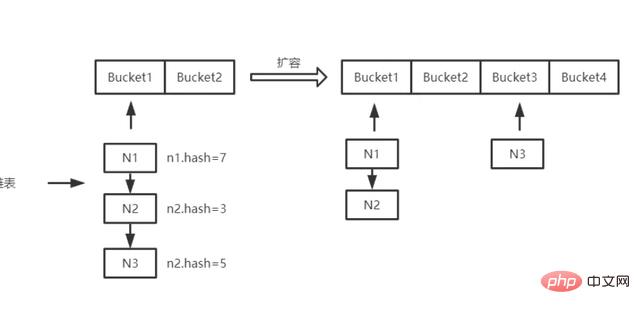
The expansion mechanism of hashmap is: recalculate the capacity and replace the original array with a new array. Recalculate all the data of the original array and insert a new array, and then point to the new array; if the array has reached the maximum value before capacity expansion, directly set the threshold to the maximum integer and return it.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, java8, Dell G3 computer.
What is resize?
?Capacity expansion (resize): It is to recalculate the capacity and continuously add elements to the HashMap object. When the array inside the HashMap object cannot load more elements, the object needs to be expanded. The length of the array so that more elements can be accommodated. Of course, arrays in Java cannot be automatically expanded. The method is to use a new array to replace the existing array with a small capacity. Just like we use a small bucket to hold water, if we want to hold more water, we have to change to a larger bucket. .
When will the capacity be expanded?
When adding elements to a container, the number of elements in the current container will be judged. If it is greater than or equal to the threshold (threshold), that is, the number of elements in the current container is greater than the length of the current array. When multiplied by the value of the loading factor, it will automatically expand.
Hashmap expansion principle
HashMap expansion is to recalculate the capacity and continuously add elements to hashMap. When hashMap cannot load new elements, The object will need to expand the array capacity to accommodate more elements.
HashMap capacity expansion characteristics, the greater the loading factor, the higher the space utilization, the more elements need to be filled before expansion, the faster the put operation, but the linked list is easy to pass Long, hash collision probability is high, and get operation is slow. The smaller the loading factor, the faster the get operation, the shorter the linked list, and the lower the probability of hash collision. However, space utilization is low. Too many put elements will lead to frequent expansion and affect performance.
The capacity expansion principle of HashMap: The Hashmap method is to replace the original array with a new array, recalculate all the data in the original array, insert the new array, and then point to the new array; If the array has reached the maximum before expansion, the threshold is directly set to the maximum integer and returned.
The following uses source code, pictures, and text descriptions to introduce the expansion process of HashMap.
/**
* HashMap 添加節(jié)點(diǎn)
*
* @param hash 當(dāng)前key生成的hashcode
* @param key 要添加到 HashMap 的key
* @param value 要添加到 HashMap 的value
* @param bucketIndex 桶,也就是這個(gè)要添加 HashMap 里的這個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)對(duì)應(yīng)到數(shù)組的位置下標(biāo)
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//數(shù)組擴(kuò)容條件:1.已經(jīng)存在的key-value mappings的個(gè)數(shù)大于等于閾值
// 2.底層數(shù)組的bucketIndex坐標(biāo)處不等于null
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);//擴(kuò)容之后,數(shù)組長(zhǎng)度變了
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;//為什么要再次計(jì)算一下hash值呢?
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);//擴(kuò)容之后,數(shù)組長(zhǎng)度變了,在數(shù)組的下標(biāo)跟數(shù)組長(zhǎng)度有關(guān),得重算。
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
/**
* 這地方就是鏈表出現(xiàn)的地方,有2種情況
* 1,原來(lái)的桶bucketIndex處是沒(méi)值的,那么就不會(huì)有鏈表出來(lái)啦
* 2,原來(lái)這地方有值,那么根據(jù)Entry的構(gòu)造函數(shù),把新傳進(jìn)來(lái)的key-value mapping放在數(shù)組上,原來(lái)的就掛在這個(gè)新來(lái)的next屬性上了
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMap.Entry<K, V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new HashMap.Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}In the above addEntry method, if size (number of elements in the current container) is greater than or equal to threshold (array length multiplied by load factor), and the bucketIndex coordinate of the underlying array is not equal to null, then it will be executed Expansion (resize) . Otherwise, the expansion will not occur.
