How are arrays in C language allocated in memory?
Jul 07, 2020 am 09:41 AMThe method of allocating C language arrays in memory: First, the corresponding header file is the iostream stream responsible for input and output; then create an array in the main function, and use the cout statement to output the location of each element in the memory. Address; finally click the Run button to compile, link, and generate an executable file.

How to allocate C language arrays in memory:
1. First, we open the C language compiler, You can choose software such as Visual Studio, Code::Blocks or Dev-C. Here is Visual Studio as an example. Wait for the entire program to be completely loaded into the memory
2. Due to VS It is managed through solutions, so first create a new solution. If there is an existing solution, you can continue to use it, and then create a new project. Since we are debugging a command line program, we need to select the Windows console here. Application
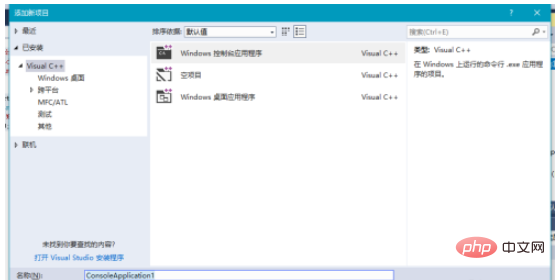
3. After ensuring that the project name is correct, click the OK button. You will see that we have successfully created a project, and then right-click in the project list to add A C file, as shown in the figure after adding it
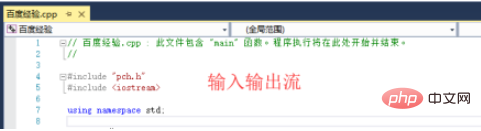
4. First, we include the corresponding header file, which is the iostream stream responsible for input and output, and set the default The namespace is std
5. Then in the main function, create an array. Here we take a double-precision array as an example. The length is 10 and assign initial values ??to it. , since the array name identifies the address of the head pointer, if you do not use the array name, you need to use the pointer form to create other types of variables.
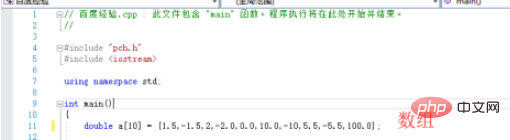
6. Then we use cout The statement outputs the address of each element in the memory respectively. Note that you need to add the address & operator. If you are using C language, you can use the printf function to output
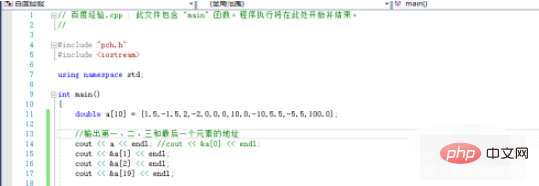
7. Confirm After the code is correct, click the run button to compile, link, and generate an executable file. After a moment, we see that the output result is a hexadecimal address value. The address of each two consecutive array elements differs by 8, which means that it is in 64 Each double type data is stored in 8 bytes on the Win10 platform.

##Related learning recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of How are arrays in C language allocated in memory?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
The performance comparison of PHP array key value flipping methods shows that the array_flip() function performs better than the for loop in large arrays (more than 1 million elements) and takes less time. The for loop method of manually flipping key values ??takes a relatively long time.
 Application of PHP array grouping function in data sorting
May 04, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
Application of PHP array grouping function in data sorting
May 04, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
PHP's array_group_by function can group elements in an array based on keys or closure functions, returning an associative array where the key is the group name and the value is an array of elements belonging to the group.
 MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The main reasons for MySQL installation failure are: 1. Permission issues, you need to run as an administrator or use the sudo command; 2. Dependencies are missing, and you need to install relevant development packages; 3. Port conflicts, you need to close the program that occupies port 3306 or modify the configuration file; 4. The installation package is corrupt, you need to download and verify the integrity; 5. The environment variable is incorrectly configured, and the environment variables must be correctly configured according to the operating system. Solve these problems and carefully check each step to successfully install MySQL.
 The role of PHP array grouping function in finding duplicate elements
May 05, 2024 am 09:21 AM
The role of PHP array grouping function in finding duplicate elements
May 05, 2024 am 09:21 AM
PHP's array_group() function can be used to group an array by a specified key to find duplicate elements. This function works through the following steps: Use key_callback to specify the grouping key. Optionally use value_callback to determine grouping values. Count grouped elements and identify duplicates. Therefore, the array_group() function is very useful for finding and processing duplicate elements.
 Can arrays be used as function parameters?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
Can arrays be used as function parameters?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
Yes, in many programming languages, arrays can be used as function parameters, and the function will perform operations on the data stored in it. For example, the printArray function in C++ can print the elements in an array, while the printArray function in Python can traverse the array and print its elements. Modifications made to the array by these functions are also reflected in the original array in the calling function.
 What are the cross-platform development environments in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
What are the cross-platform development environments in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
Cross-platform development in C is recommended to use VisualStudioCode, CLion and QtCreator. 1. VisualStudioCode is lightweight and flexible, suitable for multi-platform development, but the initial configuration is more complicated. 2. CLion integrates CMake, suitable for cross-platform projects, but licenses are expensive. 3.QtCreator supports cross-platform development, with built-in Qt library, but the learning curve is steep.
 How to sort array keys according to their length in PHP and keep the keys?
May 02, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
How to sort array keys according to their length in PHP and keep the keys?
May 02, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
Through the uksort() function and the custom comparison function compareKeyLengths, PHP arrays can be sorted according to the length of the array key names while retaining the key names. The comparison function calculates the difference in key lengths and returns an integer, and uksort() sorts the array according to this integer. In addition, a practical case demonstrates how to sort records from the database by field name length.
 PHP array key-value exchange: Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of common algorithms
May 04, 2024 pm 10:39 PM
PHP array key-value exchange: Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of common algorithms
May 04, 2024 pm 10:39 PM
Three common algorithms for exchanging array key values ??in PHP have their own advantages and disadvantages: array_flip(): simple and efficient, but the values ??must be unique and cannot handle multi-dimensional arrays. Manual traversal: can handle multi-dimensional arrays and control exceptions, but the code is longer and less efficient. ksort()+array_keys(): can handle any type of array and control the sort order, but it is less efficient. Practical cases show that array_flip() is the most efficient, but when dealing with multi-dimensional arrays, manual traversal is more appropriate.






