Java ASM uses logback log level dynamic switching method
May 09, 2023 pm 01:25 PMBackground
Everything has a cause and effect, and everything is event-driven. The log level switching of this solution comes from this background:
There are hundreds and nearly a thousand microservices in a single production environment
Log level switching does not require restarting the service, requiring immediate effects
It is up to business developers to modify the code or add related dependency configurations, etc., which involves a wide range of issues and slows progress
Later dynamic real-time filtering of junk logs to reduce IO and disk space costs
logback introduction
Before launching a war with the enemy, only the first Only by understanding the enemy's situation can we achieve victory in every battle. If you want to dynamically switch the log level of logback, you must first have at least a preliminary understanding of logback and see if it provides a ready-made implementation solution. Below is a brief introduction to logback related to this requirement.
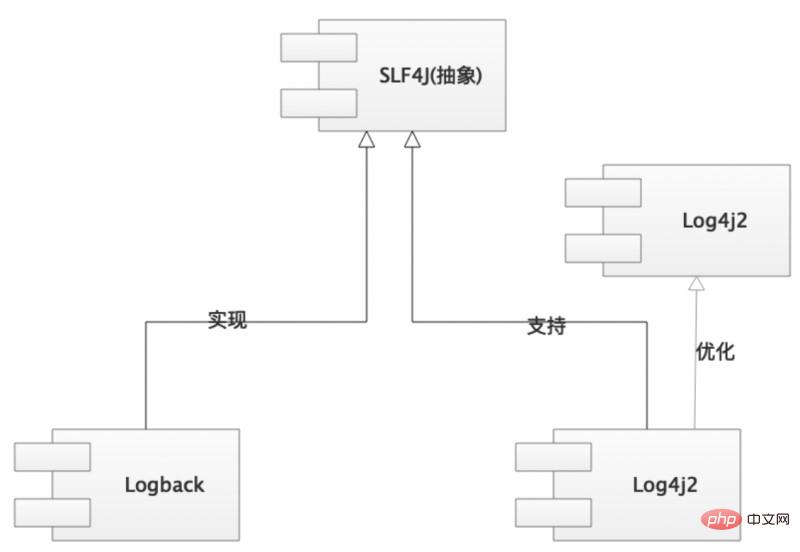
Logback is an open source component for java logs. It was written by the founder of log4j. It is currently divided into 3 modules
-
logback-core: core code module
logback-classic: An improved version of log4j, which also implements the interface of
slf4jlogback-access: access module and Servlet container integration provides the function of accessing logs through Http
ContextInitializer class is the logical implementation of the logback automatic configuration process
The log level is maintained by Logger and use. Its member variable Level is maintained by Logger
Logger has three filter log output methods with different parameters: filterAndLog_0_Or3Plus, filterAndLog_1, filterAndLog_2
setLevel in Logger is to maintain the log level
Solution
Before working hard, first understand the market plan. This is the way designers and even product bosses seek optimal solutions.
Option 1: Automatically scan and update logback
This solution is a ready-made implementation of logback. As long as the configuration is turned on, the so-called dynamic switching of log levels can be achieved. Configuration method: In the logback configuration file, just add a scheduled scanner, such as:
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="30 seconds" debug="false">
This solution does not require R&D costs, and the operation and maintenance personnel can configure and use it themselves.
The disadvantage is:
Every time the scan interval is adjusted, the service must be restarted
More than 90% of scans It's all in vain, because the log level in production cannot be frequently switched, and it is not allowed to do so.
The effect is not real-time. If you set it to scan every minute or every few minutes, Then making the log level adjustment take effect will not take effect immediately, but this can be ignored
This solution cannot meet our junk log discarding needs, such as discarding logs based on certain keywords output. For this historical reason, a lot of junk logs are printed. Considering the time cost, it is impossible for business research and development to optimize it.
Option 2: ASM dynamically modifies the bytecode
Of course, there are other solutions, such as defining the interface API yourself. To directly call the setLevel method in Logger to adjust the level; springboot integration.
None of these plans can avoid the involvement of business development roles.
