduetoitssuperiorflexibility,performance,andmoderntoolingsupport.1.Gradle’sGroovy/KotlinDSLismoreconciseandexpressivethanMaven’sverboseXML.2.GradleoutperformsMaveninbuildspeedwithincrementalcompilation,buildcac
 go by example defer statement explained
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:26 AM
go by example defer statement explained
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:26 AM
defer is used to perform specified operations before the function returns, such as cleaning resources; parameters are evaluated immediately when defer, and the functions are executed in the order of last-in-first-out (LIFO); 1. Multiple defers are executed in reverse order of declarations; 2. Commonly used for secure cleaning such as file closing; 3. The named return value can be modified; 4. It will be executed even if panic occurs, suitable for recovery; 5. Avoid abuse of defer in loops to prevent resource leakage; correct use can improve code security and readability.






