Summary of common array questions in Java interviews (2)
Nov 09, 2020 pm 03:27 PM
1. Fibonacci Sequence
[Topic]
Everyone knows the Fibonacci Sequence. Now we are asked to enter an integer n. Please output the nth term of the Fibonacci sequence (starting from 0, the 0th term is 0).
(Video tutorial recommendation: java course)
[Code]
package swear2offer.array;
public class FeiBoNaQi {
/**
* 大家都知道斐波那契數(shù)列,現(xiàn)在要求輸入一個(gè)整數(shù) n,
* 請(qǐng)你輸出斐波那契數(shù)列的第 n 項(xiàng)(從 0 開(kāi)始,第 0 項(xiàng)為 0)。
* 0,1,1,2,3,5
* n<=39
* */
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1 || n== 2) return 1;
return Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2);
}
/**
* 非遞歸方式,遞歸的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)使用的棧,那就是使用棧的方式
* */
public int NoRecursive(int n) {
if (n>2) {
int[] a = new int[n+1];
a[0] = 0;
a[1] = 1;
a[2] = 1;
for (int i=3; i<=n; i++) {
a[i] = a[i-1] + a[i-2];
}
return a[n];
} else {
if (n == 0) return 0;
else return 1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new FeiBoNaQi().Fibonacci(39));
System.out.println(new FeiBoNaQi().Fibonacci(39));
}
}2. Rectangular coverage
[Title]
We can use the small rectangle of 21 to cover the larger rectangle horizontally or vertically. How many ways are there to cover a large 2*n rectangle with n small rectangles of size 21 without overlapping?
For example, when n=3, there are 3 covering methods for a 2*3 rectangular block:
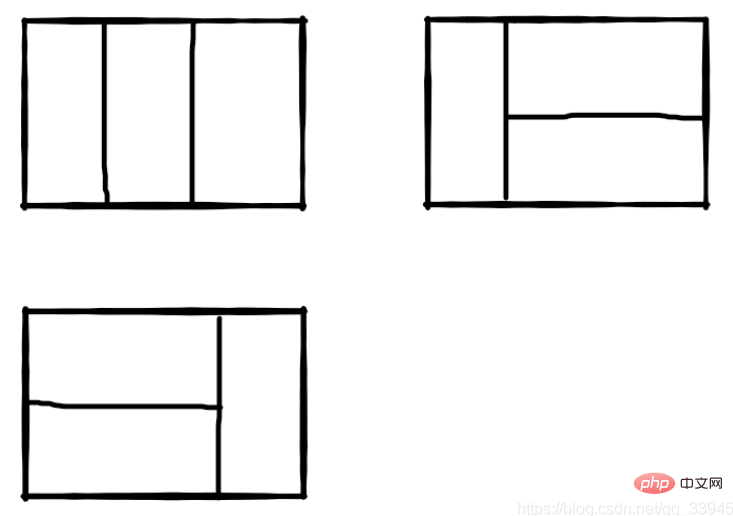
Code:
package swear2offer.array;
public class Rectangle {
/**
* f[0] = 0;
* f[1] = 1;
* f[2] = 2;
* f[3] = 3;
* f[4] = 5;
* f[5] = 8;
* f[n] = f[n-1] + f[n-2]
* */
public int RectCover(int target) {
if (target < 4) return target;
int[] f = new int[target + 1];
int i;
for (i=0; i<4; i++) f[i] = i;
for (i=4; i<=target; i++) {
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[target];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Rectangle().RectCover(5));
}
}[Thinking 】
The most straightforward way to solve the problem is to find the rules. From the summarized rules, we can see that this is the way to realize the Fibonacci sequence; the other is to answer the question according to the meaning of the question and find the method of n. , it is easy to think of solving this type of problem from n-1, and the first block is horizontal (f[n-2]) or vertical (f[n-1]), corresponding to different situations
(Recommendations for more related interview questions: java interview questions and answers)
3. The number of 1’s in binary
[Topic]
Input an integer and output the number of 1's in the binary representation of the number. Negative numbers are expressed in two's complement.
[Code]
package swear2offer.array;
public class Binary {
/**
* 輸入一個(gè)整數(shù),輸出該數(shù)二進(jìn)制表示中 1 的個(gè)數(shù)。其中負(fù)數(shù)用補(bǔ)碼表示。
* */
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count;
count = 0;
while(n != 0) {
n = n & (n-1);// 與操作就是二進(jìn)制的操作,適用原碼和補(bǔ)碼
count ++;
}
return count;
}
}[Thinking]
The one's complement of a negative number: The sign bit remains unchanged, and the remaining bits are inverted bit by bit. The complement of a negative number: in its one's complement On the basis of 1
If an integer is not 0, then at least one bit of this integer is 1. If we subtract 1 from this integer, then the original 1 on the rightmost side of the integer will become 0, and all the 0s after the original 1 will become 1 (if there are 0s after the rightmost 1). All remaining bits will be unaffected.