Through asm dynamic modification instructions, this solution can not only adjust the log level to take effect immediately. It can also meet the needs of filtering logs
The specific implementation is as follows. I will not introduce asm here. Students who don’t know it need to familiarize themselves with the instructions of asm, java agent and jvm first:
1. Idea creates a maven project
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ow2.asm</groupId>
<artifactId>asm</artifactId>
<version>7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<artifactId>asm-commons</artifactId>
<groupId>org.ow2.asm</groupId>
<version>7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun</groupId>
<artifactId>tools</artifactId>
<version>1.8</version>
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_191.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/tools.jar</systemPath>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifestEntries>
<!-- 主程序啟動類 -->
<Agent-Class>
agent.LogbackAgentMain
</Agent-Class>
<!-- 允許重新定義類 -->
<Can-Redefine-Classes>true</Can-Redefine-Classes>
<!-- 允許轉換并重新加載類 -->
<Can-Retransform-Classes>true</Can-Retransform-Classes>
</manifestEntries>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<compilerArguments>
<verbose />
<!-- 將jdk的依賴jar打入項目中-->
<bootclasspath>${java.home}/lib/rt.jar</bootclasspath>
</compilerArguments>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build> 3. Writes the attrach startup class package agent;
import java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation;
import java.lang.instrument.UnmodifiableClassException;
/**
* @author dengbp
* @ClassName LogbackAgentMain
* @Description attach 啟動器
* @date 3/25/22 6:27 PM
*/
public class LogbackAgentMain {
private static String FILTER_CLASS = "ch.qos.logback.classic.Logger";
public static void agentmain(String agentArgs, Instrumentation inst) throws UnmodifiableClassException {
System.out.println("agentArgs:" + agentArgs);
inst.addTransformer(new LogBackFileTransformer(agentArgs), true);
Class[] classes = inst.getAllLoadedClasses();
for (int i = 0; i < classes.length; i++) {
if (FILTER_CLASS.equals(classes[i].getName())) {
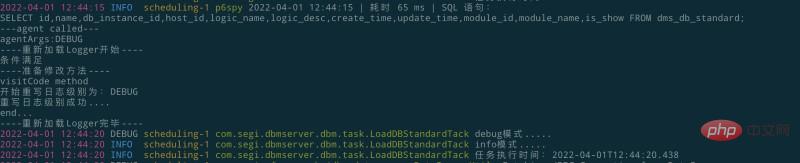
System.out.println("----重新加載Logger開始----");
inst.retransformClasses(classes[i]);
System.out.println("----重新加載Logger完畢----");
break;
}
}
}
} 4. Implements words Section code conversion processorpackage agent;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.ClassReader;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.ClassVisitor;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.ClassWriter;
import java.lang.instrument.ClassFileTransformer;
import java.security.ProtectionDomain;
/**
* @author dengbp
* @ClassName LogBackFileTransformer
* @Description 字節(jié)碼文件轉換器
* @date 3/25/22 6:25 PM
*/
public class LogBackFileTransformer implements ClassFileTransformer {
private final String level;
private static String CLASS_NAME = "ch/qos/logback/classic/Logger";
public LogBackFileTransformer(String level) {
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public byte[] transform(ClassLoader loader, String className, Class<?> classBeingRedefined, ProtectionDomain protectionDomain, byte[] classfileBuffer) {
if (!CLASS_NAME.equals(className)) {
return classfileBuffer;
}
ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(classfileBuffer);
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(cr, ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);
ClassVisitor cv1 = new LogBackClassVisitor(cw, level);
/*ClassVisitor cv2 = new LogBackClassVisitor(cv1);*/
// asm框架使用到訪問模式和責任鏈模式
// ClassReader 只需要 accept 責任鏈中的頭節(jié)點處的 ClassVisitor即可
cr.accept(cv1, ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES | ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG);
System.out.println("end...");
return cw.toByteArray();
}
}5. The visitor who implements the Logger elementpackage agent;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.ClassVisitor;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
/**
* @author dengbp
* @ClassName LogBackClassVisitor
* @Description Logger類元素訪問者
* @date 3/25/22 5:01 PM
*/
public class LogBackClassVisitor extends ClassVisitor {
private final String level;
/**
* asm版本
*/
private static final int ASM_VERSION = Opcodes.ASM4;
public LogBackClassVisitor(ClassVisitor classVisitor, String level) {
super(ASM_VERSION, classVisitor);
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature,
String[] exceptions) {
MethodVisitor mv = super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);
return new LogFilterMethodVisitor(api, mv, access, name, descriptor, level);
}
}6. The visitor who finally implements the key method of LoggerThis visitor (class), To switch log levels, you need to modify the instructions for Logger's three log filtering methods. The principle is to overwrite the value of the log level parameter entered in the command line with the value of its member variable effectiveLevelInt. Due to the large length, only the core part of the code is posted. Please see below: package agent;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.Label;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.commons.AdviceAdapter;
