
Redis has become the standard cache for Internet companies due to its excellent features of high performance and lightweight. Sometimes we want to add some custom commands, mainly in scenarios where Redis is heavily used. , like rush buying scenarios, it is necessary to ensure the transactionality of multiple Redis commands. If there is no good atomicity guarantee, data inconsistency problems may easily occur.
Although the official transaction plan is given, if it is necessary to make a judgment based on the return value of a certain command before proceeding to the next step, the transaction plan will not be able to cope with it.
Today we will use a practical case to describe how to add a Redis command. This command is mainly used in anti-swipe scenarios:
It is often necessary to ban a certain IP or a certain user for a period of time. If this command is not used, the solution is as follows:
First incr, and then determine whether it is 1. If it is 1, set the expiration time. It can be seen that if the first client that initiates the incr request hangs up during high concurrency, the key will not expire.
The command to be written today is used to ensure this transaction. The server side ensures that if the value of the key is 1, the expiration time is set.
The command usage is as follows:
incexpire key expireTime maxNum
key: the key to be processed
expireTime: expiration time, in seconds. If you write 10, it means that the key will expire in 10 seconds. ;
maxNum: Indicates the amount to which it will increase until it stops increasing. If it is set to 10, the maximum value returned is 11. Returning 11 means it has been exceeded;
2. Writing commands
1. Download the redis code
The Redis version used in this article is 3.2.11;
Download the code and cut to the 3.2.11 branch
git clone https://github.com/antirez/redis
2.Writing and adding Command code
1) Add a new command to the redisCommandTable structure in src/server.c
struct redisCommand redisCommandTable[] = {redisCommandTable is an array, each item represents a redis command, and the first one represents a command The second one is the actual processing function, and the third one is the number of parameters. The others will not be discussed in detail.
2) Add a function declaration in src/server.h:
void incrExpireCommand(client *c);
3) Then add a file as ljh.c (name it yourself) and add the following code:
#include "server.h"
4) Add a new file ljh.o in src/Makefile
REDIS_SERVER_OBJ=adlist.o quicklist.o ae.o anet.o dict.o server.o sds.o zmalloc.o lzf_c.o lzf_d.o pqsort.o zipmap.o sha1.o ziplist.o release.o networking
The execution effect is as follows
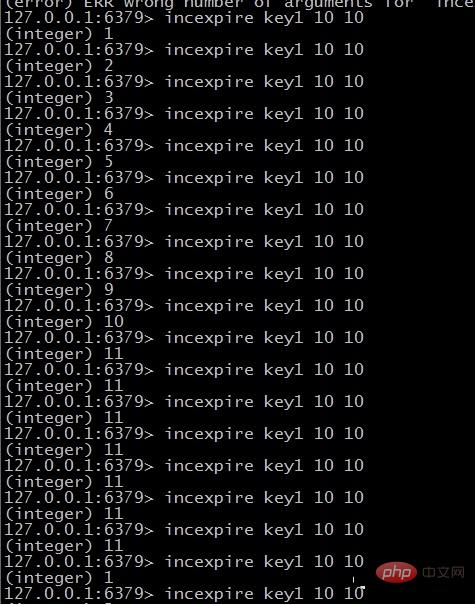
You can see that after key1 is increased to 11 It no longer increases, and after 10 seconds, it becomes 1 again.
Finally, we still have to ask ourselves whether it is necessary to add Redis commands in our scenario. If necessary, we must grasp the responsibilities between each layer and do not let Redis end up processing business; generally It is said that the middleware layer generally handles more general functions. The lower layers should be more stable and the less changes are, the normal situation is.
For more related knowledge, please pay attention to redis introductory tutorialcolumn
The above is the detailed content of How to add redis command. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Redis: A Comparison to Traditional Database Servers
May 07, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Redis: A Comparison to Traditional Database Servers
May 07, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Redis is superior to traditional databases in high concurrency and low latency scenarios, but is not suitable for complex queries and transaction processing. 1.Redis uses memory storage, fast read and write speed, suitable for high concurrency and low latency requirements. 2. Traditional databases are based on disk, support complex queries and transaction processing, and have strong data consistency and persistence. 3. Redis is suitable as a supplement or substitute for traditional databases, but it needs to be selected according to specific business needs.
 How to limit user resources in Linux? How to configure ulimit?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to limit user resources in Linux? How to configure ulimit?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Linux system restricts user resources through the ulimit command to prevent excessive use of resources. 1.ulimit is a built-in shell command that can limit the number of file descriptors (-n), memory size (-v), thread count (-u), etc., which are divided into soft limit (current effective value) and hard limit (maximum upper limit). 2. Use the ulimit command directly for temporary modification, such as ulimit-n2048, but it is only valid for the current session. 3. For permanent effect, you need to modify /etc/security/limits.conf and PAM configuration files, and add sessionrequiredpam_limits.so. 4. The systemd service needs to set Lim in the unit file
 Is Redis Primarily a Database?
May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Is Redis Primarily a Database?
May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Redis is primarily a database, but it is more than just a database. 1. As a database, Redis supports persistence and is suitable for high-performance needs. 2. As a cache, Redis improves application response speed. 3. As a message broker, Redis supports publish-subscribe mode, suitable for real-time communication.
 Redis: Beyond SQL - The NoSQL Perspective
May 08, 2025 am 12:25 AM
Redis: Beyond SQL - The NoSQL Perspective
May 08, 2025 am 12:25 AM
Redis goes beyond SQL databases because of its high performance and flexibility. 1) Redis achieves extremely fast read and write speed through memory storage. 2) It supports a variety of data structures, such as lists and collections, suitable for complex data processing. 3) Single-threaded model simplifies development, but high concurrency may become a bottleneck.
 Redis: Unveiling Its Purpose and Key Applications
May 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Redis: Unveiling Its Purpose and Key Applications
May 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Redisisanopen-source,in-memorydatastructurestoreusedasadatabase,cache,andmessagebroker,excellinginspeedandversatility.Itiswidelyusedforcaching,real-timeanalytics,sessionmanagement,andleaderboardsduetoitssupportforvariousdatastructuresandfastdataacces
 Steps and examples for building a dynamic PHP website with PhpStudy
May 16, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Steps and examples for building a dynamic PHP website with PhpStudy
May 16, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
The steps to build a dynamic PHP website using PhpStudy include: 1. Install PhpStudy and start the service; 2. Configure the website root directory and database connection; 3. Write PHP scripts to generate dynamic content; 4. Debug and optimize website performance. Through these steps, you can build a fully functional dynamic PHP website from scratch.
 Laravel Page Cache Policy
May 29, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
Laravel Page Cache Policy
May 29, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
Laravel's page caching strategy can significantly improve website performance. 1) Use cache helper functions to implement page caching, such as the Cache::remember method. 2) Select the appropriate cache backend, such as Redis. 3) Pay attention to data consistency issues, and you can use fine-grained caches or event listeners to clear the cache. 4) Further optimization is combined with routing cache, view cache and cache tags. By rationally applying these strategies, website performance can be effectively improved.
 Laravel Cache Optimization: Redis and Memcached Configuration Guide
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:30 PM
Laravel Cache Optimization: Redis and Memcached Configuration Guide
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:30 PM
In Laravel, Redis and Memcached can be used to optimize caching policies. 1) To configure Redis or Memcached, you need to set connection parameters in the .env file. 2) Redis supports a variety of data structures and persistence, suitable for complex scenarios and scenarios with high risk of data loss; Memcached is suitable for quick access to simple data. 3) Use Cachefacade to perform unified cache operations, and the underlying layer will automatically select the configured cache backend.






