 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 A small example of implementing verification code and refreshing verification code in ASP.NET
A small example of implementing verification code and refreshing verification code in ASP.NET
A small example of implementing verification code and refreshing verification code in ASP.NET
Jan 13, 2017 pm 02:27 PMImplementation code
/// <summary>
/// 生成驗證碼圖片,保存session名稱VerificationCode
/// </summary>
public static void CreateVerificationCode()
{
int number;
string checkCode = string.Empty;
//隨機數(shù)種子
Random randoms = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //校驗碼長度為4
{
//隨機的整數(shù)
number = randoms.Next();
//字符從0-9,A-Z中隨機產(chǎn)生,對應(yīng)的ASCII碼分別為
//48-57,65-90
number = number % 36;
if (number < 10)
{
number += 48;
}
else
{
number += 55;
}
checkCode += ((char)number).ToString();
}
//在session中保存校驗碼
System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Session["VerificationCode"] = checkCode;
//若校驗碼為空,則直接返回
if (checkCode == null || checkCode.Trim() == String.Empty)
{
return;
}
//根據(jù)校驗碼的長度確定輸出圖片的長度
System.Drawing.Bitmap image = new System.Drawing.Bitmap(55, 20);//(int)Math.Ceiling(Convert.ToDouble(checkCode.Length * 15))
//創(chuàng)建Graphics對象
Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(image);
try
{
//生成隨機數(shù)種子
Random random = new Random();
//清空圖片背景色
g.Clear(Color.White);
//畫圖片的背景噪音線 10條
//---------------------------------------------------
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
//噪音線起點坐標(x1,y1),終點坐標(x2,y2)
int x1 = random.Next(image.Width);
int x2 = random.Next(image.Width);
int y1 = random.Next(image.Height);
int y2 = random.Next(image.Height);
//用銀色畫出噪音線
g.DrawLine(new Pen(Color.Silver), x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
//---------------------------------------------------
//Brush b = Brushes.Silver;
//g.FillRectangle(b, 0, 0, image.Width, image.Height);
//---------------------以上兩種任選其一------------------------------
//輸出圖片中校驗碼的字體: 12號Arial,粗斜體
Font font = new Font("Arial", 12, (FontStyle.Bold | FontStyle.Italic));
//線性漸變畫刷
LinearGradientBrush brush = new LinearGradientBrush(new Rectangle(0, 0, image.Width, image.Height), Color.Blue, Color.Purple, 1.2f, true);
g.DrawString(checkCode, font, brush, 2, 2);
//畫圖片的前景噪音點 50個
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
int x = random.Next(image.Width);
int y = random.Next(image.Height);
image.SetPixel(x, y, Color.FromArgb(random.Next()));
}
//畫圖片的邊框線
g.DrawRectangle(new Pen(Color.Peru), 0, 0, image.Width - 1, image.Height - 1);
//創(chuàng)建內(nèi)存流用于輸出圖片
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
{
//圖片格式指定為png
image.Save(ms, ImageFormat.Jpeg);
//清除緩沖區(qū)流中的所有輸出
System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Response.ClearContent();
//輸出流的HTTP MIME類型設(shè)置為"image/Png"
System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Response.ContentType = "image/Jpeg";
//輸出圖片的二進制流
System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Response.BinaryWrite(ms.ToArray());
}
}
finally
{
//釋放Bitmap對象和Graphics對象
g.Dispose();
image.Dispose();
}
}Create an aspx page
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="AuthCode.aspx.cs" Inherits="AuthCode" %> <%Help.CreateVerificationCode(); %>
Add HTML code, quote
<div class="positionR">
<label>驗證碼:</label>
<span class="style1"> *</span>
<input type="text" class="yanZm" runat="Server" reg="^.+$" id="txtAuthCode" tip="請輸入驗證碼!" />
<img class="yanZm_img lazy" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="AuthCode.aspx" alt="" id="imgAuthCode" />
</div>How to achieve refresh?
<script type="text/javascript">
$("#imgAuthCode").click(function () {
$(this).attr("src", "AuthCode.aspx?code=" + (new Date()).getTime());
});
</script>Rendering
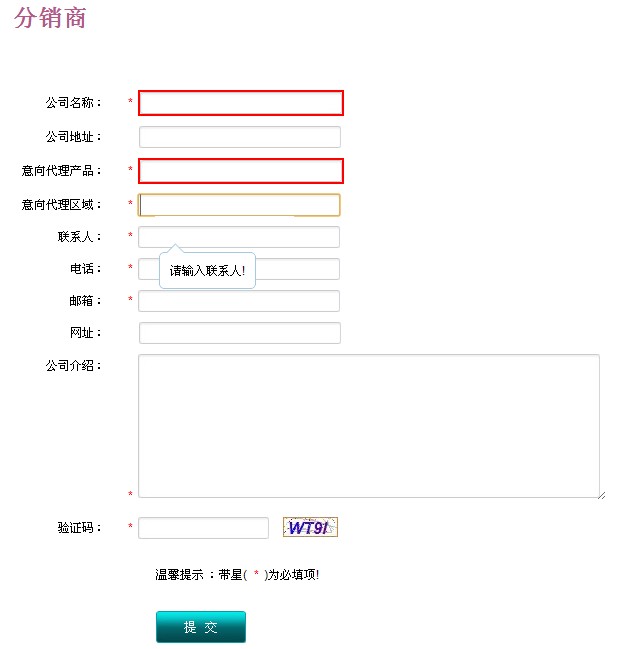
For more ASP.NET small examples of implementing verification codes and refreshing verification codes, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What is the significance of the yield keyword in C# for creating iterators?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:17 AM
What is the significance of the yield keyword in C# for creating iterators?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:17 AM
TheyieldkeywordinC#simplifiesiteratorcreationbyautomaticallygeneratingastatemachinethatenableslazyevaluation.1.Itallowsreturningitemsoneatatimeusingyieldreturn,pausingexecutionbetweeneachitem,whichisidealforlargeordynamicsequences.2.yieldbreakcanbeus
 What is Dependency Injection (DI), and how can it be implemented in C# (e.g., using built-in DI in ASP.NET Core)?