import org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
/**
* @author dengbp
* @ClassName LogFilterMethodVisitor
* @Description Logger類日志過濾方法元素訪問者
* @date 3/25/22 5:01 PM
*/
public class LogFilterMethodVisitor extends AdviceAdapter {
private String methodName;
private final String level;
private static final String filterAndLog_1 = "filterAndLog_1";
private static final String filterAndLog_2 = "filterAndLog_2";
private static final String filterAndLog_0_Or3Plus = "filterAndLog_0_Or3Plus";
protected LogFilterMethodVisitor(int api, MethodVisitor methodVisitor, int access, String name, String descriptor, String level) {
super(api, methodVisitor, access, name, descriptor);
this.methodName = name;
this.level = level;
}
/**
* Description 在訪問方法的頭部時被訪問
* @param
* @return void
* @Author dengbp
* @Date 3:36 PM 4/1/22
**/
@Override
public void visitCode() {
System.out.println("visitCode method");
super.visitCode();
}
@Override
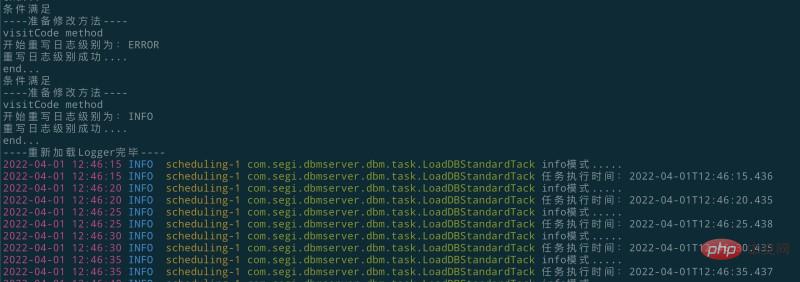
protected void onMethodEnter() {
System.out.println("開始重寫日志級別為:"+level);
System.out.println("----準備修改方法----");
if (filterAndLog_1.equals(methodName)) {
modifyLogLevel_1();
}
if (filterAndLog_2.equals(methodName)) {
modifyLogLevel_2();
}
if (filterAndLog_0_Or3Plus.equals(methodName)) {
modifyLogLevel_3();
}
System.out.println("重寫日志級別成功....");
}Among them modifyLogLevel_1(); modifyLogLevel_2() ;modifyLogLevel_3(); corresponds to the modification of filterAndLog_1, filterAndLog_2, filterAndLog_0_Or3Plus method instructions respectively. Only the implementation of modifyLogLevel_1 is posted below /**
* Description 修改目標方法:filterAndLog_1
* @param
* @return void
* @Author dengbp
* @Date 2:20 PM 3/31/22
**/
private void modifyLogLevel_1(){
Label l0 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l0);
mv.visitLineNumber(390, l0);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
mv.visitLdcInsn(level);
mv.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC, "ch/qos/logback/classic/Level", "toLevel", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Lch/qos/logback/classic/Level;", false);
mv.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETFIELD, "ch/qos/logback/classic/Level", "levelInt", "I");
mv.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.PUTFIELD, "ch/qos/logback/classic/Logger", "effectiveLevelInt", "I");
Label l1 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l1);
mv.visitLineNumber(392, l1);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
mv.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETFIELD, "ch/qos/logback/classic/Logger", "loggerContext", "Lch/qos/logback/classic/LoggerContext;");
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 2);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 3);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 4);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 5);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 6);
mv.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL, "ch/qos/logback/classic/LoggerContext", "getTurboFilterChainDecision_1", "(Lorg/slf4j/Marker;Lch/qos/logback/classic/Logger;Lch/qos/logback/classic/Level;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Throwable;)Lch/qos/logback/core/spi/FilterReply;", false);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ASTORE, 7);
Label l2 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l2);
mv.visitLineNumber(394, l2);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 7);
mv.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETSTATIC, "ch/qos/logback/core/spi/FilterReply", "NEUTRAL", "Lch/qos/logback/core/spi/FilterReply;");
Label l3 = new Label();
mv.visitJumpInsn(Opcodes.IF_ACMPNE, l3);
Label l4 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l4);
mv.visitLineNumber(395, l4);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
mv.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETFIELD, "ch/qos/logback/classic/Logger", "effectiveLevelInt", "I");
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 3);
mv.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETFIELD, "ch/qos/logback/classic/Level", "levelInt", "I");
Label l5 = new Label();
mv.visitJumpInsn(Opcodes.IF_ICMPLE, l5);
Label l6 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l6);
mv.visitLineNumber(396, l6);
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.RETURN);
mv.visitLabel(l3);
mv.visitLineNumber(398, l3);
mv.visitFrame(Opcodes.F_APPEND, 1, new Object[]{"ch/qos/logback/core/spi/FilterReply"}, 0, null);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 7);
mv.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETSTATIC, "ch/qos/logback/core/spi/FilterReply", "DENY", "Lch/qos/logback/core/spi/FilterReply;");
mv.visitJumpInsn(Opcodes.IF_ACMPNE, l5);
Label l7 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l7);
mv.visitLineNumber(399, l7);
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.RETURN);
mv.visitLabel(l5);
mv.visitLineNumber(402, l5);
mv.visitFrame(Opcodes.F_SAME, 0, null, 0, null);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 1);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 2);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 3);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 4);