The following will focus on the expansion process:
void resize(int newCapacity) { //傳入新的容量
Entry[] oldTable = table; //引用擴(kuò)容前的Entry數(shù)組
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //擴(kuò)容前的數(shù)組大小如果已經(jīng)達(dá)到最大(2^30)了
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //修改閾值為int的最大值(2^31-1),這樣以后就不會(huì)擴(kuò)容了
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; //初始化一個(gè)新的Entry數(shù)組
transfer(newTable); 此行有遺漏,勘誤見(jiàn)下面引用 //??!將數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)移到新的Entry數(shù)組里
table = newTable; //HashMap的table屬性引用新的Entry數(shù)組
threshold = (int) (newCapacity * loadFactor);此行有遺漏,勘誤見(jiàn)下面引用//修改閾值
}Corrected by wenni328 blogger: transfer(newTable); ==> transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
threshold = (int) (newCapacity * loadFactor); ==> threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 1);
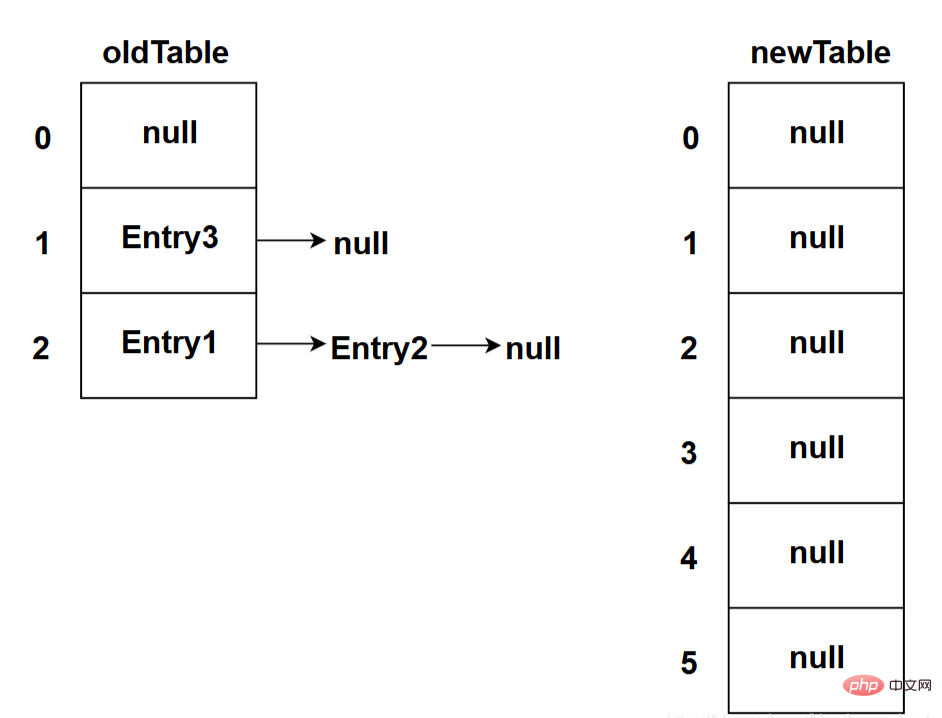
Before expansion, first obtain the reference address of the array before expansion and store it in the oldTable variable, and then determine whether the length of the array before expansion reaches int The maximum value stored in the type. If so, the expansion will be given up because the array capacity has reached the maximum and cannot be expanded.