For example: a binary number 1100, the third digit from the right is the rightmost 1. After subtracting 1, the third digit becomes 0, the two following 0s become 1, and the previous 1 remains unchanged, so the result is 1011. We find that the result of subtracting 1 is to change the rightmost one All bits starting with 1 are inverted. At this time, if we do the AND operation between the original integer and the result after subtracting 1, all bits starting from the rightmost 1 of the original integer will become 0. For example, 1100&1011=1000. In other words, if you subtract 1 from an integer and then perform an AND operation with the original integer, the 1 on the rightmost side of the integer will be turned into 0. Then there are as many 1's as there are in the binary system of an integer. times such an operation.
4. Integer power of a value
[Title]
Given a floating-point number base of double type and an integer exponent of type int. Find base raised to the exponent power.
Ensure that base and exponent are not 0 at the same time
[Code]
package swear2offer.array;
public class Power {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if (base == 0) return 0;
if (exponent == 0) return 1;
int count;
boolean flag;
double temp;
count = 1;
temp = base;
flag = true;// 標(biāo)記正負(fù)
if (exponent < 0){
exponent = -exponent;
flag = false;
}
while (count < exponent) {
base *= temp;
count ++;
}
if (flag) {
return base;
} else {
return 1/base;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Power().Power(2,-3));
}
}[Thinking]
This question is not difficult, and the algorithm is not very complicated, but the edge It is easy to miss corners and corners.
The first point is the positive and negative of exponent. It is easy to miss the negative number
Secondly, the cases of base==0 and exponent==0 are What’s different
Finally, when base is multiplied cumulatively, it cannot be used by itself, because base is constantly getting bigger.
5. Adjust the order of the array so that odd numbers are in front of even numbers
[Topic]
Input an array of integers and implement a function to adjust the order of numbers in the array so that all The odd numbers are located in the first half of the array, and all the even numbers are located in the second half of the array, ensuring that the relative positions between odd numbers and odd numbers, and even numbers and even numbers remain unchanged.
[Code]
package swear2offer.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class OddEven {
/**
* 輸入一個(gè)整數(shù)數(shù)組,實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)函數(shù)來(lái)調(diào)整該數(shù)組中數(shù)字的順序,
* 使得所有的奇數(shù)位于數(shù)組的前半部分,所有的偶數(shù)位于數(shù)組的后半部分,
* 并保證奇數(shù)和奇數(shù),偶數(shù)和偶數(shù)之間的相對(duì)位置不變。
*
* 時(shí)空復(fù)雜度較高的算法:
* 新建一個(gè)數(shù)組b,用來(lái)保存奇數(shù),在重新變量一次,保存偶數(shù)
* 時(shí)空復(fù)雜度0(n)
* */
public void reOrderArray1(int [] array) {
int n,i,j;
n = array.length;
int[] b = new int[n];
j = 0;// 用來(lái)保存數(shù)組B的下標(biāo)
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
if (array[i]%2 != 0) {
b[j] = array[i];
j ++;
}
}
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
if (array[i]%2 == 0){
b[j] = array[i];
j++;
}
}
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
array[i] = b[i];
}
}
/**
* 采用的冒泡交換以及快速排序的思想:
* 設(shè)定兩個(gè)游標(biāo),游標(biāo)分別用來(lái)標(biāo)記奇數(shù)和偶數(shù)的下標(biāo),然后交換二者
* 注意交換二者是無(wú)法保證順序的,交換的ij之間還有進(jìn)行平移。
* */
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
int n,i,j,temp,p;
n = array.length;
i = 0;
j = 0;
while (i<n && j<n) {
// i標(biāo)記偶數(shù)下標(biāo)
while (i<n) {
if (array[i]%2 ==0){
break;
} else {
i++;
}
}
j = i;
// j標(biāo)記奇數(shù)下標(biāo)
while (j<n) {
if (array[j]%2 !=0){
break;
} else {
j++;
}
}
if (i<n && j<n) {
// 此時(shí)ij已經(jīng)在遇到的第一個(gè)偶數(shù)和奇數(shù)停下,把ij之間的內(nèi)容平移
temp = array[j];
for (p=j; p>i; p--) {
array[p] = array[p-1];
}
array[i] = temp;
// 此時(shí)把i,j標(biāo)記到 未交換前的偶數(shù)位置的下一個(gè)
i ++;
j = i;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,4,6,3,2,5,8};
int[] b = {2,4,6,1,3,5,7};
new OddEven().reOrderArray(b);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
}
}[Thinking]
Obviously, the way to create a new array is a tricky way. The question requires that operations be performed on this array. , the second method is to operate on this array, and this dual-cursor progressive method is very close to the idea of ??quick sort.