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.ICONST_1);
mv.visitTypeInsn(Opcodes.ANEWARRAY, "java/lang/Object");
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.DUP);
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.ICONST_0);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 5);
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.AASTORE);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 6);
mv.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKESPECIAL, "ch/qos/logback/classic/Logger", "buildLoggingEventAndAppend", "(Ljava/lang/String;Lorg/slf4j/Marker;Lch/qos/logback/classic/Level;Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Throwable;)V", false);
Label l8 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l8);
mv.visitLineNumber(403, l8);
mv.visitInsn(Opcodes.RETURN);
Label l9 = new Label();
mv.visitLabel(l9);
mv.visitLocalVariable("this", "Lch/qos/logback/classic/Logger;", null, l0, l9, 0);
mv.visitLocalVariable("localFQCN", "Ljava/lang/String;", null, l0, l9, 1);
mv.visitLocalVariable("marker", "Lorg/slf4j/Marker;", null, l0, l9, 2);
mv.visitLocalVariable("level", "Lch/qos/logback/classic/Level;", null, l0, l9, 3);
mv.visitLocalVariable("msg", "Ljava/lang/String;", null, l0, l9, 4);
mv.visitLocalVariable("param", "Ljava/lang/Object;", null, l0, l9, 5);
mv.visitLocalVariable("t", "Ljava/lang/Throwable;", null, l0, l9, 6);
mv.visitLocalVariable("decision", "Lch/qos/logback/core/spi/FilterReply;", null, l2, l9, 7);
mv.visitMaxs(9, 8);
mv.visitEnd();
} 7. Finally, write the loading class to load the attach Agent import com.sun.tools.attach.VirtualMachine;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
/**
* @author dengbp
* @ClassName MyAttachMain
* @Description jar 執(zhí)行命令:
* @date 3/25/22 4:12 PM
*/
public class MyAttachMain {
private static final int ARGS_SIZE = 2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args == null || args.length != ARGS_SIZE) {
System.out.println("請輸入進程id和日志級別(ALL、TRACE、DEBUG、INFO、WARN、ERROR、OFF),如:31722 info");
return;
}
VirtualMachine vm = null;
try {
System.out.println("修改的進程id:" + args[0]);
vm = VirtualMachine.attach(args[0]);
System.out.println("調整日志級別為:" + args[1]);
vm.loadAgent(getJar(), args[1]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (vm != null) {
try {
vm.detach();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
private static String getJar() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String jarFilePath = MyAttachMain.class.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation().getFile();
jarFilePath = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(jarFilePath, "UTF-8");
int beginIndex = 0;
int endIndex = jarFilePath.length();
if (jarFilePath.contains(".jar")) {
endIndex = jarFilePath.indexOf(".jar") + 4;
}
if (jarFilePath.startsWith("file:")) {
beginIndex = jarFilePath.indexOf("file:") + 5;
}
jarFilePath = jarFilePath.substring(beginIndex, endIndex);
System.out.println("jar path:" + jarFilePath);
return jarFilePath;
}
} 8. Package execution - Find the target program

- ##Execute jar
java -Xbootclasspath/a:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_191.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/tools.jar -cp change-log-agent-1.0.1.jar MyAttachMain 52433 DEBUG
java -Xbootclasspath/a:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_191.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/tools.jar -cp change-log-agent-1.0.1.jar MyAttachMain 52433 ERROR
java -Xbootclasspath/a:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_191.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/tools.jar -cp change-log-agent-1.0.1.jar MyAttachMain 52433 INFO
- Effect


PS: If verification fails (caused by: java.lang.verifyerror), please provide jvm parameters :-noverify
The above is the detailed content of Java ASM uses logback log level dynamic switching method. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
How to iterate over a Map in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:54 AM
There are three common methods to traverse Map in Java: 1. Use entrySet to obtain keys and values at the same time, which is suitable for most scenarios; 2. Use keySet or values to traverse keys or values respectively; 3. Use Java8's forEach to simplify the code structure. entrySet returns a Set set containing all key-value pairs, and each loop gets the Map.Entry object, suitable for frequent access to keys and values; if only keys or values are required, you can call keySet() or values() respectively, or you can get the value through map.get(key) when traversing the keys; Java 8 can use forEach((key,value)->
 Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
Comparable vs Comparator in Java
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:31 AM