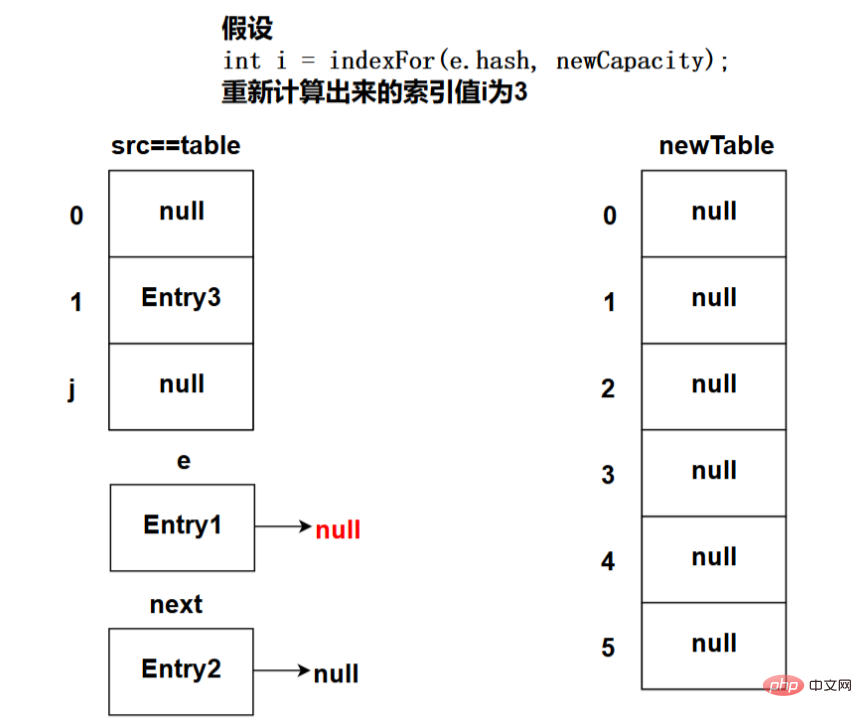
The picture below shows the state after the program executes the Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; code:
## ?
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table; //src引用了舊的Entry數(shù)組
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) { //遍歷舊的Entry數(shù)組
Entry<K, V> e = src[j]; //取得舊Entry數(shù)組的每個(gè)元素
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;//釋放舊Entry數(shù)組的對(duì)象引用(for循環(huán)后,舊的Entry數(shù)組不再引用任何對(duì)象)
do {
Entry<K, V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //?。≈匦掠?jì)算每個(gè)元素在數(shù)組中的位置
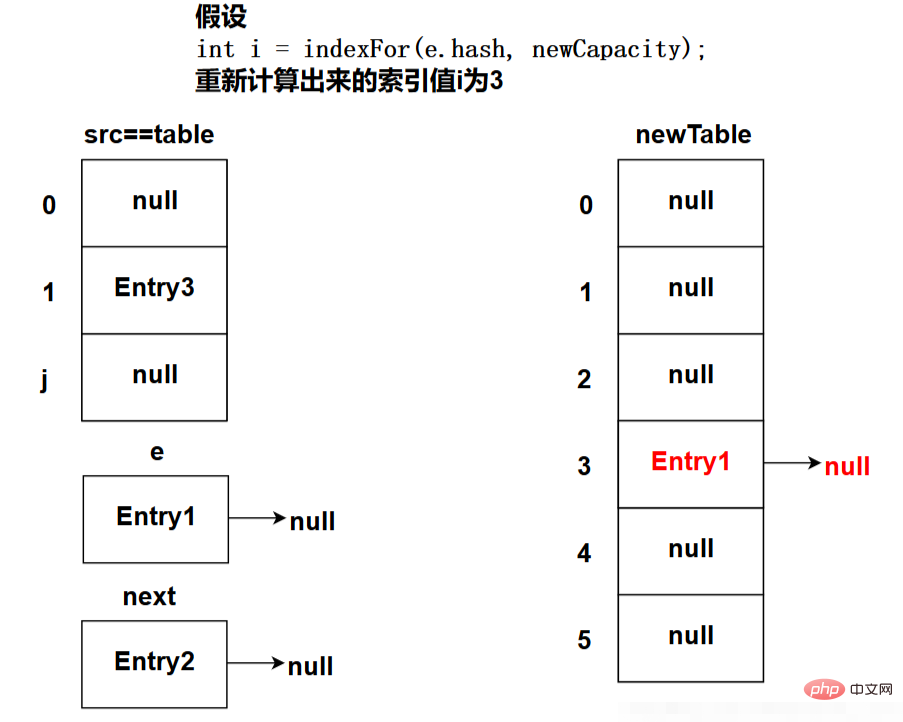
e.next = newTable[i]; //標(biāo)記[1]
newTable[i] = e; //將元素放在數(shù)組上
e = next; //訪問(wèn)下一個(gè)Entry鏈上的元素
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length - 1);
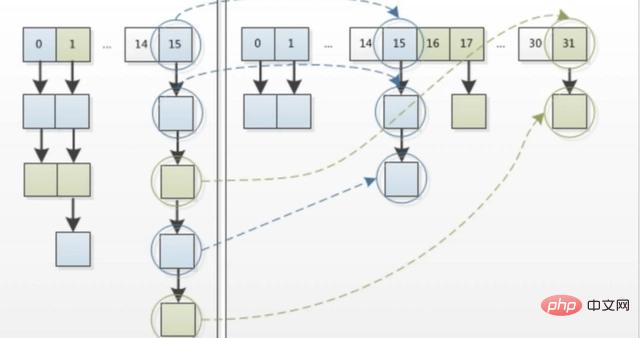