Jun 30, 2025 am 02:06 AM
What is Dependency Injection (DI), and how can it be implemented in C# (e.g., using built-in DI in ASP.NET Core)?
Jun 30, 2025 am 02:06 AM
DependencyInjection(DI)inC#isadesignpatternthatenhancesmodularity,testability,andmaintainabilitybyallowingclassestoreceivedependenciesexternally.1.DIpromotesloosecouplingbydecouplingobjectcreationfromusage.2.Itsimplifiestestingthroughmockobjectinject
 What is the purpose of the IDisposable interface and the using statement in C# for resource management?
Jun 27, 2025 am 02:18 AM
What is the purpose of the IDisposable interface and the using statement in C# for resource management?
Jun 27, 2025 am 02:18 AM
The role of IDisposable and using in C# is to efficiently and deterministically manage unmanaged resources. 1. IDisposable provides Dispose() method, so that the class can clearly define how to release unmanaged resources; 2. The using statement ensures that Dispose() is automatically called when the object is out of scope, simplifying resource management and avoiding leakage; 3. When using it, please note that the object must implement IDisposable, can declare multiple objects, and should always use using for types such as StreamReader; 4. Common best practices include not relying on destructors to clean up, correctly handling nested objects, and implementing the Dispose(bool) pattern.
 How do lambda expressions and LINQ (Language Integrated Query) enhance data manipulation in C#?
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:16 AM
How do lambda expressions and LINQ (Language Integrated Query) enhance data manipulation in C#?
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:16 AM
LambdaexpressionsandLINQsimplifydatamanipulationinC#byenablingconcise,readable,andefficientcode.1.Lambdaexpressionsallowinlinefunctiondefinitions,makingiteasiertopasslogicasargumentsforfiltering,transforming,sorting,andaggregatingdatadirectlywithinme
 What are nullable reference types (NRTs) in C# 8 , and how do they help prevent NullReferenceException?
Jun 21, 2025 am 12:36 AM
What are nullable reference types (NRTs) in C# 8 , and how do they help prevent NullReferenceException?
Jun 21, 2025 am 12:36 AM
Nullablereferencetypes(NRTs)inC#8 helpcatchNullReferenceExceptionerrorsatcompiletimebymakingreferencetypesnon-nullablebydefault,requiringexplicitdeclarationfornullability.NRTsmustbeenabledeitherinthe.csprojfilewithenableoratthetopofa.csfileusing#null
 How can Span and Memory be used in C# to optimize memory usage and reduce allocations?
Jun 18, 2025 am 12:11 AM
How can Span and Memory be used in C# to optimize memory usage and reduce allocations?
Jun 18, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Span and Memory improve C# performance by reducing memory allocation. 1. Span avoids array copying and provides light references to existing memory, which is suitable for parsing binary protocols, string operations and high-performance buffer management; 2. Memory supports passing memory slices across asynchronous methods, which is suitable for scenarios where more flexible life cycles are required; 3. Both reduce GC pressure, optimize performance by reusing buffers and avoiding temporary copying; 4. Span is limited to use on the stack and cannot be stored in classes or used in asynchronous methods. Be careful to avoid reassignment operations such as calling.ToArray().
 What are some common pitfalls or anti-patterns to avoid when developing with C#?
Jun 23, 2025 am 12:05 AM
What are some common pitfalls or anti-patterns to avoid when developing with C#?
Jun 23, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Four common "anti-pattern" problems in C# development need to be avoided. First, the unreasonable use of async/await leads to deadlocks or performance degradation. We should adhere to the principle of full asynchronousness, configure ConfigureAwait(false) and standardize naming; second, excessive dependence on var affects readability, and explicitly declare and unify team specifications when the type is unclear; third, the incorrect use of Dispose and resource management causes leakage, and the use statement should be used correctly and the IDisposable standard mode should be implemented; fourth, the abuse of static classes or singletons causes testing difficulties, and priority should be given to dependency injection, statelessness, or the life cycle managed by containers. Avoiding these misunderstandings can significantly improve code quality and maintenance.
 Can you explain the SOLID principles and their application in C# object-oriented design?
Jun 25, 2025 am 12:47 AM
Can you explain the SOLID principles and their application in C# object-oriented design?
Jun 25, 2025 am 12:47 AM
SOLID principle is five design principles to improve code maintainability and scalability in object-oriented programming. They are: 1. The single responsibility principle (SRP) requires that the class only assumes one responsibility, such as separating report generation and email sending; 2. The opening and closing principle (OCP) emphasizes that the extension is supported through interfaces or abstract classes without modifying the original code, such as using the IShape interface to realize area calculation of different graphics; 3. The Richter replacement principle (LSP) requires that the subclass can replace the parent class without destroying logic, such as Square should not mistakenly inherit Rectangle, resulting in abnormal behavior; 4. The interface isolation principle (ISP) advocates the definition of fine-grained interfaces, such as split printing and scanning functions to avoid redundant dependencies; 5. The dependency inversion principle (DIP) advocates the