In Java, Comparable is used to define default sorting rules internally, and Comparator is used to define multiple sorting logic externally. 1.Comparable is an interface implemented by the class itself. It defines the natural order by rewriting the compareTo() method. It is suitable for classes with fixed and most commonly used sorting methods, such as String or Integer. 2. Comparator is an externally defined functional interface, implemented through the compare() method, suitable for situations where multiple sorting methods are required for the same class, the class source code cannot be modified, or the sorting logic is often changed. The difference between the two is that Comparable can only define a sorting logic and needs to modify the class itself, while Compar
 How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
How to handle character encoding issues in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:46 AM
To deal with character encoding problems in Java, the key is to clearly specify the encoding used at each step. 1. Always specify encoding when reading and writing text, use InputStreamReader and OutputStreamWriter and pass in an explicit character set to avoid relying on system default encoding. 2. Make sure both ends are consistent when processing strings on the network boundary, set the correct Content-Type header and explicitly specify the encoding with the library. 3. Use String.getBytes() and newString(byte[]) with caution, and always manually specify StandardCharsets.UTF_8 to avoid data corruption caused by platform differences. In short, by
 Using std::chrono in C
Jul 15, 2025 am 01:30 AM
Using std::chrono in C
Jul 15, 2025 am 01:30 AM
std::chrono is used in C to process time, including obtaining the current time, measuring execution time, operation time point and duration, and formatting analysis time. 1. Use std::chrono::system_clock::now() to obtain the current time, which can be converted into a readable string, but the system clock may not be monotonous; 2. Use std::chrono::steady_clock to measure the execution time to ensure monotony, and convert it into milliseconds, seconds and other units through duration_cast; 3. Time point (time_point) and duration (duration) can be interoperable, but attention should be paid to unit compatibility and clock epoch (epoch)
 How does a HashMap work internally in Java?
Jul 15, 2025 am 03:10 AM
How does a HashMap work internally in Java?
Jul 15, 2025 am 03:10 AM
HashMap implements key-value pair storage through hash tables in Java, and its core lies in quickly positioning data locations. 1. First use the hashCode() method of the key to generate a hash value and convert it into an array index through bit operations; 2. Different objects may generate the same hash value, resulting in conflicts. At this time, the node is mounted in the form of a linked list. After JDK8, the linked list is too long (default length 8) and it will be converted to a red and black tree to improve efficiency; 3. When using a custom class as a key, the equals() and hashCode() methods must be rewritten; 4. HashMap dynamically expands capacity. When the number of elements exceeds the capacity and multiplies by the load factor (default 0.75), expand and rehash; 5. HashMap is not thread-safe, and Concu should be used in multithreaded
 JavaScript Data Types: Primitive vs Reference
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:43 AM
JavaScript Data Types: Primitive vs Reference
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:43 AM
JavaScript data types are divided into primitive types and reference types. Primitive types include string, number, boolean, null, undefined, and symbol. The values are immutable and copies are copied when assigning values, so they do not affect each other; reference types such as objects, arrays and functions store memory addresses, and variables pointing to the same object will affect each other. Typeof and instanceof can be used to determine types, but pay attention to the historical issues of typeofnull. Understanding these two types of differences can help write more stable and reliable code.
 What is the 'static' keyword in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:51 AM
What is the 'static' keyword in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:51 AM
InJava,thestatickeywordmeansamemberbelongstotheclassitself,nottoinstances.Staticvariablesaresharedacrossallinstancesandaccessedwithoutobjectcreation,usefulforglobaltrackingorconstants.Staticmethodsoperateattheclasslevel,cannotaccessnon-staticmembers,
 What is a ReentrantLock in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:14 AM
What is a ReentrantLock in Java?
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:14 AM
ReentrantLock provides more flexible thread control in Java than synchronized. 1. It supports non-blocking acquisition locks (tryLock()), lock acquisition with timeout (tryLock(longtimeout, TimeUnitunit)) and interruptible wait locks; 2. Allows fair locks to avoid thread hunger; 3. Supports multiple condition variables to achieve a more refined wait/notification mechanism; 4. Need to manually release the lock, unlock() must be called in finally blocks to avoid resource leakage; 5. It is suitable for scenarios that require advanced synchronization control, such as custom synchronization tools or complex concurrent structures, but synchro is still recommended for simple mutual exclusion requirements.