} The reference of newTable[i] is assigned to e.next, that is, uses the head insertion method of a singly linked list, and new elements at the same position will always be placed at the head of the linked list. position; in this way, elements placed on an index first will eventually be placed at the end of the Entry chain (if a hash conflict occurs). Elements in the same Entry chain in the old array may be placed in different positions in the new array after recalculating the index position.
The transfer process will be demonstrated in the form of pictures below (the red fonts in the pictures below indicate the differences from the above pictures, the following pictures are like this, and the descriptions in red fonts will not be repeated) The picture below shows the state after the program executes the src[j] = null; code (this is the state during the first loop):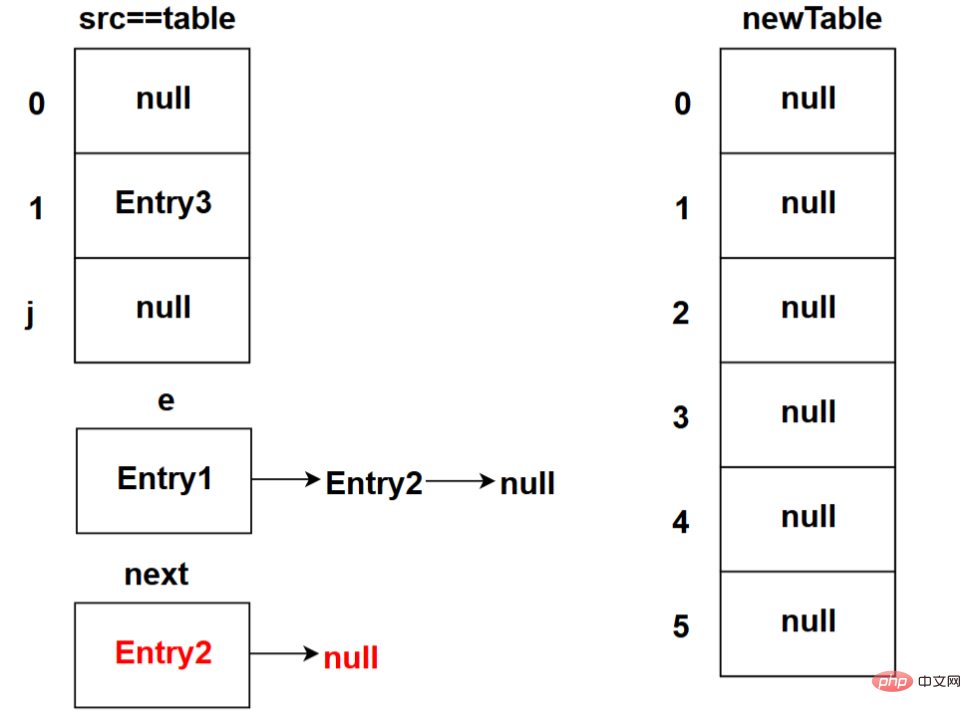
First, assign the reference address of the table[] array to the src[] array.