Related recommendations:Getting started with java
The above is the detailed content of Summary of common array questions in Java interviews (2). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
There are three common methods to traverse Map in Java: 1. Use entrySet to obtain keys and values at the same time, which is suitable for most scenarios; 2. Use keySet or values to traverse keys or values respectively; 3. Use Java8's forEach to simplify the code structure. entrySet returns a Set set containing all key-value pairs, and each loop gets the Map.Entry object, suitable for frequent access to keys and values; if only keys or values are required, you can call keySet() or values() respectively, or you can get the value through map.get(key) when traversing the keys; Java 8 can use forEach((key,value)->
 Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
In Java, Comparable is used to define default sorting rules internally, and Comparator is used to define multiple sorting logic externally. 1.Comparable is an interface implemented by the class itself. It defines the natural order by rewriting the compareTo() method. It is suitable for classes with fixed and most commonly used sorting methods, such as String or Integer. 2. Comparator is an externally defined functional interface, implemented through the compare() method, suitable for situations where multiple sorting methods are required for the same class, the class source code cannot be modified, or the sorting logic is often changed. The difference between the two is that Comparable can only define a sorting logic and needs to modify the class itself, while Compar
 How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
To deal with character encoding problems in Java, the key is to clearly specify the encoding used at each step. 1. Always specify encoding when reading and writing text, use InputStreamReader and OutputStreamWriter and pass in an explicit character set to avoid relying on system default encoding. 2. Make sure both ends are consistent when processing strings on the network boundary, set the correct Content-Type header and explicitly specify the encoding with the library. 3. Use String.getBytes() and newString(byte[]) with caution, and always manually specify StandardCharsets.UTF_8 to avoid data corruption caused by platform differences. In short, by
 JavaScript Data Types: Primitive vs Reference
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:43 AM
JavaScript Data Types: Primitive vs Reference
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:43 AM
JavaScript data types are divided into primitive types and reference types. Primitive types include string, number, boolean, null, undefined, and symbol. The values are immutable and copies are copied when assigning values, so they do not affect each other; reference types such as objects, arrays and functions store memory addresses, and variables pointing to the same object will affect each other. Typeof and instanceof can be used to determine types, but pay attention to the historical issues of typeofnull. Understanding these two types of differences can help write more stable and reliable code.
 What is the 'static' keyword in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:51 AM
What is the 'static' keyword in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:51 AM
InJava,thestatickeywordmeansamemberbelongstotheclassitself,nottoinstances.Staticvariablesaresharedacrossallinstancesandaccessedwithoutobjectcreation,usefulforglobaltrackingorconstants.Staticmethodsoperateattheclasslevel,cannotaccessnon-staticmembers,
 Using std::chrono in C
Jul 15, 2025 am 01:30 AM
Using std::chrono in C
Jul 15, 2025 am 01:30 AM
std::chrono is used in C to process time, including obtaining the current time, measuring execution time, operation time point and duration, and formatting analysis time. 1. Use std::chrono::system_clock::now() to obtain the current time, which can be converted into a readable string, but the system clock may not be monotonous; 2. Use std::chrono::steady_clock to measure the execution time to ensure monotony, and convert it into milliseconds, seconds and other units through duration_cast; 3. Time point (time_point) and duration (duration) can be interoperable, but attention should be paid to unit compatibility and clock epoch (epoch)
 How does a HashMap work internally in Java?
Jul 15, 2025 am 03:10 AM
How does a HashMap work internally in Java?
Jul 15, 2025 am 03:10 AM
HashMap implements key-value pair storage through hash tables in Java, and its core lies in quickly positioning data locations. 1. First use the hashCode() method of the key to generate a hash value and convert it into an array index through bit operations; 2. Different objects may generate the same hash value, resulting in conflicts. At this time, the node is mounted in the form of a linked list. After JDK8, the linked list is too long (default length 8) and it will be converted to a red and black tree to improve efficiency; 3. When using a custom class as a key, the equals() and hashCode() methods must be rewritten; 4. HashMap dynamically expands capacity. When the number of elements exceeds the capacity and multiplies by the load factor (default 0.75), expand and rehash; 5. HashMap is not thread-safe, and Concu should be used in multithreaded
 How to Check if an Array Includes a Value in JavaScript
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:16 AM
How to Check if an Array Includes a Value in JavaScript
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:16 AM
In JavaScript, check whether an array contains a certain value. The most common method is include(), which returns a boolean value and the syntax is array.includes(valueToFind), for example fruits.includes('banana') returns true; if it needs to be compatible with the old environment, use indexOf(), such as numbers.indexOf(20)!==-1 returns true; for objects or complex data, some() method should be used for in-depth comparison, such as users.some(user=>user.id===1) returns true.