Then, Entry
The picture below shows the state after the program executes the Entry

The value of e.next is first backed up to the next variable. Subsequent code will change the pointer of e.next, so the value of e.next is backed up here.
The picture below shows the state after the program executes the e.next = newTable[i]; code (this is the state during the first loop):
#?
?
 ## The following picture shows the state after the program executes the e = next; code (this is the state during the first loop):
## The following picture shows the state after the program executes the e = next; code (this is the state during the first loop):
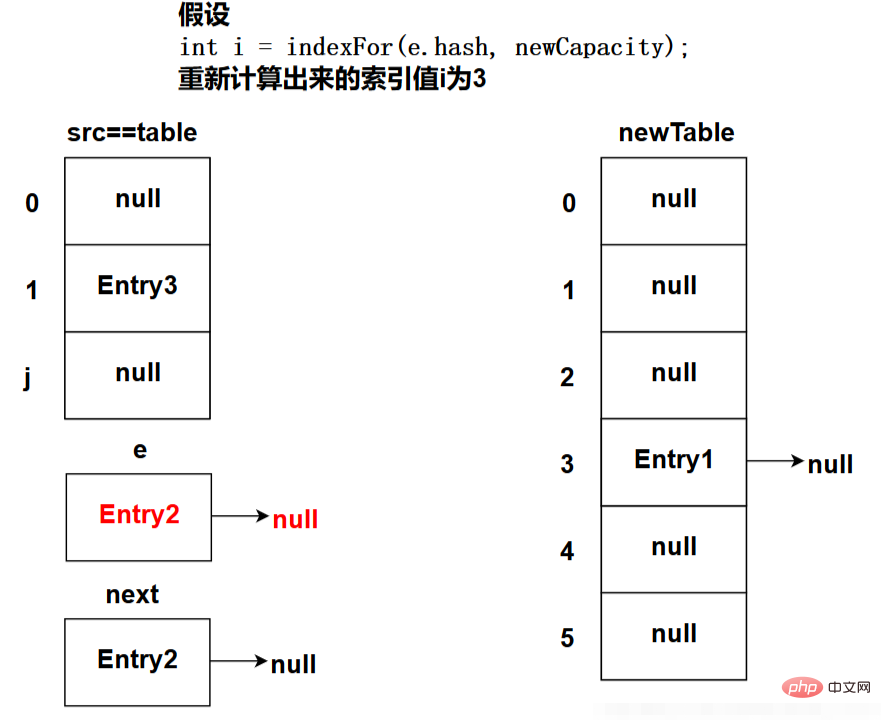 As shown above, Entry1 This node is successfully inserted into newTable. At the end of the cycle, because e!=null is judged, the above process will be repeated until all nodes are moved to newTable.
As shown above, Entry1 This node is successfully inserted into newTable. At the end of the cycle, because e!=null is judged, the above process will be repeated until all nodes are moved to newTable.
Summary
Expansion is a particularly performance-intensive operation, so when programmers use HashMap, they estimate the size of the map and provide it during initialization. A rough value to avoid frequent map expansion.- The load factor can be modified, or it can be greater than 1, but it is recommended not to modify it easily unless the situation is very special.
- HashMap is thread-unsafe. Do not operate HashMap at the same time in a concurrent environment. It is recommended to use ConcurrentHashMap.
- JDK1.8 introduces red-black trees to greatly optimize the performance of HashMap.
- For more programming-related knowledge, please visit:
The above is the detailed content of What is the expansion mechanism of hashmap?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
To correctly handle JDBC transactions, you must first turn off the automatic commit mode, then perform multiple operations, and finally commit or rollback according to the results; 1. Call conn.setAutoCommit(false) to start the transaction; 2. Execute multiple SQL operations, such as INSERT and UPDATE; 3. Call conn.commit() if all operations are successful, and call conn.rollback() if an exception occurs to ensure data consistency; at the same time, try-with-resources should be used to manage resources, properly handle exceptions and close connections to avoid connection leakage; in addition, it is recommended to use connection pools and set save points to achieve partial rollback, and keep transactions as short as possible to improve performance.
 How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
Use classes in the java.time package to replace the old Date and Calendar classes; 2. Get the current date and time through LocalDate, LocalDateTime and LocalTime; 3. Create a specific date and time using the of() method; 4. Use the plus/minus method to immutably increase and decrease the time; 5. Use ZonedDateTime and ZoneId to process the time zone; 6. Format and parse date strings through DateTimeFormatter; 7. Use Instant to be compatible with the old date types when necessary; date processing in modern Java should give priority to using java.timeAPI, which provides clear, immutable and linear
 Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Pre-formanceTartuptimeMoryusage, Quarkusandmicronautleadduetocompile-Timeprocessingandgraalvsupport, Withquarkusoftenperforminglightbetterine ServerLess scenarios.2.Thyvelopecosyste,
 How does garbage collection work in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 01:55 PM
How does garbage collection work in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 01:55 PM
Java's garbage collection (GC) is a mechanism that automatically manages memory, which reduces the risk of memory leakage by reclaiming unreachable objects. 1.GC judges the accessibility of the object from the root object (such as stack variables, active threads, static fields, etc.), and unreachable objects are marked as garbage. 2. Based on the mark-clearing algorithm, mark all reachable objects and clear unmarked objects. 3. Adopt a generational collection strategy: the new generation (Eden, S0, S1) frequently executes MinorGC; the elderly performs less but takes longer to perform MajorGC; Metaspace stores class metadata. 4. JVM provides a variety of GC devices: SerialGC is suitable for small applications; ParallelGC improves throughput; CMS reduces
 Using HTML `input` Types for User Data
Aug 03, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Using HTML `input` Types for User Data
Aug 03, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Choosing the right HTMLinput type can improve data accuracy, enhance user experience, and improve usability. 1. Select the corresponding input types according to the data type, such as text, email, tel, number and date, which can automatically checksum and adapt to the keyboard; 2. Use HTML5 to add new types such as url, color, range and search, which can provide a more intuitive interaction method; 3. Use placeholder and required attributes to improve the efficiency and accuracy of form filling, but it should be noted that placeholder cannot replace label.
 go by example http middleware logging example
Aug 03, 2025 am 11:35 AM
go by example http middleware logging example
Aug 03, 2025 am 11:35 AM
HTTP log middleware in Go can record request methods, paths, client IP and time-consuming. 1. Use http.HandlerFunc to wrap the processor, 2. Record the start time and end time before and after calling next.ServeHTTP, 3. Get the real client IP through r.RemoteAddr and X-Forwarded-For headers, 4. Use log.Printf to output request logs, 5. Apply the middleware to ServeMux to implement global logging. The complete sample code has been verified to run and is suitable for starting a small and medium-sized project. The extension suggestions include capturing status codes, supporting JSON logs and request ID tracking.
 Comparing Java Build Tools: Maven vs. Gradle
Aug 03, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Comparing Java Build Tools: Maven vs. Gradle
Aug 03, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Gradleisthebetterchoiceformostnewprojectsduetoitssuperiorflexibility,performance,andmoderntoolingsupport.1.Gradle’sGroovy/KotlinDSLismoreconciseandexpressivethanMaven’sverboseXML.2.GradleoutperformsMaveninbuildspeedwithincrementalcompilation,buildcac
 go by example defer statement explained
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:26 AM
go by example defer statement explained
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:26 AM
defer is used to perform specified operations before the function returns, such as cleaning resources; parameters are evaluated immediately when defer, and the functions are executed in the order of last-in-first-out (LIFO); 1. Multiple defers are executed in reverse order of declarations; 2. Commonly used for secure cleaning such as file closing; 3. The named return value can be modified; 4. It will be executed even if panic occurs, suitable for recovery; 5. Avoid abuse of defer in loops to prevent resource leakage; correct use can improve code security and readability.






